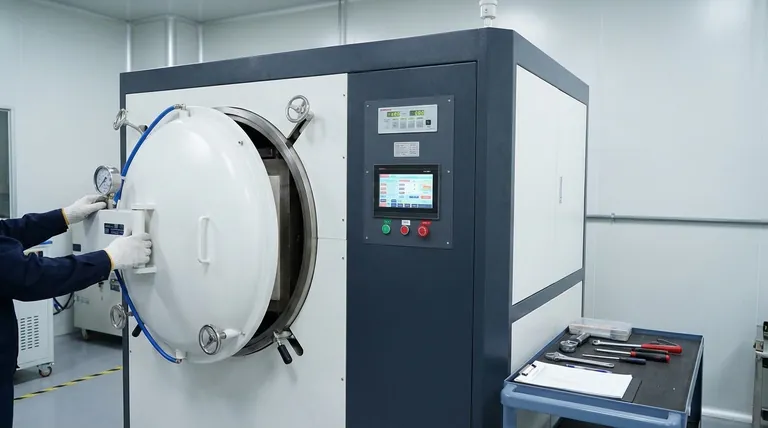
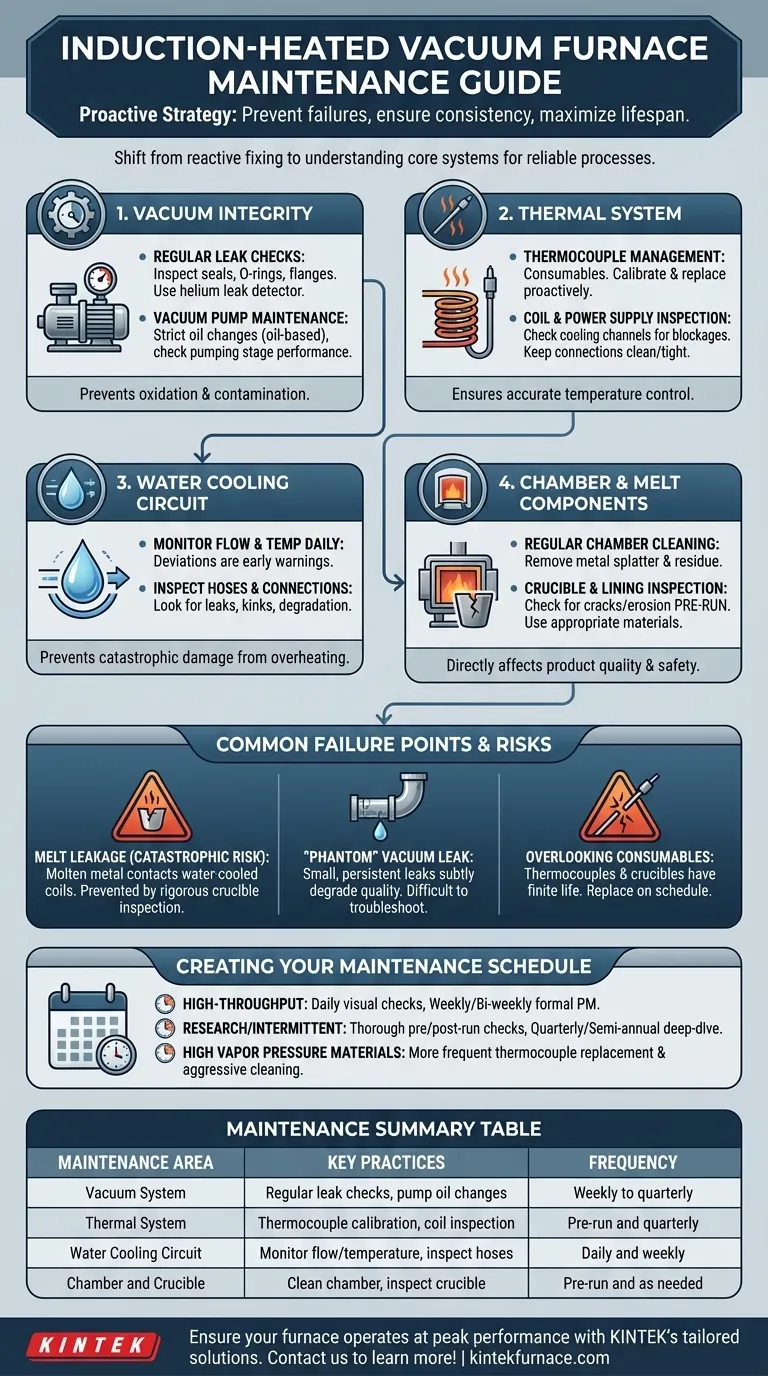
The most critical maintenance practices for an induction-heated vacuum furnace center on four key areas: the water cooling circuit, the vacuum system, the thermal control components, and the physical integrity of the furnace chamber and crucible. Regular, proactive checks of these systems are essential for preventing catastrophic failures, ensuring process consistency, and maximizing the operational lifespan of the equipment.
The core principle of effective furnace maintenance is shifting from a reactive mindset of fixing failures to a proactive strategy of preventing them. This isn't about a simple checklist; it's about understanding how each system contributes to a reliable, repeatable process.

