In short, rotary furnaces are insulated using a system of materials, primarily high-temperature refractory materials like bricks or cement for the main furnace body, and specialized ceramics like alumina or quartz for the process tube. This layered approach is essential for managing extreme temperatures, resisting chemical corrosion, and ensuring the furnace operates efficiently and safely.
The choice of insulation in a rotary furnace is not about a single material, but a strategic system. The outer body relies on robust refractories for thermal containment, while the internal process tube is selected based on its direct interaction with the material being heated, balancing temperature stability, chemical inertness, and thermal shock resistance.
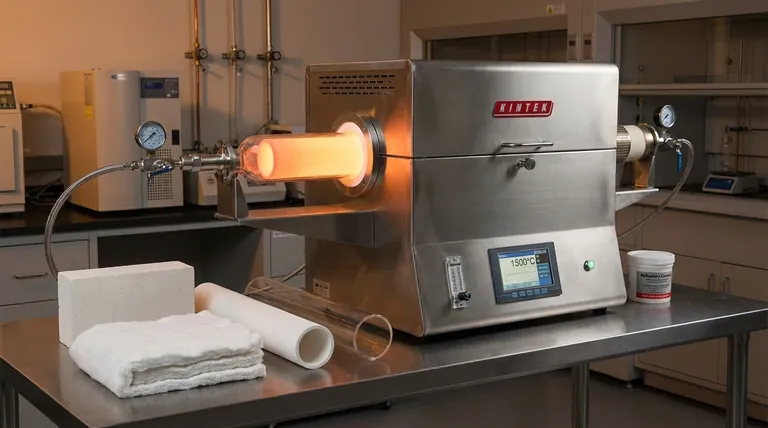

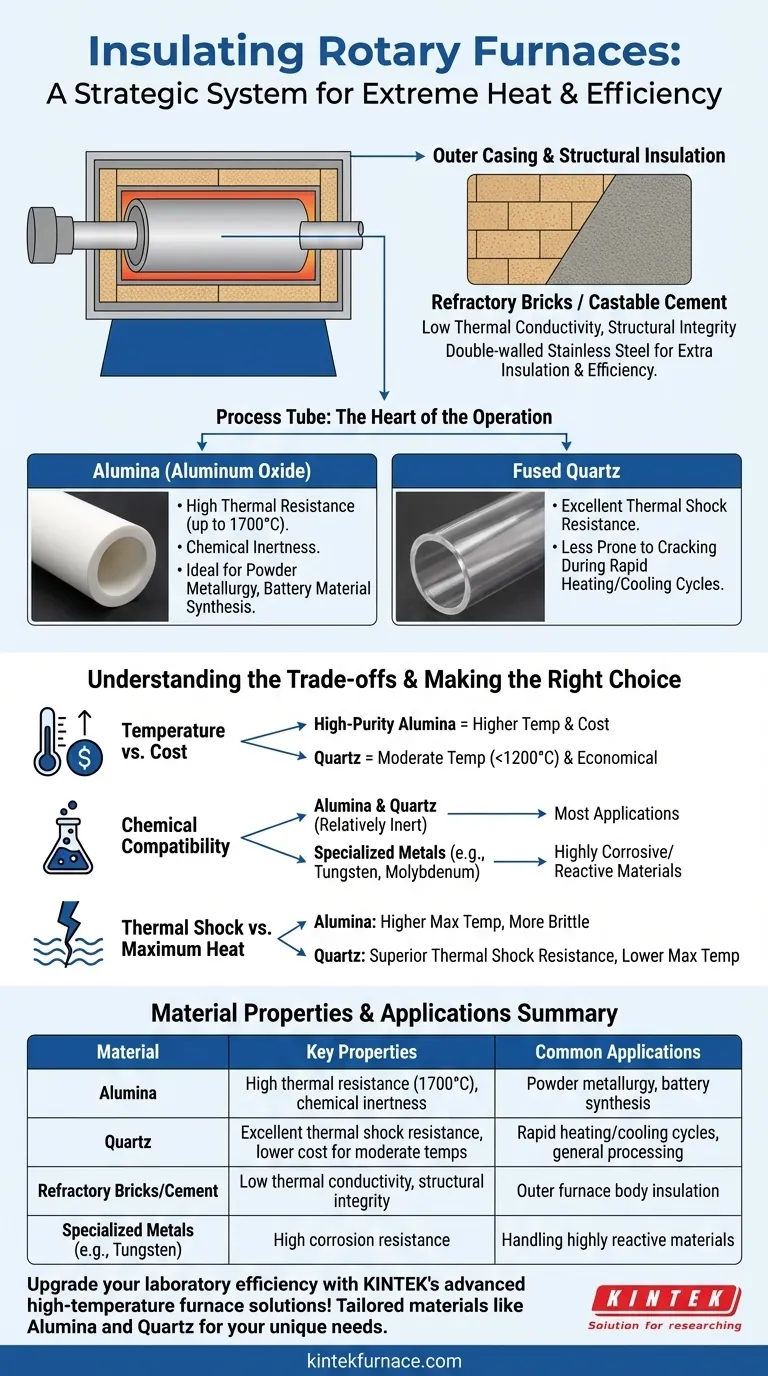
The Anatomy of Rotary Furnace Insulation
Insulating a rotary furnace involves more than one component. Think of it as a system with two primary layers, each serving a distinct but critical function: the outer structural insulation and the inner process tube.
