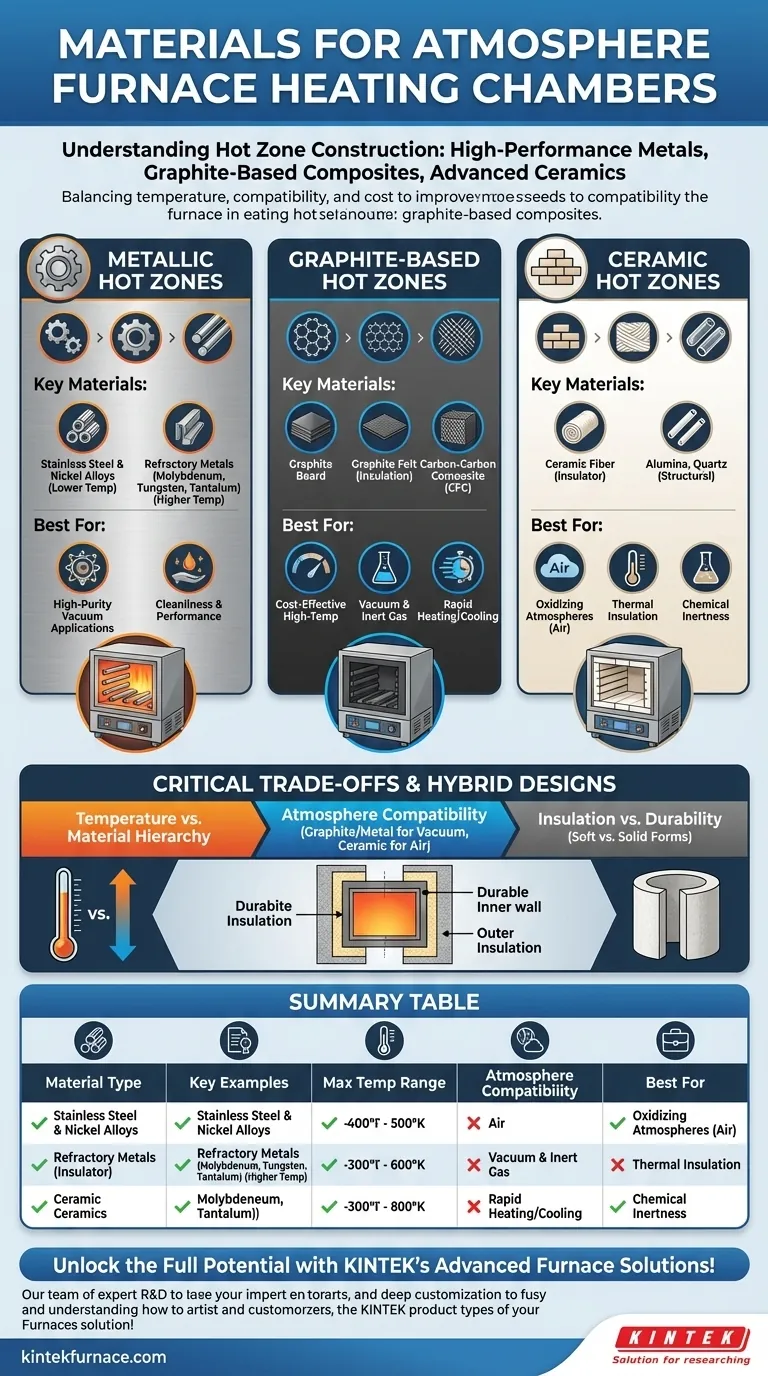
The heart of any atmosphere furnace, its heating chamber or "hot zone," is constructed from a select group of materials engineered for extreme conditions. The choice typically falls into three main categories: high-performance metals, graphite-based composites, and advanced ceramics. The specific material is chosen to withstand the target temperature while remaining compatible with the controlled gas atmosphere inside the furnace.
The selection of a hot zone material is not just about heat resistance. It is a critical trade-off between the required processing temperature, chemical compatibility with the furnace atmosphere, and the long-term operational cost and durability of the system.

The Three Pillars of Hot Zone Construction
The construction of a hot zone is fundamentally a materials science challenge. The goal is to contain immense heat, insulate the rest of the furnace, and avoid reacting with the product or process gases.
Metallic Hot Zones
Metallic hot zones are prized for their cleanliness and performance in high-vacuum applications. The material choice is directly tied to the maximum operating temperature.
Lower-temperature furnaces may use stainless steel or nickel-based alloys.
