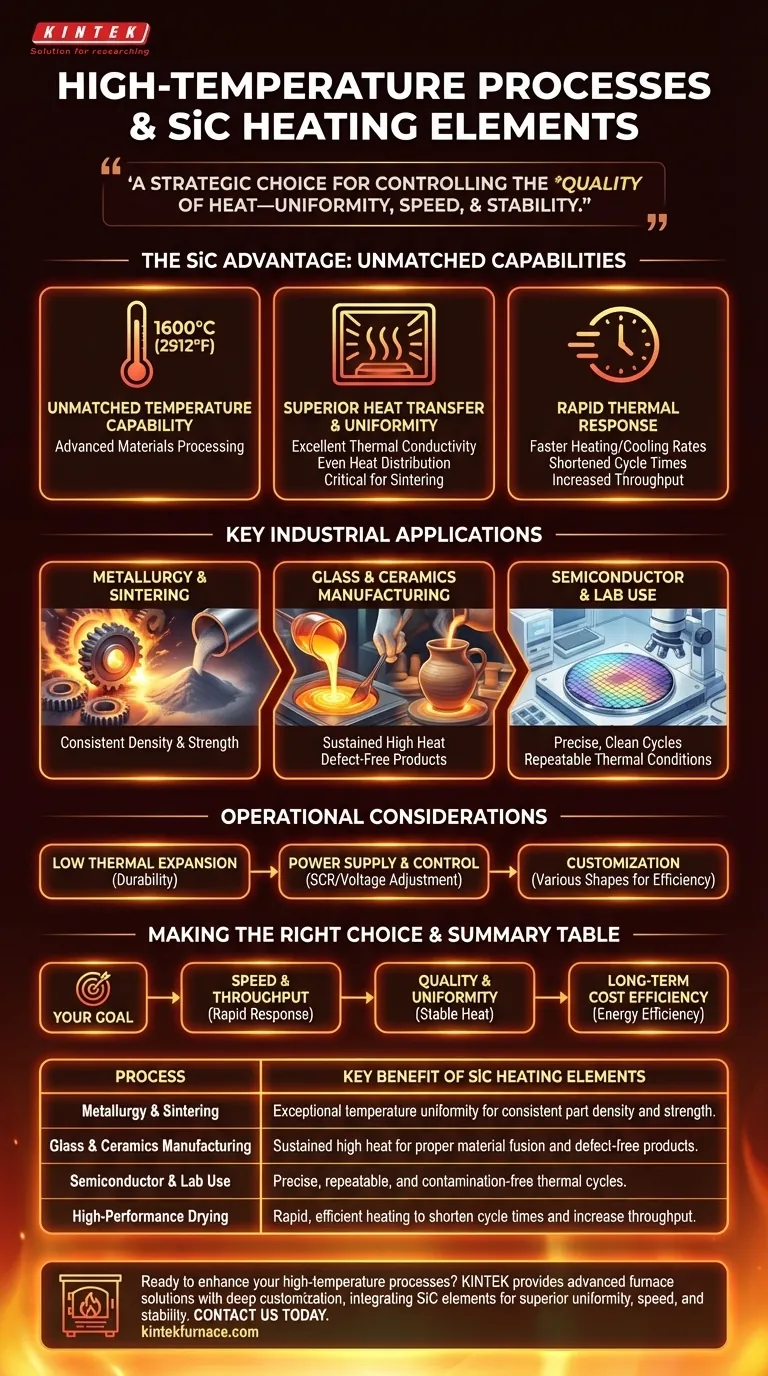
In short, processes that require extremely high, uniform, and reliable heat benefit most from Silicon Carbide (SiC) heating elements. These include industrial applications like the sintering of metals and ceramics, the melting of glass and non-ferrous metals, and high-performance material drying, all of which depend on precise thermal control that conventional elements cannot provide.
The decision to use SiC heating elements goes beyond simply reaching a target temperature. It is a strategic choice for controlling the quality of heat—its uniformity, speed, and stability—which directly dictates final product quality, production throughput, and long-term operational costs.
