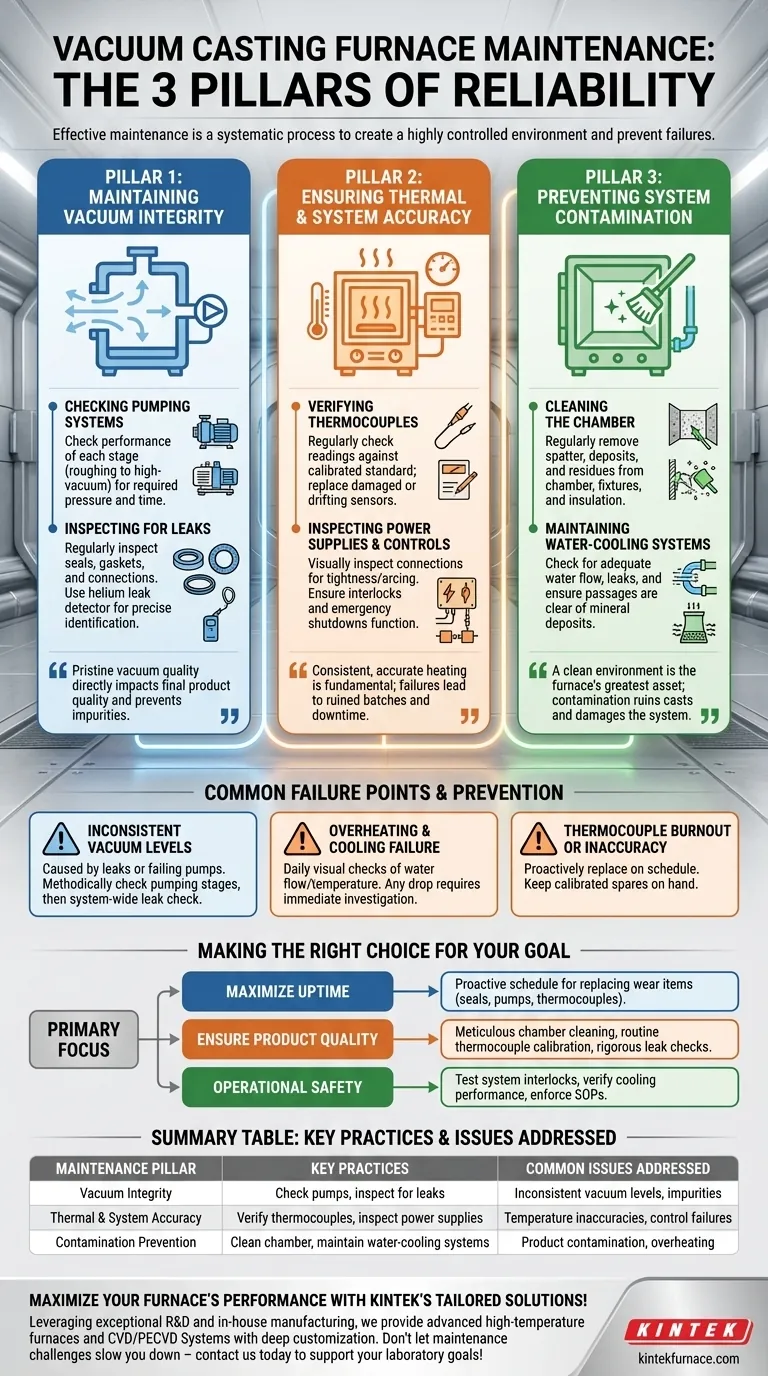
Effective maintenance for a vacuum casting furnace is not a single task, but a systematic process built on three core pillars. It requires regular inspection of water-cooling systems to prevent overheating, meticulous cleaning of the vacuum chamber to avoid product contamination, and consistent verification of all system components—from vacuum pumps to thermocouples—to ensure operational integrity and safety.
The goal of vacuum furnace maintenance is not simply to fix what is broken, but to create a highly controlled environment. True reliability comes from proactively managing vacuum integrity, thermal accuracy, and system cleanliness to prevent failures before they impact production.
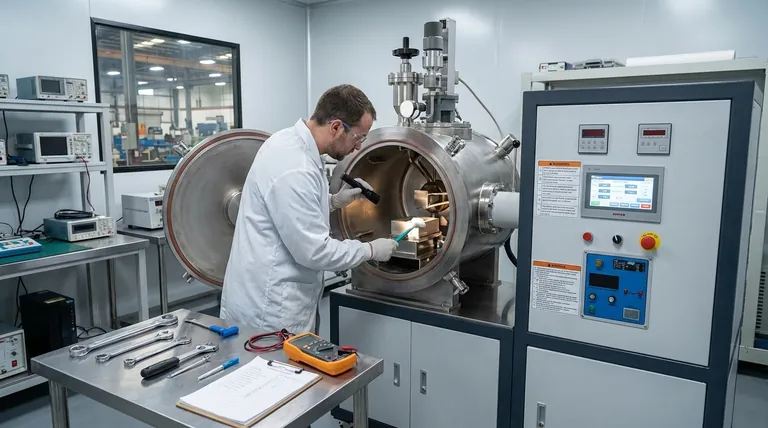

The Three Pillars of Furnace Reliability
A robust maintenance program is best understood by focusing on the three critical systems that dictate the performance and longevity of your vacuum casting furnace.
