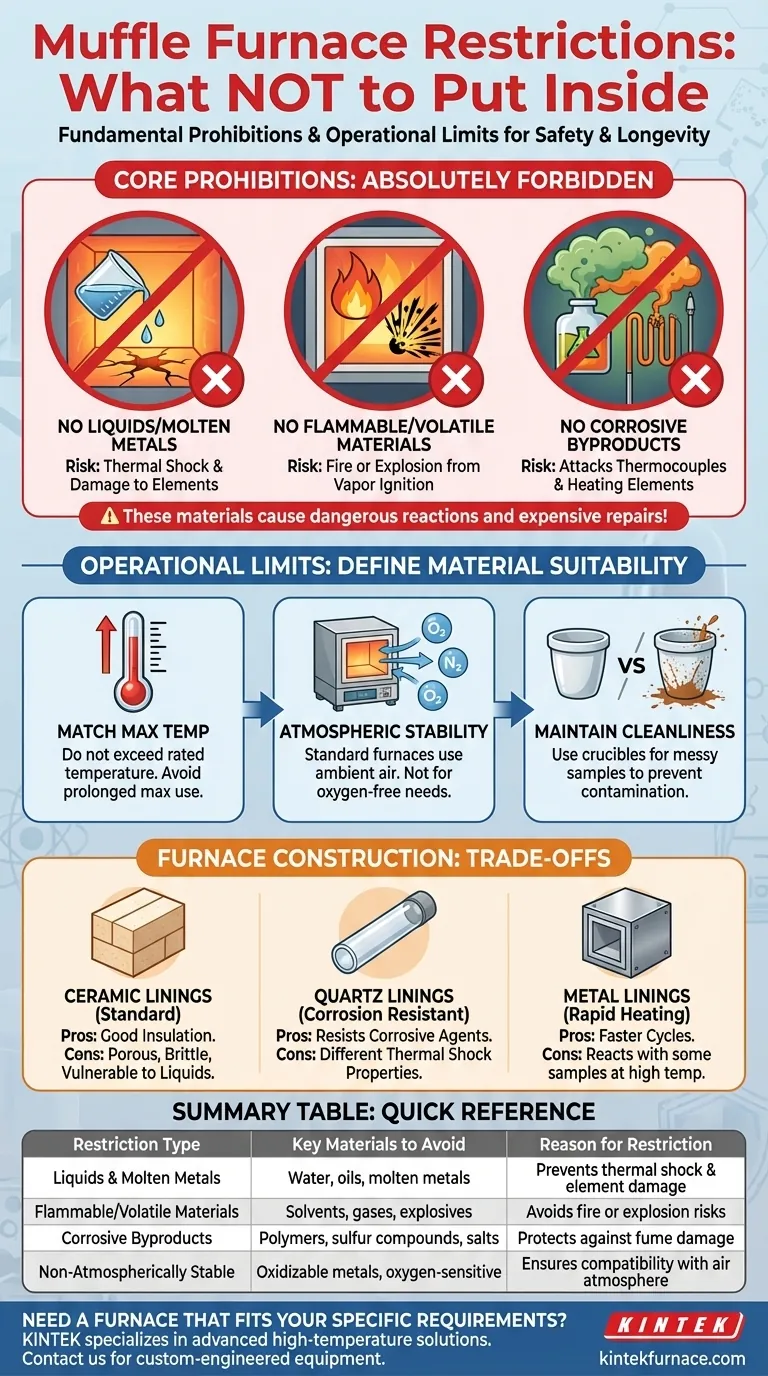
At its core, a muffle furnace has three fundamental restrictions. You are strictly prohibited from placing any volatile or flammable materials, liquids, or molten metals directly into the chamber. The furnace is designed exclusively for high-temperature processing of solid, atmospherically stable materials in a controlled thermal environment, not for chemical reactions with unknown or hazardous byproducts.
The restrictions on a muffle furnace are not arbitrary rules; they are based on its fundamental design as a high-temperature, air-atmosphere heating chamber. The primary goal is to prevent thermal shock, chemical attacks on the furnace components, and dangerous uncontrolled reactions like fires or explosions.

Understanding the Core Prohibitions
To operate a muffle furnace safely and ensure its longevity, it is critical to understand the reasoning behind its most important restrictions. These rules protect both the user and the equipment.
The Ban on Liquids and Molten Metals
Pouring liquids or placing samples that will melt into a liquid state directly onto the furnace floor is forbidden. This is because the furnace’s interior, typically made of a refractory ceramic, is highly susceptible to thermal shock.
