The most critical precautions for installing heating elements involve three distinct areas: careful physical handling due to their brittle nature, precise alignment within the furnace to ensure proper function, and meticulous attention to electrical connections to prevent premature failure. These steps are not merely suggestions; they are essential for the element's operational lifespan and the furnace's overall performance.
The core challenge of heating element installation is managing the material's inherent brittleness. Your primary goal is not just to fit a part, but to preserve its structural and electrical integrity from the moment it leaves the box to the moment it reaches operating temperature.

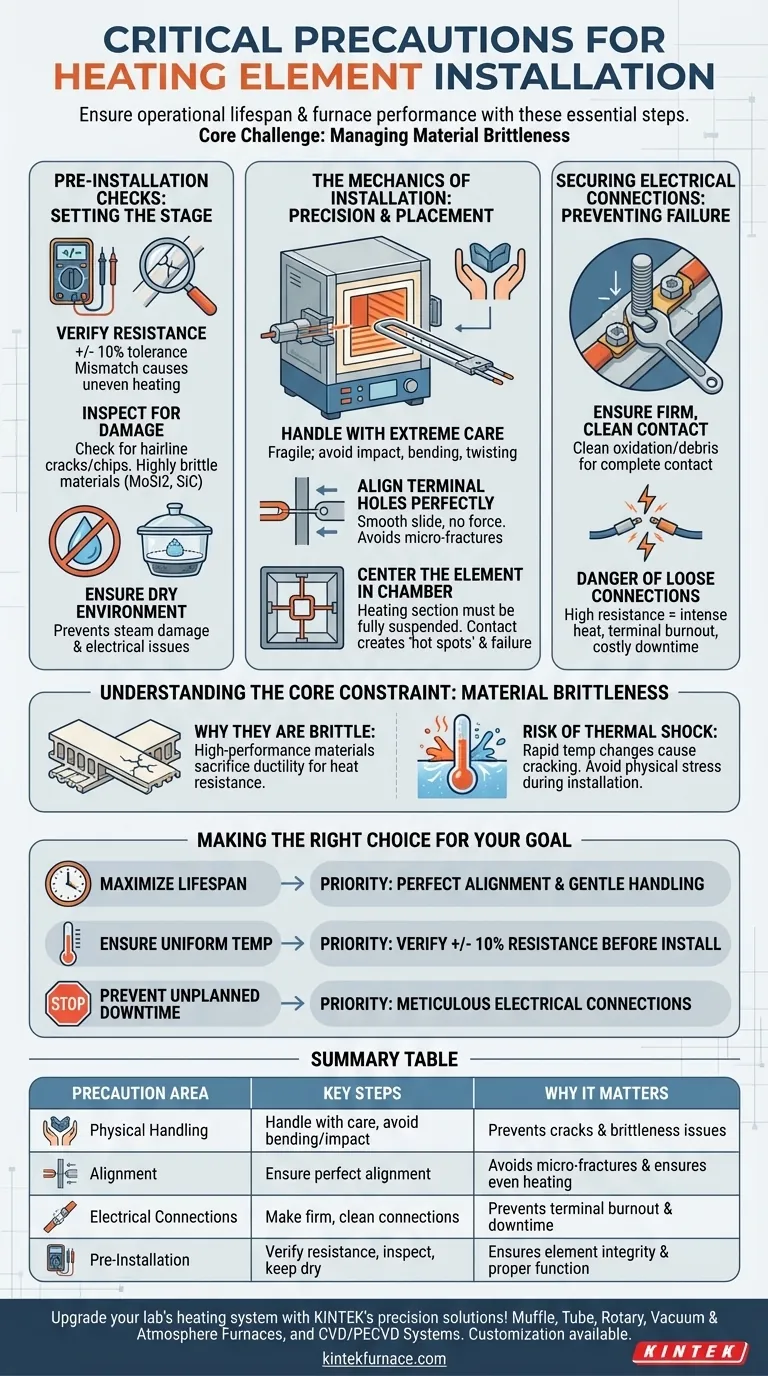
Pre-Installation Checks: Setting the Stage for Success
Before the element even approaches the furnace, a few preparatory steps are crucial to prevent installing a faulty or mismatched component.
Verify Electrical Resistance
Each element has a specified resistance value. You must verify that the actual resistance of the new element is within a +/- 10% tolerance of the manufacturer's specification.
Using elements with mismatched resistance values will cause uneven heating within the furnace. Some elements will run hotter and burn out prematurely, while others will run cooler, compromising temperature uniformity.
Inspect for Physical Damage
Heating elements, especially those made from materials like Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) or Silicon Carbide (SiC), are very hard but also extremely brittle, similar to ceramic.
Carefully inspect each element for hairline cracks or chips that may have occurred during shipping or handling. Installing a damaged element guarantees a short service life.