Pillar 1: Maintaining Vacuum Integrity
The quality of your vacuum directly impacts the quality of your final product. Any compromise in the vacuum system can introduce impurities and defects.
Checking Pumping Systems
Your vacuum pumps are the heart of the system. Maintenance should involve checking the performance of each pumping stage, from the roughing pump to the high-vacuum pump, to ensure they achieve the required pressure levels in the specified time.
Inspecting for Leaks
Even minor leaks can degrade the vacuum environment. Regularly inspect all seals, gaskets, and connections for signs of wear or damage. A helium leak detector can be used for precise identification of leak points in the system.
Pillar 2: Ensuring Thermal & System Accuracy
Consistent and accurate heating is fundamental to the casting process. Failures in the thermal or control systems can lead to ruined batches and significant downtime.
Verifying Thermocouples
Thermocouples are essential for accurate temperature measurement but can fail or drift, especially when exposed to high vapor pressures from certain materials. Regularly check their readings against a calibrated standard and replace any that are damaged or inaccurate.
Inspecting Power Supplies and Controls
The power supply and heating elements are critical components. Visually inspect all connections for tightness and signs of arcing or overheating. Ensure all control system interlocks and emergency shutdowns are functioning correctly.
Pillar 3: Preventing System Contamination
The pristine environment inside a vacuum furnace is its greatest asset. Contamination can ruin casts and damage the furnace itself.
Cleaning the Chamber
The vacuum chamber must be kept impeccably clean. Regularly remove any spatter, deposits, or residues from the chamber walls, fixtures, and insulation. This prevents outgassing, which can compromise the vacuum level and contaminate the melt.
Maintaining Water-Cooling Systems
The water-cooling system prevents the furnace shell and critical components from overheating. Routinely check for adequate water flow, look for leaks, and ensure water passages are clear of mineral deposits or blockages that could restrict cooling.
Common Failure Points and How to Avoid Them
Understanding common problems helps you focus your maintenance efforts where they matter most. Neglecting these areas is the fastest path to costly downtime.
Inconsistent Vacuum Levels
If your furnace struggles to reach or hold its target vacuum level, the issue is almost always a leak or a failing pump. Start by methodically checking each pumping stage, then move to a system-wide leak check if the pumps are performing correctly.
Overheating and Cooling Failure
A catastrophic failure of the cooling system can cause irreparable damage to the furnace. Daily visual checks of water flow and temperature are non-negotiable. Any drop in pressure or flow should trigger an immediate investigation.
Thermocouple Burnout or Inaccuracy
Sudden thermocouple failure can scrap a batch in progress. Proactively replacing thermocouples on a set schedule, especially in high-wear applications, is far cheaper than reacting to a failure. Keep calibrated spares on hand at all times.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your maintenance strategy should align with your primary operational priority.
- If your primary focus is maximizing uptime: Prioritize a proactive schedule for replacing wear items like seals, pumps, and thermocouples before they fail.
- If your primary focus is ensuring product quality: Emphasize meticulous chamber cleaning, routine thermocouple calibration, and rigorous vacuum leak checks.
- If your primary focus is operational safety: Concentrate on testing system interlocks, verifying cooling system performance, and enforcing standardized operating procedures (SOPs).
Ultimately, consistent maintenance is an investment in reliability, ensuring your furnace operates as a precision instrument, not an unpredictable variable.
Summary Table:
| Maintenance Pillar | Key Practices | Common Issues Addressed |
|---|---|---|
| Vacuum Integrity | Check pumps, inspect for leaks | Inconsistent vacuum levels, impurities |
| Thermal & System Accuracy | Verify thermocouples, inspect power supplies | Temperature inaccuracies, control failures |
| Contamination Prevention | Clean chamber, maintain water-cooling systems | Product contamination, overheating |
Maximize your furnace's performance with KINTEK's tailored solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide advanced high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, enhancing reliability and efficiency. Don't let maintenance challenges slow you down—contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the common applications of Vacuum Induction Melting? Essential for High-Performance Metals and Alloys
- What role does a vacuum induction melting furnace play in Fe-5%Mn-C alloys? Ensure Chemical Integrity and High Purity
- How does the Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) process work? Achieve Superior Metal Purity and Control
- What is vacuum induction melting technology and why is it important? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- What are some common applications of vacuum induction melting and casting (VIM&C)? Essential for Aerospace, Medical, and Nuclear Industries



















