In short, a vacuum furnace can perform a wide range of thermal processes, including hardening, annealing, tempering, brazing, and sintering. Its primary function is to heat materials to specific temperatures in a controlled, sub-atmospheric environment, which prevents oxidation and other unwanted chemical reactions that occur in the presence of air.
The core value of a vacuum furnace isn't just the heat it provides, but the controlled environment it creates. By removing air and other gases, it enables metallurgical processes that result in cleaner, stronger, and higher-purity components than are possible with conventional atmospheric furnaces.

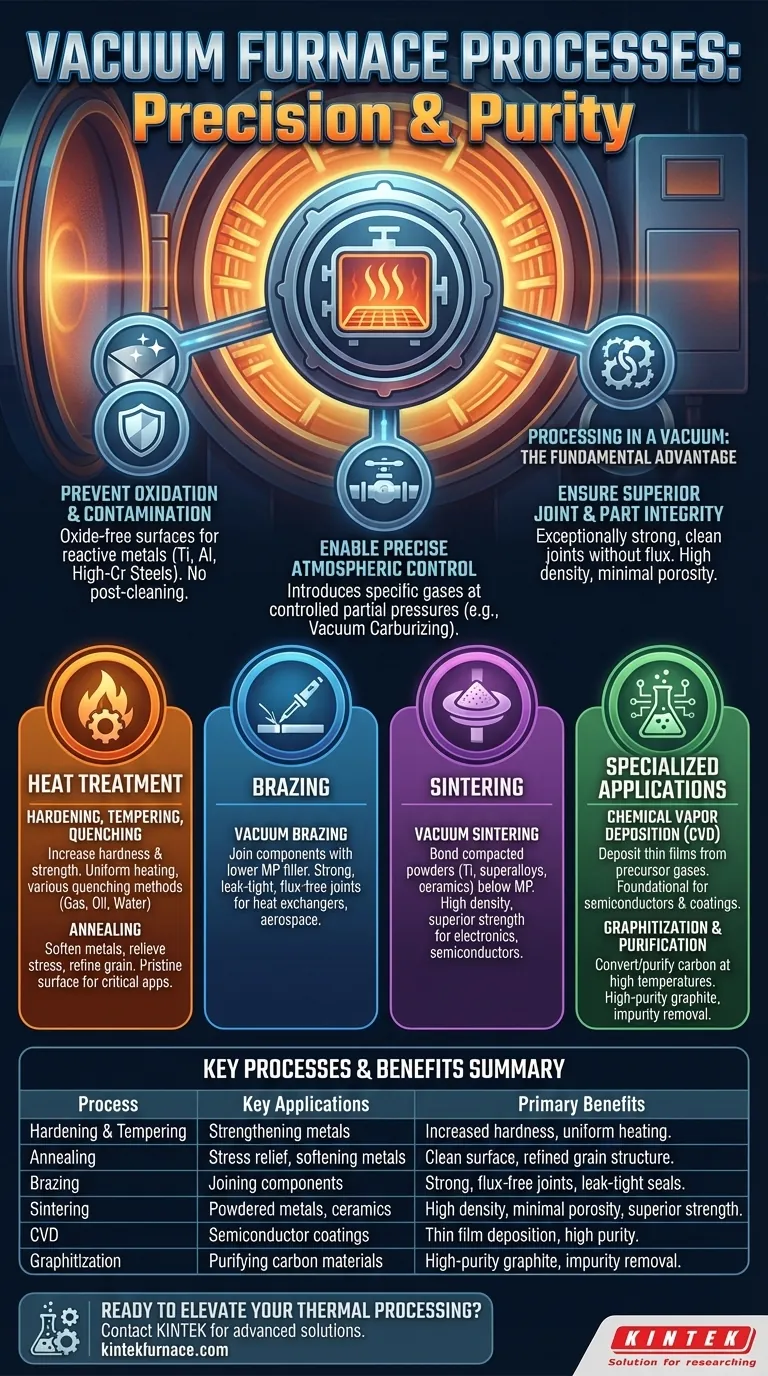
The Fundamental Advantage: Processing in a Vacuum
Before detailing the specific processes, it's crucial to understand why a vacuum is so powerful. Removing the atmosphere fundamentally changes how materials react to heat, unlocking significant quality and performance benefits.
Preventing Oxidation and Contamination
Most metals, especially reactive ones like titanium alloys, aluminum alloys, and high-chromium steels, will rapidly form an oxide layer when heated in air. A vacuum environment eliminates the oxygen, preventing this from happening.