The Outer Casing and Structural Insulation
The main body of the furnace is the first line of defense against heat loss. Its insulation is designed for maximum thermal containment and structural integrity.
This layer is typically built with refractory materials, such as specialized bricks or castable cement. These materials are chosen for their extremely low thermal conductivity and ability to withstand constant high temperatures without degrading.
Furthermore, many furnaces feature a double-walled stainless steel construction. This design creates an air gap or a space for additional insulation, further reducing heat transfer to the external environment and enhancing the furnace's overall energy efficiency.
The Process Tube: The Heart of the Operation
The process tube is where the actual heating and material processing occurs. This component is in direct contact with the process atmosphere and the material, making its composition absolutely critical.
The selection of the tube material is dictated by the specific requirements of the process, with two materials being the most common: alumina and quartz.
Why Alumina Is a Go-To Material
Alumina (Aluminum Oxide) is a high-performance ceramic known for its exceptional stability at very high temperatures, often rated for continuous use up to 1700°C (3092°F).
Its key advantages are high thermal resistance and excellent chemical inertness, making it suitable for a wide range of applications in powder metallurgy, battery material synthesis, and new energy research.
Why Quartz Is a Key Alternative
Fused Quartz is another common tube material, valued for a different primary reason: its outstanding resistance to thermal shock.
If a process requires rapid heating or cooling cycles, quartz is often the superior choice because it is far less likely to crack under sudden temperature changes. While its maximum temperature is lower than alumina's, its thermal stability makes it indispensable for specific applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right material is a matter of balancing competing priorities. There is no single "best" material, only the most appropriate material for the intended application.
Temperature vs. Cost
Higher-purity alumina tubes can withstand the most extreme temperatures, but they come at a higher cost. For processes that operate at more moderate temperatures (typically below 1200°C), quartz can be a more economical and perfectly suitable option.
Chemical Compatibility
The material being processed directly influences the choice of tube. While both alumina and quartz are relatively inert, certain highly corrosive or reactive materials may require specialized tubes. In these niche cases, metal tubes made of tungsten or molybdenum might be used.
Thermal Shock vs. Maximum Heat
This is the classic trade-off. Alumina offers a higher ceiling for sustained temperature, but it is more brittle and susceptible to cracking if heated or cooled too quickly. Quartz offers superior performance in dynamic temperature environments but has a lower maximum operating temperature.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your specific goal dictates the optimal material selection.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum operating temperatures and chemical stability: High-purity alumina is the most reliable choice for your process tube.
- If your primary focus is running processes with rapid heating and cooling cycles: Quartz is the superior option due to its excellent resistance to thermal shock.
- If your primary focus is processing highly corrosive or specific reactive materials: You may need to look beyond ceramics to specialized metal tubes like tungsten or molybdenum.
Ultimately, selecting the right insulation and tube material is a strategic engineering decision that directly impacts your process's efficiency, reliability, and success.
Summary Table:
| Material | Key Properties | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Alumina | High thermal resistance (up to 1700°C), chemical inertness | Powder metallurgy, battery material synthesis |
| Quartz | Excellent thermal shock resistance, lower cost for moderate temps | Rapid heating/cooling cycles, general processing |
| Refractory Bricks/Cement | Low thermal conductivity, structural integrity | Outer furnace body insulation |
| Specialized Metals (e.g., Tungsten) | High corrosion resistance | Handling highly reactive materials |
Upgrade your laboratory efficiency with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with tailored rotary furnaces, muffle furnaces, tube furnaces, and more. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise insulation and tube materials—like alumina or quartz—to meet your unique experimental needs for temperature stability, chemical resistance, and thermal shock management. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can enhance your process reliability and performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- How does a vertical tube furnace facilitate the simulation of the industrial sintering process for iron ores?
- What function does a tube furnace serve in the PVT growth of J-aggregate molecular crystals? Mastery of Thermal Control
- How do roller kilns and tube furnaces differ in their use of Alumina ceramic tubes? Compare Transport vs. Containment
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency



















