At its core, an induction melting furnace serves as the heart of modern metal recycling operations. It uses clean, electromagnetic energy to rapidly and efficiently melt scrap metal, allowing for the precise separation and purification of valuable resources with minimal waste.
The true value of induction technology in recycling isn't just melting metal; it's about maximizing the recovery of high-quality material while minimizing energy consumption, environmental impact, and operational costs.

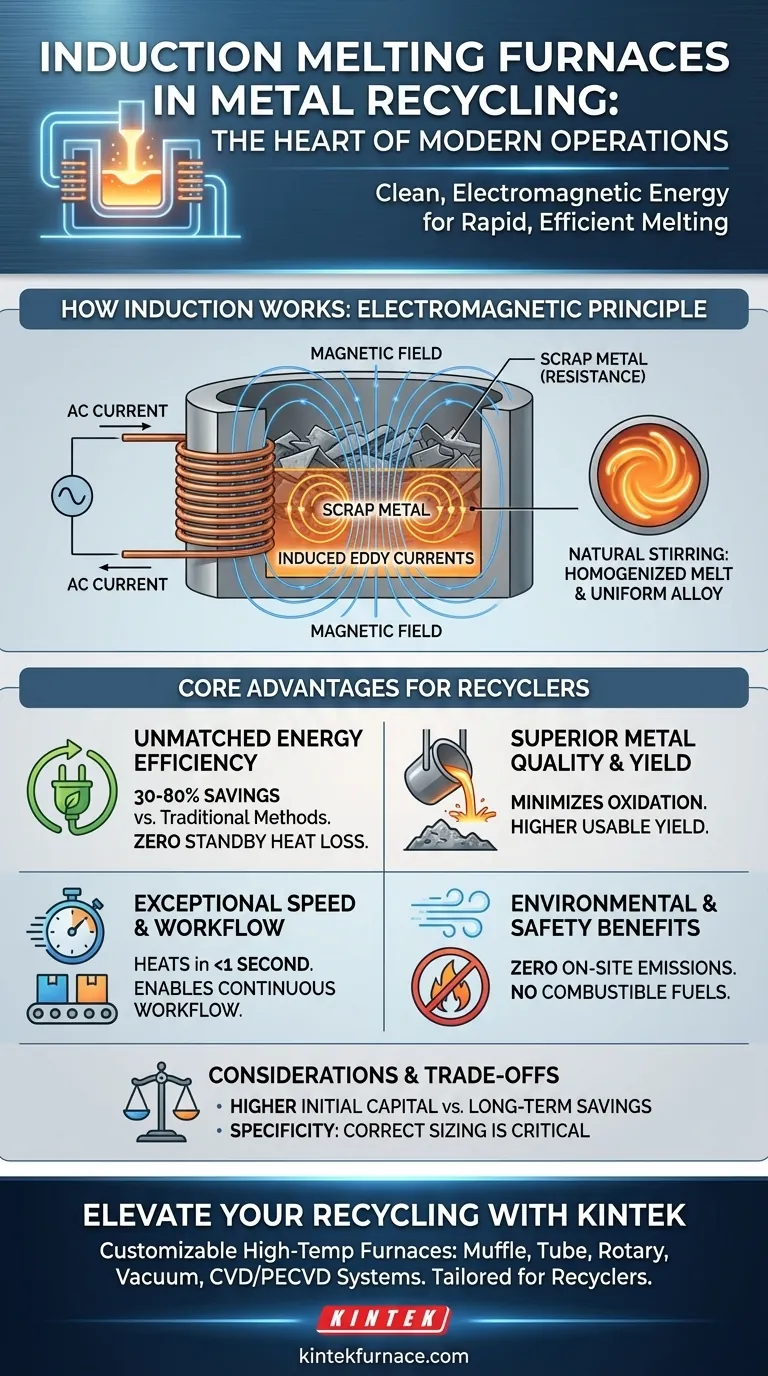
How Induction Melting Works in a Recycling Context
Understanding the underlying principle of induction reveals why it is uniquely suited for recycling complex scrap materials.
The Principle of Electromagnetic Induction
An induction furnace does not use external flames or heating elements. Instead, powerful alternating currents are passed through a copper coil, generating a strong magnetic field.
When conductive scrap metal is placed inside this field, the field induces electrical currents (called eddy currents) directly within the metal itself. The metal's natural resistance to these currents generates intense, rapid, and highly controlled heat.
