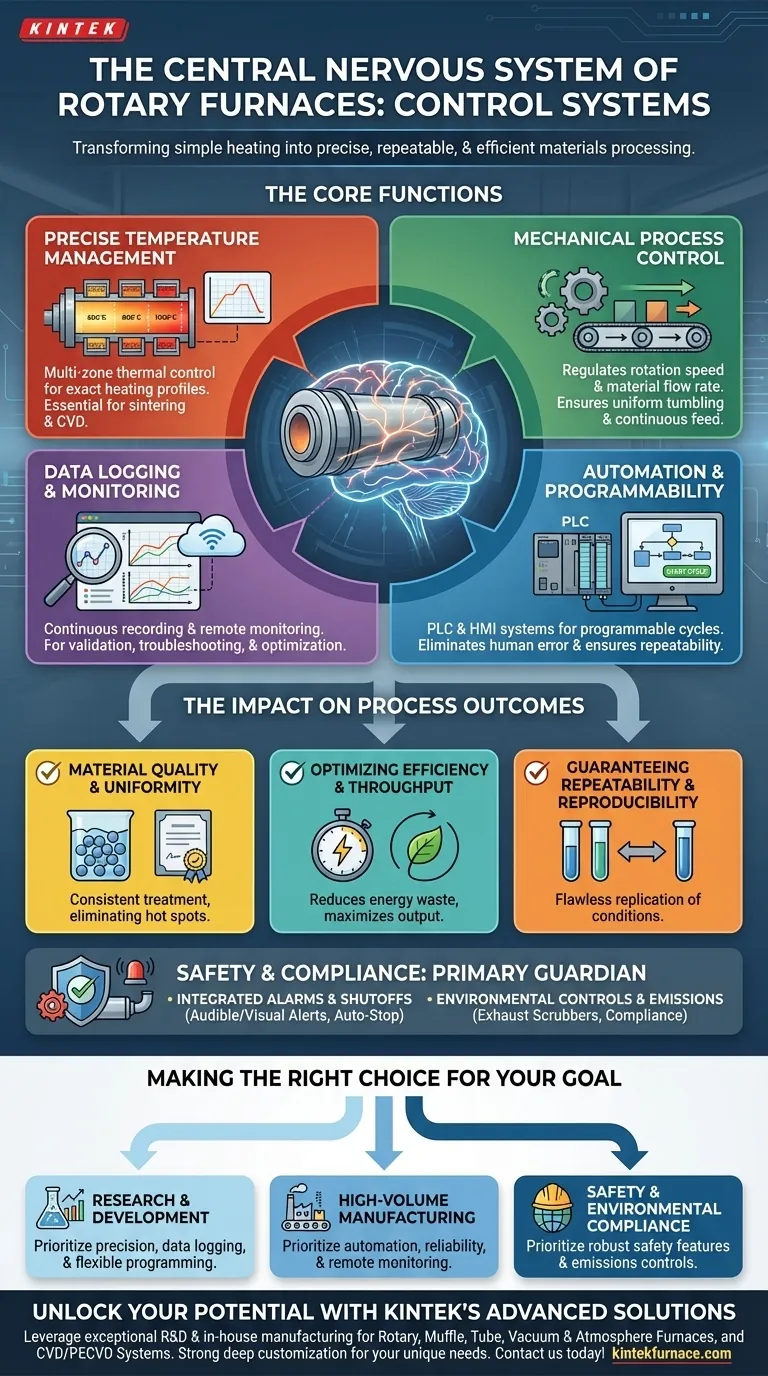
At its core, the control system in a rotary furnace functions as its central nervous system. It is responsible for monitoring all critical parameters and making real-time adjustments to ensure the entire process operates with precision. This includes managing multi-zone temperatures, the rotation speed of the furnace barrel, and the flow rate of material to guarantee a consistent and high-quality final product.
The control system is what transforms a rotary furnace from a simple heating apparatus into a precise, repeatable, and efficient materials processing tool. Its role is not merely to operate the furnace, but to guarantee the quality of the outcome, optimize resource use, and ensure operational safety.
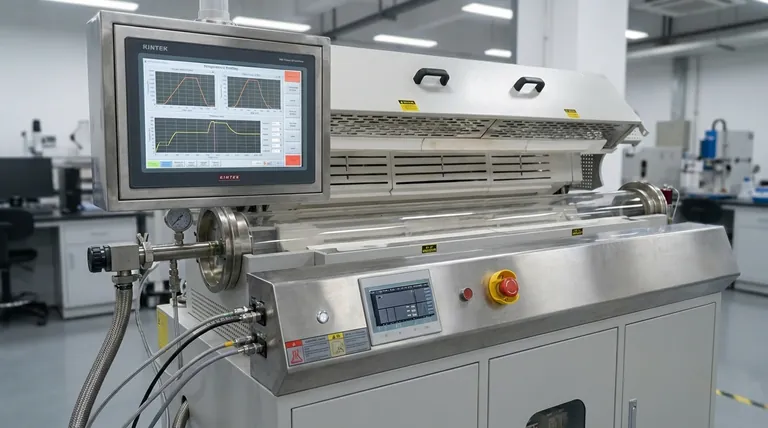

The Core Functions of a Furnace Control System
A modern control system integrates multiple functions into a single, cohesive unit. These functions work together to achieve the desired processing conditions with minimal manual intervention.
