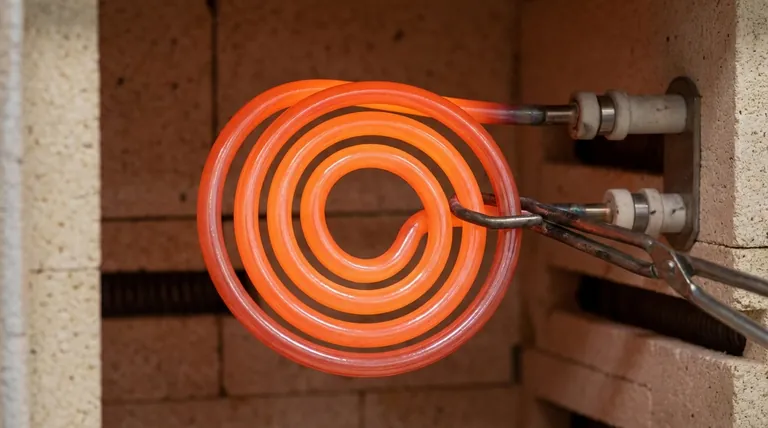
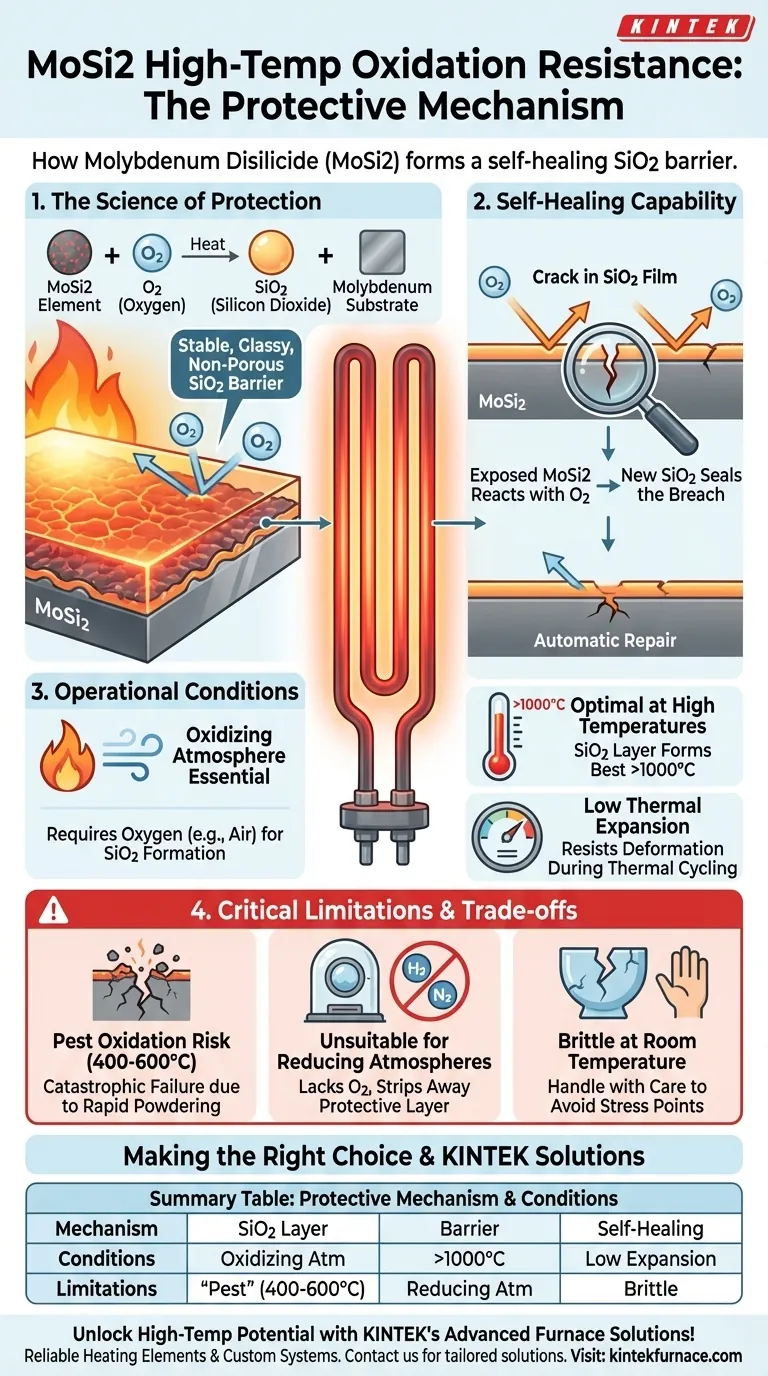
At elevated temperatures, Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) heating elements are protected from oxidation by forming a thin, stable, and self-healing layer of silicon dioxide (SiO2) on their surface. This glassy film, often called a passivation layer, acts as a highly effective barrier that prevents oxygen from reaching and degrading the underlying material.
