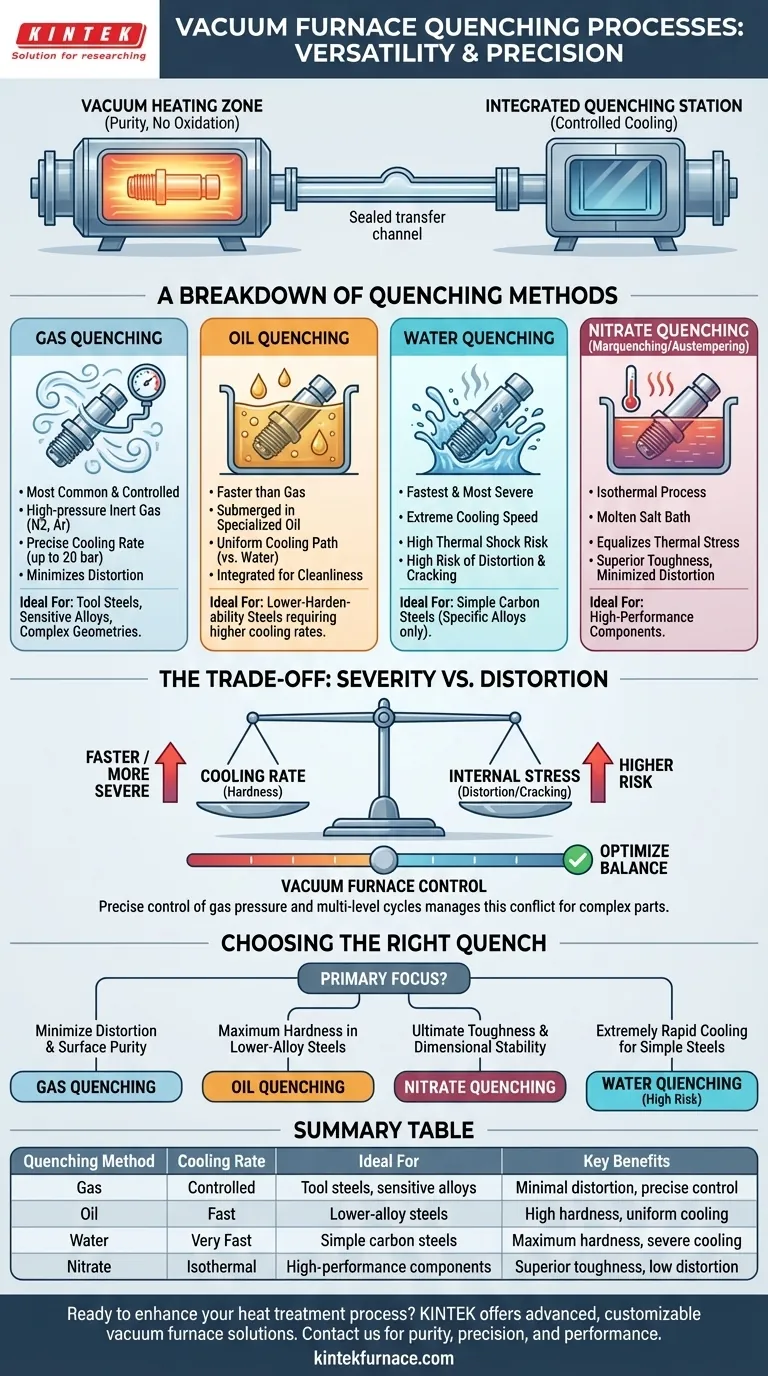
In short, a modern vacuum heat treatment furnace is highly versatile, capable of performing several distinct quenching processes to achieve specific material properties. These integrated systems can execute gas quenching, oil quenching, water quenching, and specialized nitrate quenching, all within a single, controlled production cycle.
The true advantage of a vacuum furnace is not just the variety of quenching options it offers, but its ability to pair the absolute purity of vacuum heating with a precisely controlled cooling method. This integration allows you to achieve targeted metallurgical outcomes without the surface oxidation, scaling, or decarburization common in atmospheric furnaces.

The Role of Quenching in a Vacuum Environment
Quenching is the process of rapidly cooling a metal part from its austenitizing temperature. This rapid cooling "locks in" a desired crystal structure, such as martensite, which dramatically increases the material's hardness and strength.
The Purity of the Vacuum Process
A vacuum furnace first heats the material in an environment free of oxygen and other reactive gases. This prevents surface reactions, resulting in a clean, bright part that requires no subsequent cleaning.