This ensures the material's surface remains bright, clean, and free from contamination, preserving its inherent properties and often eliminating the need for post-process cleaning.
Enabling Precise Atmospheric Control
A vacuum furnace doesn't always operate in a pure vacuum. It allows for the precise introduction of specific gases at controlled partial pressures.
This technique is used to manage effects like the vaporization of chromium from a steel's surface or to perform processes like vacuum carburizing, where a carbon-rich gas is introduced to harden the surface of a part.
Ensuring Superior Joint and Part Integrity
Processes like brazing and sintering benefit immensely from the vacuum. Brazing in a vacuum creates exceptionally strong and clean joints without the need for corrosive flux.
Similarly, sintering powdered metals or ceramics in a vacuum removes trapped gases, resulting in finished parts with higher density, minimal porosity, and superior mechanical strength.
Core Heat Treatment Processes Explained
Most applications for vacuum furnaces fall into several key categories of thermal processing.
Hardening, Tempering, and Quenching
These processes are used to alter the mechanical properties of metals, primarily to increase hardness and strength. The material is heated to a critical temperature and then rapidly cooled (quenched).
Vacuum furnaces offer extremely uniform heating and can be integrated with various quenching methods—including high-pressure gas quenching, oil quenching, or even water quenching—to achieve precise, repeatable results.
Annealing
Vacuum annealing is a process used to soften metals, relieve internal stresses created during manufacturing, and refine a material's grain structure.
By performing this in a vacuum, the material's surface remains pristine, which is critical for applications in the aerospace, medical, and electronics industries.
Brazing
Vacuum brazing is used to join two or more components using a filler metal that has a lower melting point.
The process is prized for creating strong, leak-tight joints with a clean finish. It is the standard for critical assemblies like heat exchangers and aerospace fuel systems.
Sintering
Vacuum sintering is the process of taking compacted material powders—such as titanium, superalloys, or advanced ceramics like silicon carbide—and heating them to just below their melting point.
The heat and vacuum cause the particles to bond together, creating a solid, dense object. This is essential for manufacturing high-performance parts for the electronics, semiconductor, and battery industries.
Specialized and Advanced Applications
Beyond standard heat treatment, the unique environment of a vacuum furnace enables highly specialized industrial processes.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
In CVD, precursor gases are introduced into the heated furnace, where they react and deposit a thin, solid film onto a substrate. This is a foundational process in the semiconductor and coatings industries.
Graphitization and Purification
At very high temperatures, a vacuum furnace can be used to convert carbonaceous materials into high-purity graphite or to purify existing graphite by vaporizing impurities.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a vacuum furnace is driven by the material you are processing and the final quality requirements.
- If your primary focus is joining complex or critical components: Vacuum brazing offers superior strength and cleanliness without the use of corrosive flux.
- If your primary focus is creating dense, high-purity parts from powders: Vacuum sintering is the ideal method for advanced ceramics, superalloys, and other sensitive materials.
- If your primary focus is strengthening or stress-relieving reactive metals: Vacuum hardening and annealing prevent surface oxidation, preserving the material's integrity and appearance.
- If your primary focus is advanced surface modification or purification: Specialized vacuum processes like CVD or graphitization provide control and purity that is unachievable in open-air systems.
Ultimately, choosing a vacuum furnace is a commitment to achieving the highest possible quality by controlling the process environment at a molecular level.
Summary Table:
| Process | Key Applications | Primary Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Hardening & Tempering | Strengthening metals | Increased hardness, uniform heating |
| Annealing | Stress relief, softening metals | Clean surface, refined grain structure |
| Brazing | Joining components | Strong, flux-free joints, leak-tight seals |
| Sintering | Powdered metals, ceramics | High density, minimal porosity, superior strength |
| CVD | Semiconductor coatings | Thin film deposition, high purity |
| Graphitization | Purifying carbon materials | High-purity graphite, impurity removal |
Ready to elevate your thermal processing with precision and purity? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for industries like aerospace, medical, and electronics. Our product line—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—is backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our vacuum furnaces can deliver cleaner, stronger results for your applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Control
- What is the vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Surface Quality and Material Performance
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in LP-DED? Optimize Alloy Integrity Today
- What are the components of a vacuum furnace? Unlock the Secrets of High-Temperature Processing
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion



