Mastering the Core Systems: A Proactive Maintenance Plan
A comprehensive maintenance plan treats the furnace not as a single object, but as a group of interconnected systems. Each requires specific attention to prevent common, and often costly, failure modes.
1. Ensuring Vacuum Integrity
The quality of your vacuum directly impacts product purity by preventing oxidation and contamination. An insufficient vacuum is a common issue that degrades results.
Regular Leak Checks are non-negotiable. Inspect all seals, O-rings, flanges, and feedthroughs for signs of wear or damage. A helium leak detector is the standard for identifying small, hard-to-find leaks that can compromise your process.
Vacuum Pump Maintenance is foundational. For oil-based pumps, adhere to a strict oil change schedule to prevent contamination. For all pump types, regularly check pumping stage performance to ensure the system is drawing down to the required pressure efficiently.
2. Validating the Thermal System
Inaccurate temperature control can ruin a melt or, at worst, damage the furnace. This system includes the power supply, induction coil, and thermocouples.
Thermocouple Management is critical. Thermocouples are consumables that degrade over time, especially when exposed to high temperatures and vapor pressure from certain metals. Calibrate them regularly and replace them proactively.
Induction Coil and Power Supply Inspection should focus on the cooling channels. Ensure there are no blockages or leaks. Keep all electrical connections clean and tight to prevent arcing and ensure efficient power delivery.
3. Maintaining the Water Cooling Circuit
The water cooling system is the lifeblood of an induction furnace. A failure here can lead to the induction coil or power supply melting, resulting in catastrophic damage.
Monitor Flow and Temperature Daily. Any deviation from the normal operating parameters for flow rate or temperature is an early warning sign that requires immediate investigation.
Inspect Hoses and Connections. Look for leaks, kinks, or signs of hose degradation. A failed hose during operation can cause extensive damage and significant downtime.
4. Preserving the Chamber and Melt Components
The interior of the furnace is where the process happens. Its condition directly affects product quality and operational safety.
Regular Chamber Cleaning is essential to remove metal splatter and residue. Contamination left in the chamber can vaporize in subsequent runs and ruin the purity of a new melt.
Crucible and Lining Inspection must be performed before every run. Look for cracks or erosion. Using a damaged crucible is the primary cause of melt leakage, a highly destructive failure mode. Always use a crucible and lining material appropriate for the metal being processed.
Understanding the Common Failure Points
Beyond routine checks, it's crucial to understand the most severe and common failure points to appreciate the importance of preventative maintenance.
The Catastrophic Risk of Melt Leakage
A melt-through is the most destructive failure. It occurs when molten metal leaks from a cracked crucible and comes into contact with the water-cooled induction coils. This can cause a steam explosion and destroy the entire hot zone. This is prevented almost entirely by rigorous crucible inspection.
The "Phantom" Vacuum Leak
A major vacuum leak is obvious, but a small, persistent one is more insidious. It may not prevent the furnace from reaching a seemingly acceptable vacuum level, but it can introduce enough oxygen or nitrogen to subtly degrade metallurgical properties, leading to inconsistent product quality that is difficult to troubleshoot.
Overlooking Consumables
Treating thermocouples and crucibles as permanent parts is a frequent mistake. They are consumables with a finite life. Tracking their usage and replacing them on a schedule—before they fail—is a key practice that separates reliable operations from those plagued by unexpected downtime.
Creating Your Maintenance Schedule
The right maintenance frequency depends on your operational tempo and the materials you process. Use the following as a guide.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput production: Implement daily visual checks of water flow and system readouts, with a formal, in-depth preventative maintenance schedule performed weekly or bi-weekly.
- If your primary focus is research or intermittent use: A thorough pre-run and post-run checklist is your most powerful tool, supplemented by a deep-dive maintenance service on a quarterly or semi-annual basis.
- If you are processing materials with high vapor pressure: Plan for more frequent thermocouple replacement and aggressive chamber cleaning to manage the higher rate of contamination and component degradation.
Ultimately, proactive and diligent maintenance is a direct investment in process control, reliability, and operational safety.
Summary Table:
| Maintenance Area | Key Practices | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Vacuum System | Regular leak checks, pump oil changes | Weekly to quarterly |
| Thermal System | Thermocouple calibration, coil inspection | Pre-run and quarterly |
| Water Cooling Circuit | Monitor flow/temperature, inspect hoses | Daily and weekly |
| Chamber and Crucible | Clean chamber, inspect crucible for cracks | Pre-run and as needed |
Ensure your induction-heated vacuum furnace operates at peak performance with KINTEK's tailored solutions. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide advanced high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capability precisely meets your unique experimental needs, enhancing reliability and process consistency. Don't let maintenance issues disrupt your workflow—contact us today to learn how our expertise can benefit your laboratory!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the functions of a high-vacuum furnace for CoReCr alloys? Achieve Microstructural Precision and Phase Stability
- Why does heating steel rod bundles in a vacuum furnace eliminate heat transfer paths? Enhance Surface Integrity Today
- What are the benefits of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Control
- What is the vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Surface Quality and Material Performance
- What are the proper procedures for handling the furnace door and samples in a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Integrity & Safety



















