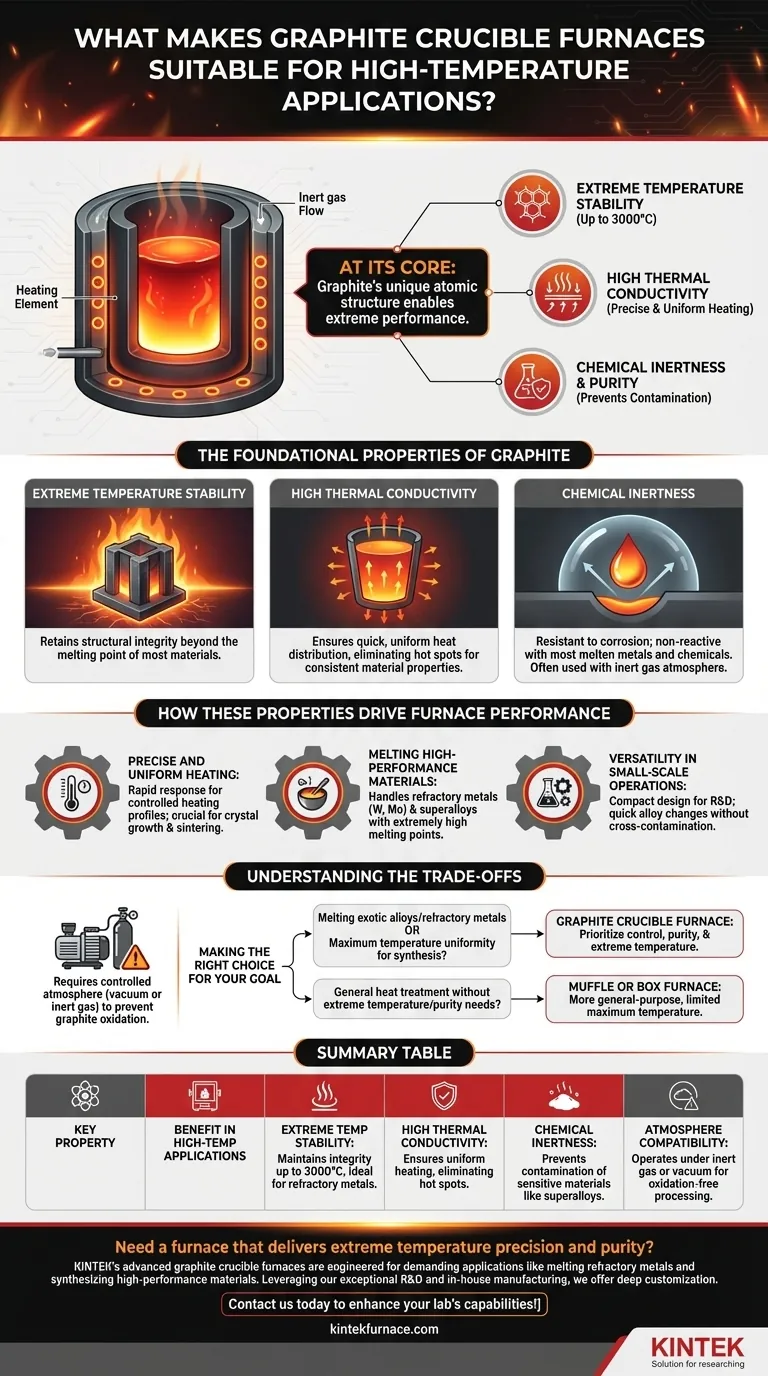
At its core, the suitability of graphite crucible furnaces for high-temperature applications stems from graphite's unique atomic structure. This structure grants it an exceptional combination of high thermal conductivity, chemical inertness, and the ability to maintain mechanical stability at extreme temperatures, reaching as high as 3000°C.
The decision to use a graphite crucible furnace is not just about reaching a high temperature. It is about achieving a precisely controlled, uniform, and clean heating environment that is essential for processing sensitive, high-performance materials.

The Foundational Properties of Graphite
Graphite's performance in furnaces is a direct result of its fundamental material characteristics. Understanding these properties explains why it is the material of choice for demanding thermal processes.
