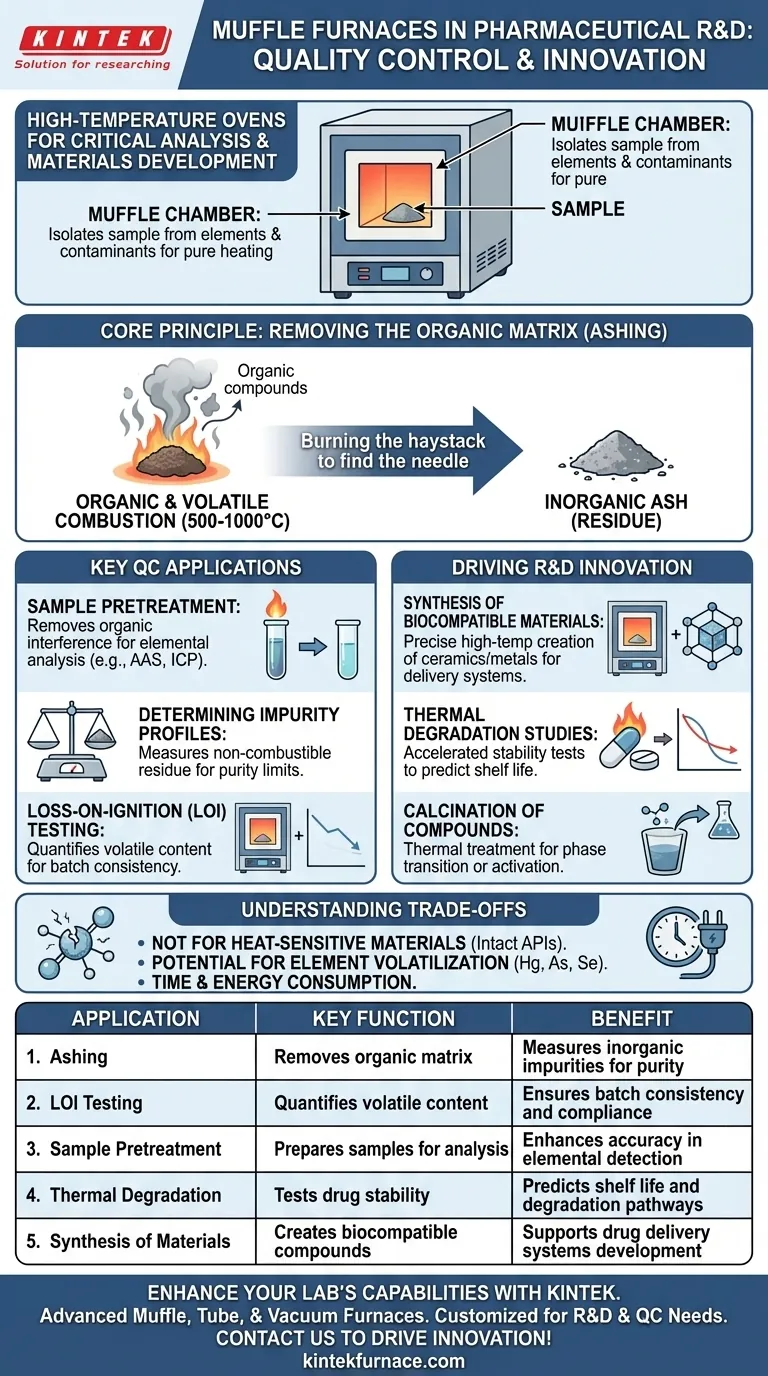
In the pharmaceutical industry, a muffle furnace is an essential high-temperature oven used for critical quality control tests and materials research. Its primary functions are to prepare medical and drug samples for further analysis, determine the quantity of non-combustible materials, and facilitate the development of new heat-stable compounds.
The core value of a muffle furnace is its ability to create an extremely hot, yet clean, environment. By thermally removing all organic and volatile components from a sample in a process called ashing, it allows researchers and technicians to precisely measure the inorganic residues left behind, which is fundamental to ensuring drug purity and safety.

The Core Principle: Removing the Organic Matrix
A muffle furnace is not just any oven. Its design is key to its function in a tightly regulated environment like pharmaceuticals.
What Makes it a "Muffle" Furnace?
The defining feature is the "muffle" – an inner chamber that isolates the sample from direct contact with the heating elements and any contaminants from combustion.
This ensures the sample is heated uniformly and purely through radiation and convection, preventing any new impurities from being introduced during the process.