Direct and Contained Heating
This process heats the metal from the inside out. This is fundamentally different from traditional furnaces that heat the outside of the material and rely on conduction to melt the interior.
The electromagnetic field also creates a natural stirring action within the molten metal. This homogenizes the melt, ensuring a consistent temperature and a uniform alloy composition, which is critical for producing high-quality recycled metal.
Core Advantages for Metal Recycling
The unique physics of induction translate directly into tangible operational and financial benefits for recyclers.
Unmatched Energy Efficiency
Induction furnaces convert electrical energy into heat with remarkable efficiency, offering 30–80% energy savings compared to traditional fuel-fired methods.
Because heat is generated only when the system is active and directly within the charge material, there is zero standby heat loss. This eliminates the significant energy waste associated with keeping conventional furnaces at temperature.
Superior Metal Quality and Yield
A key challenge in recycling is oxidation, where molten metal reacts with oxygen in the air, forming dross or slag. This represents a direct loss of valuable material.
Induction melting minimizes oxidation loss because the heating is so rapid and contained. This means a higher percentage of the input scrap is converted into usable, high-quality recycled metal, directly improving profitability.
Exceptional Speed and Workflow Integration
Induction systems can heat metal to over 2,000°F in less than a second, eliminating the long pre-heating and wait times of conventional furnaces.
The equipment also cools rapidly, allowing for a continuous workflow rather than batch processing. This speed allows melting operations to be performed directly on the work floor, streamlining the entire recycling process.
Environmental and Safety Benefits
Induction furnaces produce zero on-site emissions, including no smoke, harmful fumes, or excessive dust. This helps facilities meet increasingly stringent environmental regulations.
By eliminating the need for combustible fuels or consumable electrodes, these furnaces also reduce operational costs and remove the safety risks associated with handling and storing fuel.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, induction technology is not a universal solution. It's important to recognize its specific context and limitations.
Initial Capital Investment
The advanced technology behind induction melting systems typically requires a higher upfront capital investment compared to some simpler, traditional furnace types. However, this cost is often justified by long-term operational savings in energy and material yield.
Scale and Application Specificity
Induction furnaces are not one-size-fits-all. Systems range from small, box-type units designed for laboratories or small-scale alloy production to massive industrial furnaces capable of melting many tons at a time.
Choosing the correct size and frequency for the specific type of metal and throughput requirement is critical for achieving optimal performance and efficiency. An improperly sized system can be inefficient and fail to deliver the expected benefits.
Making the Right Choice for Your Operation
Selecting the right melting technology depends entirely on your primary operational goals.
- If your primary focus is maximizing profitability and yield: Induction is the superior choice due to its low energy costs and minimal material loss from oxidation.
- If your primary focus is improving environmental compliance: Induction is the clear leader, as its zero-emissions operation simplifies and reduces the cost of regulatory adherence.
- If your primary focus is operational speed and process flexibility: The rapid heating and cooling cycles of induction enable a continuous, integrated workflow that is difficult to match with other technologies.
Ultimately, adopting induction melting empowers recyclers to transform waste streams into valuable assets with unmatched precision and efficiency.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Impact in Metal Recycling |
|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency | 30–80% savings vs. traditional methods, zero standby heat loss |
| Metal Quality | Minimizes oxidation, ensures uniform alloy composition |
| Speed | Melts metal in seconds, enables continuous workflow |
| Environmental Benefits | Zero on-site emissions, reduces regulatory costs |
| Safety | No combustible fuels, lowers operational risks |
Ready to elevate your metal recycling with advanced induction melting solutions? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide high-temperature furnaces tailored for recyclers. Our products, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, are designed for deep customization to meet your unique operational needs. Contact us today to boost efficiency, reduce costs, and achieve superior metal recovery!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- How does the Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) process work? Achieve Superior Metal Purity and Control
- What is the purpose of vacuum melting, casting and re-melting equipment? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- How has vacuum smelting impacted the development of superalloys? Unlock Higher Strength and Purity
- How does vacuum melting technology contribute to sustainability? Boost Durability and Recycling Efficiency
- What are some common applications of vacuum induction melting and casting (VIM&C)? Essential for Aerospace, Medical, and Nuclear Industries



