The key to MoSi2's high-temperature durability is not simply its composition, but its ability to actively create its own protection. This "self-healing" silica layer makes it an ideal choice for demanding applications in oxidizing environments.

The Science of the Protective Layer
To use MoSi2 elements effectively, it is essential to understand how this protective mechanism functions at a chemical level. The process is a direct reaction between the material and its operating environment.
The Formation of Silicon Dioxide (SiO2)
When a MoSi2 element is heated in the presence of oxygen, the silicon (Si) at the surface preferentially reacts with that oxygen. This chemical reaction forms a new, stable compound: silicon dioxide (SiO2), also known as silica.
A Glassy, Non-Porous Barrier
This SiO2 layer is not a loose powder; it forms a dense, non-porous, and glassy film that adheres tightly to the element's surface. This film physically blocks oxygen from penetrating deeper into the MoSi2 substrate, effectively stopping further oxidation.
A "Self-Healing" Mechanism
One of the most valuable properties of this layer is its ability to self-repair. If a thermal shock or physical impact creates a crack in the SiO2 film, the newly exposed MoSi2 underneath will immediately react with the ambient oxygen to form new SiO2, sealing the breach.
Operational Context and Requirements
The formation of the protective layer is not automatic; it depends entirely on the correct operating conditions. Understanding these conditions is critical for ensuring the longevity of the elements.
The Need for an Oxidizing Atmosphere
The entire protective mechanism relies on the availability of oxygen. Therefore, MoSi2 elements perform exceptionally well in air and other oxidizing atmospheres. Their protective layer cannot form or be maintained in reducing or inert environments.
The Role of Temperature
The stable, protective SiO2 layer forms most effectively at very high temperatures, typically above 1000°C. This high-temperature operation is where MoSi2 elements excel.
Complementary Material Properties
Beyond oxidation resistance, MoSi2 has a very small coefficient of thermal expansion. This means it does not significantly expand or contract when heated and cooled, which reduces internal stress and makes it highly resistant to deformation and failure during thermal cycling.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No material is perfect for every situation. While MoSi2 is exceptional for high-temperature oxidizing work, its protective mechanism comes with specific vulnerabilities that you must account for.
The "Pest" Oxidation Risk
At intermediate temperatures, generally between 400°C and 600°C, MoSi2 is vulnerable to a catastrophic failure known as "pest" oxidation. In this range, the material can rapidly disintegrate into a powder. This occurs because the protective SiO2 layer does not form effectively, allowing for a different, destructive type of oxidation.
Unsuitability for Reducing Atmospheres
Using MoSi2 in a reducing atmosphere (like hydrogen, nitrogen, or vacuum) is a common mistake. These environments lack the oxygen needed to form the SiO2 layer. Worse, a reducing gas can actively strip away any existing protective film, leaving the element vulnerable to rapid degradation.
Brittleness at Room Temperature
Like many advanced ceramics, MoSi2 is hard but very brittle at room temperature. It must be handled with care during installation and maintenance to avoid chipping or cracking, which can create stress points that lead to failure once in operation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your operational goals will determine if MoSi2 is the correct material for your heating system.
- If your primary focus is reliable, high-temperature heating in an oxidizing atmosphere (like air): MoSi2 is an exceptional choice due to its self-forming, self-healing SiO2 protective layer.
- If your application involves prolonged operation between 400-600°C or uses a reducing atmosphere: You must select an alternative heating element material to avoid rapid "pest" failure or material degradation.
Understanding this core protective mechanism is the key to successfully designing and operating durable high-temperature systems.
Summary Table:
| Protective Mechanism | Key Features | Operating Conditions | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Formation of SiO2 layer | Thin, stable, glassy barrier; self-healing | Requires oxidizing atmosphere (e.g., air); optimal above 1000°C | Vulnerable to 'pest' oxidation at 400-600°C; not suitable for reducing atmospheres |
Unlock the full potential of your high-temperature processes with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with reliable heating elements and systems, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, enhancing durability and efficiency in oxidizing environments. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific applications and deliver tailored solutions for superior performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance



