Extreme Temperature Stability
Graphite's hexagonal, layered structure of carbon atoms is incredibly stable. This allows it to retain its structural integrity and mechanical strength at temperatures far beyond the melting point of most metals and ceramics.
High Thermal Conductivity
Unlike many materials that resist heat, graphite conducts it exceptionally well. This high thermal conductivity ensures that heat is distributed quickly and evenly throughout the crucible.
The result is excellent temperature uniformity, eliminating hot spots and ensuring the entire material being processed experiences the same thermal conditions. This is critical for consistent material properties.
Chemical Inertness and Purity
Graphite is highly resistant to corrosion and does not readily react with most molten metals, alloys, or chemicals. This inertness is crucial for preventing contamination during high-temperature processing.
Furthermore, these furnaces can be operated with an inert gas atmosphere (like argon), which prevents oxidation and other unwanted reactions when working with sensitive materials like superalloys or refractory metals.
How These Properties Drive Furnace Performance
The material science of graphite translates directly into key operational advantages that define the furnace's capabilities.
Precise and Uniform Heating
The high thermal conductivity of the graphite crucible allows for rapid response to temperature adjustments. This enables precise control over the heating profile and ensures the temperature remains stable and uniform across the entire workload.
This level of control is essential for applications like crystal growth, sintering advanced ceramics, and creating specialized alloys where slight temperature deviations can ruin the final product.
Melting High-Performance Materials
Many advanced materials, such as refractory metals (e.g., tungsten, molybdenum) and high-temperature superalloys, have extremely high melting points. Standard furnaces simply cannot reach the necessary temperatures.
Graphite crucible furnaces are specifically designed to operate in this range, making them one of the few viable options for melting and processing these demanding materials.
Versatility in Small-Scale Operations
These furnaces are often compact, making them ideal for laboratory research, development, and small-scale production runs.
Their design allows for quick changes between different types of alloys without the risk of cross-contamination, offering a level of flexibility that is difficult to achieve with other furnace types.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, graphite crucible furnaces are a specialized tool. Their advantages come with considerations that make them different from more general-purpose furnaces.
The Need for a Controlled Atmosphere
Graphite will oxidize (burn away) in the presence of air at high temperatures. Therefore, operating these furnaces requires a vacuum or an inert gas backfill to protect the graphite components.
This adds a layer of operational complexity compared to a standard air-atmosphere box furnace.
Comparison to Other Furnace Types
Muffle furnaces can also reach high temperatures quickly, but they isolate the material from the heating elements, which can sometimes lead to less temperature uniformity compared to a direct-heating graphite crucible.
Box furnaces are durable workhorses built for a wide range of applications. However, they typically use metallic heating elements and fibrous insulation, which limits their maximum temperature and makes them unsuitable for the extreme conditions that graphite handles easily.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the correct furnace, you must align the equipment's strengths with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is melting exotic alloys or refractory metals: The ultra-high temperature capability and chemically inert environment of a graphite crucible furnace are essential.
- If your primary focus is maximum temperature uniformity for material synthesis: The superior thermal conductivity of graphite makes it the ideal choice for creating homogenous, high-quality materials.
- If your primary focus is general heat treatment without extreme temperature or purity needs: A more conventional and cost-effective muffle or box furnace is likely the better tool for the job.
Ultimately, choosing a graphite crucible furnace is a decision to prioritize control, purity, and temperature capability above all else.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Benefit in High-Temp Applications |
|---|---|
| Extreme Temperature Stability | Maintains integrity up to 3000°C, ideal for refractory metals |
| High Thermal Conductivity | Ensures uniform heating, eliminating hot spots |
| Chemical Inertness | Prevents contamination of sensitive materials like superalloys |
| Atmosphere Compatibility | Operates under inert gas or vacuum for oxidation-free processing |
Need a furnace that delivers extreme temperature precision and purity? KINTEK's advanced graphite crucible furnaces are engineered for demanding applications like melting refractory metals and synthesizing high-performance materials. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our high-temperature solutions can enhance your lab's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals



















