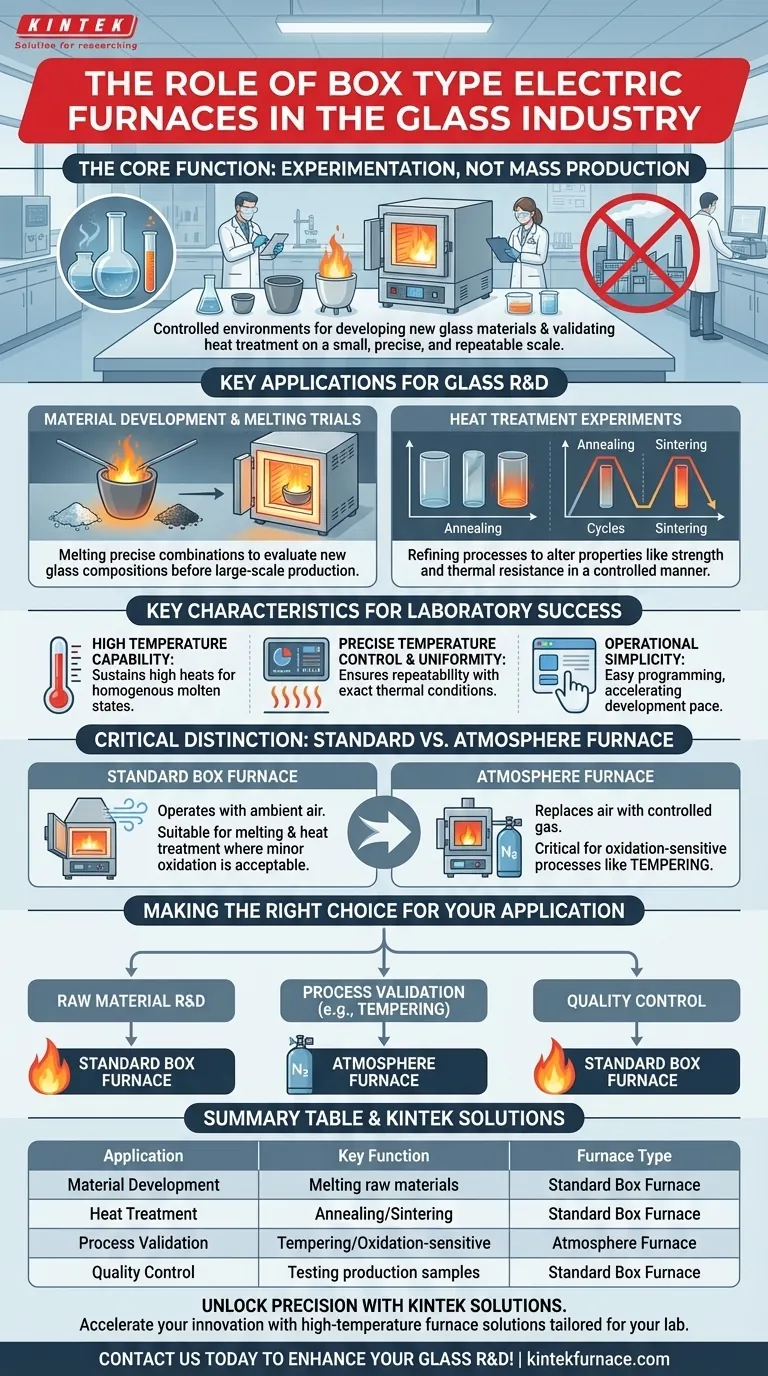
In the glass industry, box type electric furnaces serve a highly specific and critical role primarily centered on research, development, and small-scale testing. They are the controlled environments where new glass materials are born and existing ones are perfected, rather than tools for large-scale manufacturing.
The core function of a box type electric furnace in the glass sector is not mass production, but experimentation. It is an essential laboratory instrument for developing new glass formulations and validating heat treatment processes on a small, precise, and repeatable scale.

The Core Function: A Controlled Environment for Experimentation
A box furnace provides a self-contained, high-temperature chamber, making it an ideal platform for the iterative work that underpins glass science and manufacturing. Its primary applications fall into two main categories.