For higher temperatures, true refractory metals are required. This includes molybdenum (often with its alloy TZM), tungsten, and tantalum, which can operate at extremely high temperatures.
Graphite-Based Hot Zones
Graphite is an excellent and cost-effective high-temperature material, making it a very common choice for vacuum and inert gas furnaces.
These hot zones can be built from rigid graphite board, flexible graphite felt for insulation, or high-strength carbon-carbon composite (CFC) for structural elements and heating elements.
Graphite offers rapid heating and cooling cycles and is easy to machine, but it will readily oxidize and degrade if operated in the presence of oxygen at high temperatures.
Ceramic Hot Zones
Ceramics are defined by their exceptional thermal insulation properties and chemical inertness, especially in oxidizing atmospheres where metals and graphite would fail.
Ceramic fiber boards and blankets are widely used as the primary insulator. For process tubes or structural components, high-purity materials like alumina and quartz are common choices due to their high-temperature stability and resistance to chemical attack.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Why Material Choice is Critical
There is no single "best" material. The optimal choice is always a compromise based on the specific demands of the application. An incorrect choice can lead to contamination, component failure, and poor processing results.
Temperature vs. Material
The maximum operating temperature is the first and most important filter. A simple hierarchy is stainless steel (lowest), followed by nickel alloys, then molybdenum, and finally tungsten (highest). Graphite and many ceramics also fall into the very high-temperature category.
Atmosphere Compatibility
This is the defining factor for an "atmosphere furnace." A graphite hot zone is ideal for nitrogen, argon, or vacuum, but it is unsuitable for a process running in air.
Conversely, a ceramic hot zone is one of the few options that can perform reliably in an air or oxygen-rich atmosphere at high temperatures. Refractory metals are sensitive to certain gases and are best suited for high-purity vacuum or inert gas environments.
Insulation vs. Durability
Material form plays a major role. Soft insulators like ceramic fiber or graphite felt provide excellent thermal efficiency but can be fragile and shed particles.
Solid components made of metal, CFC, or rigid graphite boards are far more durable and structurally sound but have different insulation characteristics that must be designed into the overall system.
The Rise of Hybrid Designs
Modern furnaces frequently use a combination of materials to optimize performance and cost. It is common to see a hot zone with a durable CFC or metallic inner wall, backed by layers of highly efficient graphite felt or ceramic fiber insulation.
Selecting the Right Material for Your Process
Your specific application dictates the ideal hot zone construction. By defining your primary goal, you can narrow down the best material system for your needs.
- If your primary focus is high-purity processing or deep vacuum: Metallic hot zones, particularly those made from molybdenum or tungsten, offer the cleanest environment.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective, high-temperature work in inert gas or vacuum: Graphite-based hot zones provide an unmatched combination of performance and value.
- If your primary focus is processing in an air or oxidizing atmosphere: An all-ceramic hot zone, using materials like alumina and ceramic fiber, is the only reliable choice.
Ultimately, understanding these material trade-offs empowers you to select a furnace that is not just a tool, but a precise instrument engineered for your specific application.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Key Examples | Max Temp Range | Atmosphere Compatibility | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metallic | Molybdenum, Tungsten, Stainless Steel | Low to Very High | High-vacuum, Inert Gas | High-purity, Vacuum Processing |
| Graphite-Based | Graphite Board, Carbon-Carbon Composite | High | Vacuum, Inert Gas | Cost-effective, Rapid Heating |
| Ceramic | Alumina, Quartz, Ceramic Fiber | High | Oxidizing (e.g., Air) | Chemical Inertness, Air Processing |
Unlock the Full Potential of Your Laboratory with KINTEK's Advanced Furnace Solutions!
Are you struggling to choose the right heating chamber material for your atmosphere furnace? Our expert team leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide tailored high-temperature furnace solutions. Whether you need Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, or CVD/PECVD Systems, we offer deep customization to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements.
Contact us today via our contact form to discuss how we can enhance your lab's efficiency, durability, and performance with the perfect furnace setup for your needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does the inert atmosphere heat treating process work? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Material Quality
- How does a chemically inert atmosphere function in a furnace? Prevent Oxidation and Ensure Material Purity
- What are the environmental benefits of using inert gases in furnaces? Reduce Waste and Emissions for a Greener Process
- How does nitrogen atmosphere heat treatment improve surface strengthening? Enhance Durability and Performance
- What is nitrogen used for in a furnace? Prevent Oxidation and Control Heat Treatment Quality



