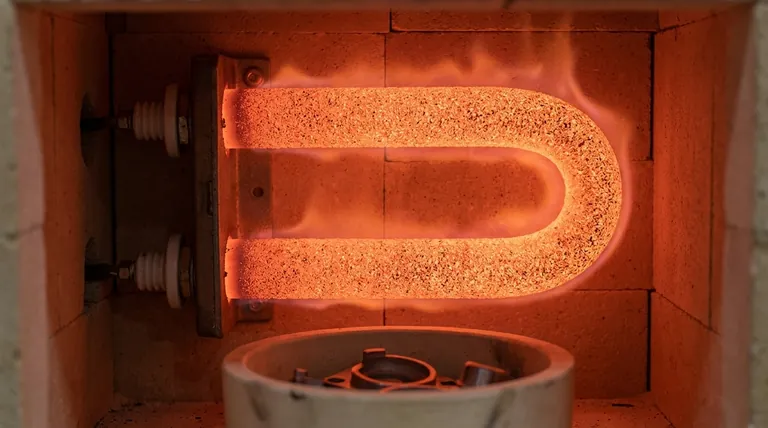
Why SiC Excels in Demanding Environments
Silicon Carbide is not just another heating material; its fundamental properties make it uniquely suited for the most intensive thermal processes. Understanding these properties reveals why it is indispensable in modern manufacturing.
Unmatched Temperature Capability
SiC elements reliably operate at surface temperatures up to 1600°C (2912°F). This high-temperature threshold allows industries to work with advanced materials that have extremely high melting or processing points.
Superior Heat Transfer and Uniformity
SiC possesses excellent thermal conductivity. This means it transfers heat energy very efficiently from the element to the workload, ensuring the entire chamber heats evenly and quickly.
This uniformity is critical in processes like sintering, where temperature variations of even a few degrees can ruin an entire batch.
Rapid Thermal Response
These elements can achieve rapid heating and cooling rates. This shortens process cycle times, directly increasing factory throughput.
Faster cycles also minimize the time the furnace spends idling at high temperatures, which reduces overall energy consumption and lowers operational costs.
Key Industrial Applications
The unique combination of high heat, uniformity, and speed makes SiC elements essential across several high-value industries.
Metallurgy and Sintering
Sintering involves fusing powdered materials together just below their melting point. This requires exceptionally stable and uniform heat to ensure consistent density and strength in the final part. SiC provides the necessary control for producing high-quality metal and ceramic components.
Glass and Ceramics Manufacturing
Melting raw materials for glass or firing advanced ceramics demands sustained, high temperatures. SiC elements provide the consistent heat needed to maintain material viscosity and ensure proper chemical reactions, resulting in clear, defect-free products.
Semiconductor and Laboratory Use
In semiconductor manufacturing, processes like thermal annealing require pristine, highly controlled heating cycles. Researchers in laboratory settings also depend on SiC for experiments that demand precise and repeatable thermal conditions without contamination.
Understanding the Operational Trade-offs
While incredibly effective, SiC elements are a high-performance component with specific operational considerations. Understanding them is key to maximizing their value and lifespan.
Low Thermal Expansion
A key factor in their durability is a low coefficient of thermal expansion. This property minimizes the internal stress on the element as it heats and cools, drastically reducing the risk of fracture and extending its operational life compared to more brittle materials.
Power Supply and Control
The electrical resistance of SiC elements can change over their lifespan. A well-designed system requires a power controller (typically an SCR) that can adjust the voltage to maintain consistent power output, ensuring stable process temperatures over thousands of hours.
Customization for Efficiency
SiC elements can be manufactured in a wide variety of shapes, such as rods, U-shapes, or spirals. This allows furnace designers to optimize heat distribution for a specific chamber or process, ensuring no energy is wasted and the workload receives heat exactly where it is needed.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When evaluating heating elements, your primary process goal should guide your decision.
- If your primary focus is process speed and throughput: The rapid heating and cooling capabilities of SiC are your greatest asset for reducing cycle times.
- If your primary focus is product quality and uniformity: The high thermal conductivity and stable temperature of SiC ensure repeatable, defect-free results batch after batch.
- If your primary focus is long-term cost efficiency: The combination of energy efficiency and long operational lifespan gives SiC a lower total cost of ownership in demanding applications.
Ultimately, leveraging SiC heating elements is about gaining precise control over thermal energy to achieve superior manufacturing outcomes.
Summary Table:
| Process | Key Benefit of SiC Heating Elements |
|---|---|
| Metallurgy & Sintering | Exceptional temperature uniformity for consistent part density and strength. |
| Glass & Ceramics Manufacturing | Sustained high heat for proper material fusion and defect-free products. |
| Semiconductor & Lab Use | Precise, repeatable, and contamination-free thermal cycles. |
| High-Performance Drying | Rapid, efficient heating to shorten cycle times and increase throughput. |
Ready to enhance your high-temperature processes with precision heating?
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, and Rotary Furnaces, as well as Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability. We can integrate SiC heating elements to precisely meet your unique requirements for uniformity, speed, and stability, ensuring superior product quality and operational efficiency.
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can benefit your specific application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions



