The Goal of Ashing
The most common use of a muffle furnace is ashing. This involves heating a sample to a high temperature (typically 500-1000°C) until all organic and volatile substances burn away or vaporize.
Think of it as carefully burning away the haystack to find the needle. The "haystack" is the organic drug compound, and the "needle" is the trace amount of inorganic impurity or mineral content you need to measure.
Key Applications in Pharmaceutical Quality Control (QC)
In QC, the muffle furnace is a workhorse for verifying that raw materials and finished products meet stringent purity and composition standards.
Sample Pretreatment for Analysis
Many analytical techniques, such as Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (AAS) or Inductively Coupled Plasma (ICP), are designed to detect trace metals but can be thrown off by the presence of a complex organic matrix.
Ashing in a muffle furnace effectively removes this organic interference, leaving a simple inorganic ash that can be dissolved and analyzed with much greater accuracy.
Determining Impurity Profiles
Pharmaceutical guidelines set strict limits on inorganic impurities. By ashing a sample of a known weight and then weighing the remaining residue, analysts can calculate the percentage of non-combustible material.
If this percentage exceeds the specified limit, it indicates a contaminated batch that must be rejected.
Loss-on-Ignition (LOI) Testing
Loss-on-Ignition is a specific test that quantifies the mass of a sample that is lost after high-temperature heating.
This is a direct measure of the total volatile and organic content. It is a critical data point for validating material composition and ensuring consistency between batches.
Driving Innovation in Research & Development (R&D)
Beyond routine testing, the muffle furnace is a tool for innovation, enabling the creation and analysis of new pharmaceutical materials.
Synthesis of Biocompatible Materials
The development of new drug delivery systems or medical implants often involves creating novel inorganic materials, such as ceramics or treated metals.
A muffle furnace provides the precise, controlled high-temperature environment needed for the synthesis and thermal processing of these materials.
Thermal Degradation and Stability Studies
To understand a drug's shelf life, researchers must know how it behaves under stress. A muffle furnace is used to conduct accelerated stability studies by exposing the drug to extreme heat.
By analyzing the byproducts, researchers can understand its degradation pathways and predict its long-term stability under normal storage conditions.
Calcination of Compounds
Calcination is a specific thermal treatment process used to purify materials or induce a phase transition. In pharma R&D, it might be used to activate a catalyst or create a specific crystalline form of an inorganic excipient (an inactive ingredient).
Understanding the Trade-offs
While indispensable, a muffle furnace is a specialized tool with clear limitations that users must respect.
Not for Heat-Sensitive Materials
This is the most obvious limitation. Muffle furnaces are designed for thermal destruction. They cannot be used for any process involving organic compounds or active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) that must remain intact.
Potential for Element Volatilization
While most metals remain in the ash, some elements (like mercury, arsenic, and selenium) can volatilize and be lost at the high temperatures used for ashing. This requires special consideration and modified procedures if these elements are the target of the analysis.
Time and Energy Consumption
Ashing procedures are not quick. A cycle can take several hours to complete, including the ramp-up, hold time at temperature, and cool-down phases. They are also significant consumers of electricity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The application of a muffle furnace depends entirely on your objective, whether it's routine verification or novel discovery.
- If your primary focus is Quality Control: You will use the furnace for routine ashing and Loss-on-Ignition tests to verify that raw materials and finished products comply with pharmacopeial standards.
- If your primary focus is Analytical Chemistry: You will use the furnace as a critical sample preparation tool to eliminate organic matrices before performing elemental analysis.
- If your primary focus is Materials R&D: You will leverage the furnace's precise temperature control for the thermal synthesis, calcination, and stability testing of new inorganic compounds and drug formulations.
Ultimately, the muffle furnace serves as a fundamental gatekeeper of quality and an enabler of innovation in the pharmaceutical world.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Function | Benefit in Pharmaceuticals |
|---|---|---|
| Ashing | Removes organic matrix | Measures inorganic impurities for purity |
| Loss-on-Ignition Testing | Quantifies volatile content | Ensures batch consistency and compliance |
| Sample Pretreatment | Prepares samples for analysis | Enhances accuracy in elemental detection |
| Thermal Degradation Studies | Tests drug stability | Predicts shelf life and degradation pathways |
| Synthesis of Materials | Creates biocompatible compounds | Supports development of drug delivery systems |
Ready to enhance your pharmaceutical lab's capabilities with tailored high-temperature solutions? KINTEK specializes in advanced muffle, tube, and vacuum furnaces, backed by deep customization to meet your unique R&D and QC needs. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can drive your innovation and ensure compliance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis



