A sudden temperature drop caused by a cooler liquid can crack the furnace hearth or walls. Spilled liquids can also seep into the insulation and damage the underlying heating elements, creating an electrical hazard and requiring expensive repairs.
The Hazard of Flammable and Volatile Materials
A muffle furnace is not a sealed environment. Placing flammable, explosive, or volatile substances inside is exceptionally dangerous.
As these materials heat up, they release vapors that will mix with the air inside the chamber. These hot, combustible fumes can ignite upon contact with the glowing-hot heating elements, potentially causing a fire or a violent explosion.
The Problem with Corrosive Byproducts
You must consider not only the material itself but also the gases it may release when heated. Many materials, including certain polymers, salts, and sulfur-containing compounds, can produce corrosive fumes.
These gases can chemically attack the furnace's thermocouple, leading to inaccurate temperature readings, and aggressively degrade the metallic heating elements, causing them to fail prematurely.
Operational Limits That Define Material Suitability
Beyond explicit prohibitions, the operational characteristics of a muffle furnace implicitly restrict the types of materials and processes it can handle.
Matching Material to Maximum Temperature
Every furnace has a maximum rated temperature that should never be exceeded. Likewise, materials have temperature limits where they might melt, decompose, or otherwise transform.
It is essential to ensure your material is suitable for the intended processing temperature and that the furnace is not operated at its absolute maximum for extended periods, which shortens its lifespan.
The Need for Atmospheric Stability
A standard muffle furnace heats materials in the presence of ambient air (primarily nitrogen and oxygen). It is not designed to operate under a vacuum or with a controlled inert gas atmosphere.
Therefore, materials that oxidize undesirably or require an oxygen-free environment for proper processing are not suitable for a muffle furnace. For those applications, a vacuum or tube furnace is the appropriate tool.
Maintaining Furnace Cleanliness
The requirement to keep the furnace clean implies a restriction on materials that are inherently messy. Samples that spatter, bubble, or leave a hard-to-remove residue should be avoided or contained within a suitable crucible.
A contaminated furnace can ruin future experiments and, if the residue is conductive or corrosive, can cause long-term damage to the equipment.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Furnace Construction
The material used to construct the furnace chamber itself can influence which samples are most appropriate. Knowing your furnace's design helps you avoid negative interactions.
Ceramic Linings: The Standard Workhorse
Most muffle furnaces use a lightweight, insulating refractory ceramic fiber or brick. This material offers excellent insulation but is porous and brittle, making it especially vulnerable to chemical attack and thermal shock from liquids.
Quartz Linings: For Corrosion Resistance
Some specialized furnaces use a quartz chamber. Quartz offers superior resistance to corrosive agents at high temperatures, making it a better choice for certain chemical analysis applications. However, it may have different thermal shock properties than ceramic.
Metal Linings: For Rapid Heating
Furnaces with metal bodies or linings provide excellent thermal conductivity, allowing for faster heating and cooling cycles. This makes them suitable for some mass-production applications, but the metal itself can react with certain sample materials or atmospheres at high temperatures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Use these principles to guide your material selection and ensure a safe, successful outcome.
- If your primary focus is safety and equipment longevity: Always place solid samples inside a proper ceramic or high-temperature alloy crucible to contain any potential melting or spillage.
- If your primary focus is material processing (e.g., ashing, sintering): Verify that your material is stable in an air atmosphere at the target temperature and will not release corrosive gases that attack the furnace elements.
- If your process involves sensitive, reactive, or volatile materials: A muffle furnace is the wrong tool; you must use a furnace designed with appropriate atmospheric controls, such as a tube or vacuum furnace.
Ultimately, understanding your furnace's limitations is as important as understanding your material's properties.
Summary Table:
| Restriction Type | Key Materials to Avoid | Reason for Restriction |
|---|---|---|
| Liquids and Molten Metals | Water, oils, molten metals | Prevents thermal shock, cracking, and damage to heating elements |
| Flammable and Volatile Materials | Solvents, gases, explosives | Avoids fire or explosion risks from vapor ignition |
| Corrosive Byproducts | Polymers, sulfur compounds, salts | Protects against fume damage to thermocouples and heating elements |
| Non-Atmospherically Stable Materials | Oxidizable metals, oxygen-sensitive samples | Ensures compatibility with air atmosphere; use vacuum furnaces for inert needs |
Need a furnace that fits your specific material requirements? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature solutions tailored to your lab's unique needs. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer a diverse product line including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise alignment with your experimental goals, enhancing safety and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your high-temperature processing with reliable, custom-engineered equipment!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control



