Precise Temperature Management
The primary function is maintaining exact temperature setpoints. Advanced systems use multi-zone thermal control, allowing different sections of the long furnace barrel to be held at different temperatures, creating a precise heating profile for the material as it passes through.
This ensures that the material is subjected to the exact heating and cooling cycle required, which is critical for processes like sintering or chemical vapor deposition.
Mechanical Process Control
The control system dictates the rotation speed of the furnace barrel. This is crucial for ensuring the material tumbles correctly, leading to uniform heat exposure across the entire batch.
It also governs the rate of material flow, ensuring a continuous and consistent feed that matches the thermal processing capacity of the furnace.
Automation and Programmability
Modern furnaces rely on Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) and Human-Machine Interface (HMI) systems. These allow operators to program entire processing cycles from start to finish.
This automation means that complex, multi-step recipes can be executed perfectly every time, eliminating human error and ensuring process repeatability.
Data Logging and Monitoring
A critical function for both quality control and research is data logging. The system continuously records all key parameters, such as temperature in each zone, rotation speed, and processing time.
This data provides an invaluable record for process validation, troubleshooting, and optimization. Many systems also enable remote monitoring, allowing technicians to check furnace status from a central control room or even off-site.
The Impact on Process Outcomes
The sophistication of the control system directly translates to tangible improvements in the manufacturing or research process. It moves the operation from an approximation to a science.
Ensuring Material Quality and Uniformity
By precisely controlling temperature and rotation, the system guarantees that every particle of the material receives the same treatment. This eliminates hot spots and under-processed sections, resulting in exceptional material uniformity and consistent quality from batch to batch.
Optimizing Efficiency and Throughput
An intelligent control system optimizes processing times and increases energy efficiency. By holding temperatures exactly at the required setpoint without overshooting, it minimizes wasted energy. Automated cycles ensure the furnace operates at its maximum effective throughput.
Guaranteeing Repeatability and Reproducibility
For both industrial production and scientific research, the ability to reproduce results is paramount. Programmable controls and data logging ensure that the exact same conditions can be replicated flawlessly, which is essential for achieving reproducible experimental results or maintaining strict manufacturing standards.
Understanding the Critical Role of Safety and Compliance
Beyond process efficiency, the control system is the primary guardian of operational safety and environmental responsibility.
Integrated Safety Alarms and Shutoffs
The system continuously monitors all furnace conditions for anomalies. If a temperature exceeds a safe limit, a gas flow deviates, or a mechanical fault is detected, it will trigger audible and visual alarms and can initiate an automatic safety shutoff.
Environmental Controls and Emissions
Many industrial processes release harmful particulates or gases. Advanced control systems are often integrated with peripheral equipment like exhaust scrubbers. The system monitors the exhaust stream and controls the scrubber to neutralize harmful components before they are released, ensuring environmental compliance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The level of control system you require is directly tied to your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is research and development: You need a system with precise multi-zone temperature control, extensive data logging, and flexible programming to ensure experimental reproducibility.
- If your primary focus is high-volume manufacturing: You need a system that prioritizes automation, reliability, and remote monitoring to maximize throughput and reduce operational costs.
- If your primary focus is safety and environmental compliance: You need a system with robust, integrated safety alarms, automatic shutoffs, and controls for emissions equipment like scrubbers.
Ultimately, investing in a sophisticated control system unlocks the full potential of a rotary furnace, transforming it into a highly reliable and precise instrument for advanced materials processing.
Summary Table:
| Function | Key Features | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Management | Multi-zone thermal control, precise setpoints | Ensures uniform heating and material quality |
| Mechanical Control | Rotation speed, material flow rate | Guarantees consistent exposure and throughput |
| Automation | PLCs, HMI systems, programmable cycles | Eliminates human error, ensures repeatability |
| Data Logging | Continuous monitoring, remote access | Aids in validation, troubleshooting, and optimization |
| Safety & Compliance | Alarms, shutoffs, environmental controls | Protects operations and meets regulatory standards |
Unlock the full potential of your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with precision tools like Rotary Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Tube Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we meet your unique experimental needs, enhancing efficiency, safety, and reproducibility. Contact us today to discuss how we can tailor a solution for you!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What factors should be considered when selecting a tube for a rotary tube furnace? Ensure Optimal Performance and Longevity
- What materials can be used to make the rotating tube assembly of these furnaces? Choose the Best for Your High-Temp Needs
- What is the basic construction of a rotary tube furnace? Key Components for Uniform Heating
- What are the common approaches to mixing in rotary furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- What supplementary features can enhance rotary tube furnace performance? Boost Efficiency with Precision Control



