Integrated Cooling Stations
After heating, the part is moved from the vacuum chamber to an integrated quenching station. This transition happens within the sealed system, ensuring the part is never exposed to atmosphere while hot, thereby preserving the benefits of the vacuum environment.
A Breakdown of Vacuum Quenching Methods
The choice of quenching method is determined by the material's hardenability, the part's geometry, and the final required mechanical properties. Each method offers a different cooling rate and level of severity.
Gas Quenching
This is the most common and controlled quenching method in modern vacuum furnaces. High-pressure inert gas, typically nitrogen or argon, is rapidly circulated through the hot zone to cool the parts.
The cooling rate can be precisely controlled by adjusting the gas pressure (up to 20 bar or more in advanced systems) and circulation speed. This makes it ideal for highly sensitive alloys or complex geometries where minimizing distortion is critical.
Oil Quenching
For materials with lower hardenability that require a faster cooling rate than gas can provide, oil quenching is used. The heated part is submerged into a sealed tank of specialized quenching oil.
While more severe than gas quenching, oil provides a more uniform cooling path than water, reducing the risk of cracking. The process is integrated to maintain the vacuum system's cleanliness.
Water Quenching
Water quenching provides the fastest and most severe cooling rate. It is reserved for specific alloys, typically simple carbon steels, that require an extreme cooling speed to achieve full hardness.
Due to the high thermal shock and significant risk of distortion and cracking, water quenching is the least common method used in precision vacuum heat treatment.
Nitrate Quenching (Marquenching/Austempering)
This specialized process involves quenching the part in a molten nitrate salt bath held at a specific temperature. This is a form of isothermal quenching.
By holding the part at a temperature just above where martensite forms, thermal stress is equalized throughout the part before final cooling. This technique, known as marquenching or austempering, is unparalleled for minimizing distortion and producing superior toughness in high-performance components.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Severity vs. Distortion
The central challenge in quenching is balancing the need for rapid cooling with the risk of introducing internal stress, which leads to distortion or cracking.
The Core Conflict: Cooling Rate vs. Internal Stress
A faster quench is more effective at producing a hard martensitic structure. However, it also creates a larger temperature difference between the surface and the core of the part, generating significant internal stresses.
Why Vacuum Furnaces Excel at Managing This Trade-off
The precise control of a vacuum furnace system allows for optimizing this balance. Gas pressure can be ramped up or down, and multi-level quenching cycles can be programmed to cool a part rapidly through its critical transformation range and then more slowly to minimize stress.
This level of control is fundamental to processing complex, high-value components where dimensional stability is just as important as hardness.
Choosing the Right Quench for Your Application
Your choice of quenching process directly impacts the final properties, cost, and reliability of your component.
- If your primary focus is minimizing distortion and maintaining surface purity: Gas quenching is the default and most technically advanced choice for tool steels and sensitive alloys.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum hardness in lower-alloy steels: Oil quenching provides the necessary cooling rate that gas quenching cannot match for these materials.
- If your primary focus is ultimate toughness and dimensional stability for complex parts: Nitrate quenching (marquenching) is the superior method for controlling stress and achieving specific microstructures.
- If your primary focus is processing simple carbon steels that require extremely rapid cooling: Water quenching is the most severe option, but it must be used with a full understanding of the high risk of distortion.
By understanding these distinct processes, you can precisely specify the heat treatment required to achieve your desired material performance.
Summary Table:
| Quenching Method | Cooling Rate | Ideal For | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gas Quenching | Controlled | Tool steels, sensitive alloys | Minimal distortion, precise control |
| Oil Quenching | Fast | Lower-alloy steels | High hardness, uniform cooling |
| Water Quenching | Very Fast | Simple carbon steels | Maximum hardness, severe cooling |
| Nitrate Quenching | Isothermal | High-performance components | Superior toughness, low distortion |
Ready to enhance your heat treatment process with tailored vacuum furnace solutions? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, delivering purity, precision, and performance for industries like aerospace, automotive, and tooling. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can optimize your quenching processes and achieve superior material properties!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the components of a vacuum furnace? Unlock the Secrets of High-Temperature Processing
- What is the vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Surface Quality and Material Performance
- Why does heating steel rod bundles in a vacuum furnace eliminate heat transfer paths? Enhance Surface Integrity Today
- How does a vacuum heat treatment furnace influence Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Optimize Ductility and Fatigue Resistance
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in LP-DED? Optimize Alloy Integrity Today



