Material Development and Melting Trials
The creation of a new glass formula begins with small, experimental batches. A box furnace allows engineers and scientists to melt precise combinations of raw materials.
This controlled melting is crucial for evaluating the properties of a new glass composition before committing to expensive, large-scale production runs.
Heat Treatment Experiments
Heat treatment alters the final properties of glass, such as its strength and thermal resistance. Box furnaces are used to test and refine these processes.
This includes running experiments for annealing (relieving internal stresses), sintering (fusing powdered glass), or developing other custom thermal cycles in a highly controlled and documented manner.
Key Characteristics for Glass R&D
Box furnaces are valued in laboratory settings for a few key attributes that make them uniquely suited for experimental work.
High Temperature Capability
Glass melting requires significant heat. Box furnaces are designed to reach and sustain the high temperatures necessary to turn raw materials into a homogenous molten state.
Precise Temperature Control and Uniformity
Successful experiments depend on repeatability. These furnaces offer excellent temperature uniformity throughout the chamber and precise digital control, ensuring that each test is conducted under the exact same thermal conditions.
Operational Simplicity
Designed for laboratory use, box furnaces typically feature user-friendly interfaces. This allows researchers to easily program complex temperature profiles without needing specialized furnace operators, accelerating the pace of development.
Understanding the Critical Distinction: Standard vs. Atmosphere Furnaces
A common point of confusion is the difference between a standard box furnace and a specialized atmosphere furnace, both of which may have a "box" shape. Understanding this is crucial for selecting the right tool.
The Standard Box Furnace
A standard box type electric furnace operates with the ambient air that is naturally inside the chamber. This is perfectly suitable for many melting and heat treatment experiments where minor surface oxidation is not a concern.
The Atmosphere Furnace: A Specialized Tool
An atmosphere furnace is a more advanced type of box furnace that allows the air to be replaced with a controlled gas mixture, such as nitrogen or argon. This is critical for processes where the glass surface must be protected from oxygen.
The most common example in the glass industry is tempering. This process requires heating glass and then cooling it rapidly to increase its strength. A controlled, non-oxidizing atmosphere is essential to ensure uniform heating and prevent defects on the glass surface, resulting in a high-quality final product.
Making the Right Choice for Your Glass Application
Selecting the correct furnace depends entirely on your specific objective within the glass development or production lifecycle.
- If your primary focus is raw material R&D: A standard box type electric furnace is your essential tool for creating and testing new glass formulas in small, experimental melts.
- If your primary focus is process validation like tempering: You must use a specialized atmosphere furnace capable of preventing oxidation and facilitating the required thermal cycles.
- If your primary focus is quality control: A standard box furnace is excellent for testing small samples from a production line to verify their melting behavior or response to heat treatment.
Ultimately, understanding that the box furnace is a tool for precision and discovery empowers you to use it effectively in the pursuit of better glass.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Function | Furnace Type |
|---|---|---|
| Material Development | Melting raw materials for new glass compositions | Standard Box Furnace |
| Heat Treatment | Annealing, sintering, and custom thermal cycles | Standard Box Furnace |
| Process Validation | Tempering and oxidation-sensitive processes | Atmosphere Furnace |
| Quality Control | Testing samples from production lines | Standard Box Furnace |
Unlock Precision in Your Glass R&D with KINTEK Solutions
Are you advancing glass material development or optimizing heat treatment processes? KINTEK specializes in high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for laboratories like yours. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer a diverse product line—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—with strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental needs. Whether you require a standard box furnace for melting trials or an atmosphere furnace for tempering validation, we deliver reliable, user-friendly equipment to accelerate your innovation.
Contact us today to discuss how our advanced furnaces can enhance your glass research and development!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the development prospects of atmosphere box furnaces in the aerospace industry? Unlock Advanced Material Processing for Aerospace Innovation
- Can box type high-temperature resistance furnaces control the atmosphere? Unlock Precision in Material Processing
- What are the key features of an atmosphere box furnace? Unlock Precise Heat Processing in Controlled Environments
- How do argon and nitrogen protect samples in vacuum furnaces? Optimize Your Thermal Process with the Right Gas
- What is an atmosphere protection muffle furnace? Unlock Precise Heat Treatment in Controlled Environments



