Ensure a Dry Environment
Installation should always occur in dry conditions. Moisture can compromise the insulating properties of the furnace lining and can lead to electrical issues or even steam-related damage upon initial heat-up.
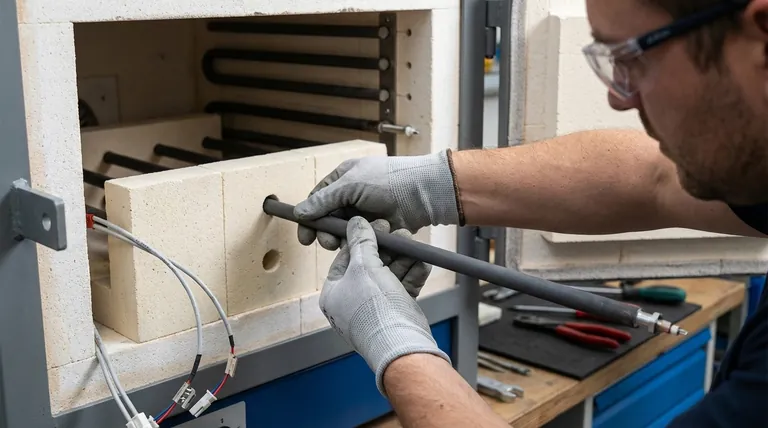
The Mechanics of Installation: Precision and Placement
The physical act of inserting the element into the furnace is where most mechanical damage occurs.
Handle with Extreme Care
Always handle the elements as if they are fragile. Avoid any impact, bending, or twisting forces. Support the element's weight evenly during movement and insertion.
Align Terminal Holes Perfectly
Ensure that the terminal holes in the furnace wall insulation are perfectly aligned. The element should slide smoothly through the opening without being forced.
If the element strikes the opposite side of the hole or requires force, it can create invisible micro-fractures that will lead to failure under thermal stress.
Center the Element in the Chamber
The active heating section of the element must be fully suspended within the furnace chamber, free from any contact with the insulation or brickwork.
If any part of the heating section touches the furnace wall, it will create a "hot spot." This prevents the element from radiating heat properly at that point, causing it to overheat and fail rapidly.
Securing Electrical Connections: Preventing Terminal Failure
A poor electrical connection is one of the most common and preventable causes of heating element failure.
Ensure Firm, Clean Contact
The electrical clamps and connecting straps must make firm, clean, and complete contact with the element's "cold ends" or terminals. Any oxidation or debris should be cleaned off before connection.
The Danger of Loose Connections
A loose connection creates high electrical resistance. This resistance generates intense heat concentrated at the terminal, which can destroy the connection strap and damage the element itself, leading to costly downtime.
Understanding the Core Constraint: Material Brittleness
The strict handling precautions are a direct result of the materials used to achieve high temperatures.
Why These Elements Are Brittle
High-performance heating elements are engineered to withstand extreme heat, often sacrificing the ductility found in common metals. This trade-off results in a ceramic-like brittleness at room temperature.
The Risk of Thermal Shock
This brittleness also makes the elements vulnerable to thermal shock. Rapid heating or cooling can cause them to crack.
While this is primarily an operational concern (e.g., not exceeding a ramp-up rate of 10°C per minute), it underscores why avoiding any physical stress during installation is so critical. A tiny, installation-induced fracture is a guaranteed failure point when the element is first heated.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your installation procedure should reflect your primary operational priority.
- If your primary focus is maximizing element lifespan: Prioritize perfect alignment and gentle handling to avoid any physical stress or micro-fractures during installation.
- If your primary focus is ensuring uniform furnace temperature: Your most important step is verifying that all new elements are within the +/- 10% resistance tolerance before they are installed.
- If your primary focus is preventing unplanned downtime: Pay meticulous attention to creating firm, clean electrical connections to eliminate terminal burnout as a failure point.
By treating installation as a precision process, you ensure the long-term reliability and performance of your entire heating system.
Summary Table:
| Precaution Area | Key Steps | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Handling | Handle with care, avoid bending or impact | Prevents cracks and brittleness issues |
| Alignment | Ensure perfect alignment in terminal holes | Avoids micro-fractures and ensures even heating |
| Electrical Connections | Make firm, clean connections | Prevents terminal burnout and downtime |
| Pre-Installation Checks | Verify resistance, inspect for damage, ensure dry environment | Ensures element integrity and proper function |
Upgrade your lab's heating system with KINTEK's precision solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide advanced high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capability ensures they meet your unique experimental needs, enhancing reliability and performance. Contact us today to discuss how our heating elements and furnaces can optimize your operations and prevent installation issues!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism



















