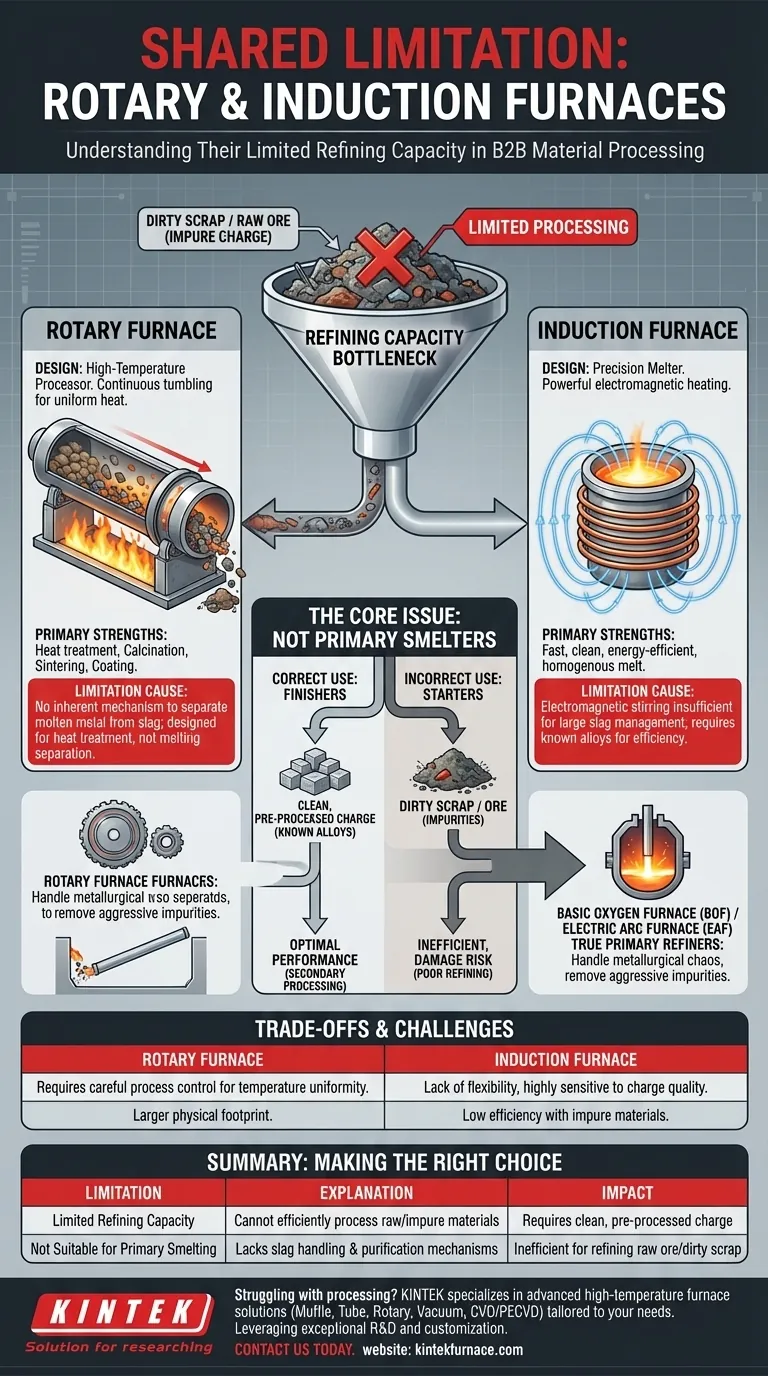
At their core, the most significant operational limitation shared by both rotary and induction furnaces is their limited refining capacity. Both technologies are ill-suited for processing raw, impure materials. They function best when fed a "charge"—the input material—that is already of a known chemical composition and free from significant oxides or other contaminants.
While they operate on entirely different principles, both furnace types are designed as secondary processing tools, not primary smelters. Their shared weakness is an inability to efficiently separate valuable metal from the large amounts of slag and impurities found in raw ore or dirty scrap.

What "Limited Refining Capacity" Actually Means
This limitation is not a design flaw but a consequence of their specialized purpose. Understanding this requires distinguishing between melting and refining.
The Need for a "Clean Charge"
Both furnace types demand a clean, pre-processed charge. This means the material you put into the furnace must be relatively pure and of a known alloy.
They lack the robust mechanisms to handle and separate large volumes of slag, which is the non-metallic byproduct generated when impurities are removed from metal. Feeding them "dirty" scrap or raw ore would be highly inefficient and could damage the equipment.
They Are Not Primary Smelters
Furnaces designed for true refining, like a Basic Oxygen Furnace (BOF) or an Electric Arc Furnace (EAF), are built to handle metallurgical chaos. They can take raw iron ore or a mix of scrap metals and actively remove impurities like carbon, silicon, and phosphorus through powerful chemical reactions.
Rotary and induction furnaces are simply not equipped for this aggressive purification. They are finishers, not starters.
Why Each Furnace Type Has This Limitation
The reasons for this shared limitation stem from their unique designs and heating methods.
The Rotary Furnace: A High-Temperature Processor
A rotary furnace is essentially a long, rotating, inclined cylinder heated externally. Material tumbles through it, ensuring every particle receives uniform heat exposure.
Its purpose is heat treatment, not melting and separating. It excels at processes like calcination (thermal decomposition), sintering (fusing powders together), or applying a coating. It has no inherent mechanism to separate a molten metal pool from a layer of slag.
The Induction Furnace: A Precision Melter
An induction furnace uses a powerful electromagnetic field to heat the conductive metal charge directly. This process is incredibly fast, clean, and energy-efficient.
Its strength is its precision. However, the electromagnetic currents that heat the metal also create a stirring action. While this ensures a homogenous melt, it is not turbulent enough to manage large quantities of slag. Introducing significant impurities would disrupt the efficiency and precise temperature control that are the furnace's primary advantages.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a furnace means accepting its inherent compromises.
Rotary Furnace Challenges
The primary function of a rotary furnace—continuous movement—can also introduce problems. Slight temperature variations can occur along the length of the furnace, requiring careful process control to ensure a uniform product.
Furthermore, their horizontal design often requires a larger physical footprint compared to vertical furnaces.
Induction Furnace Challenges
The main trade-off for an induction furnace's speed and precision is its lack of flexibility. It is highly sensitive to the quality of the charge material.
Its performance depends on using known alloys and clean scrap. Attempting to use it as a primary refining tool will lead to poor results, low energy efficiency, and potential damage to the furnace lining from reactive slag.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your specific goal determines the correct technology.
- If your primary focus is on continuous heat treatment, calcination, or sintering of powders and pellets: A rotary furnace is the ideal tool, providing uniform thermal processing for pre-prepared materials.
- If your primary focus is on melting clean, pre-alloyed metals with high precision and efficiency: An induction furnace offers unparalleled speed and temperature control for secondary melting applications like foundries.
- If your primary focus is on refining raw ore or processing large volumes of mixed, impure scrap metal: You must look to true refining technologies like an Electric Arc Furnace (EAF), as neither a rotary nor an induction furnace is suitable.
Understanding that these are specialized finishing tools, not general-purpose refiners, is the key to leveraging their strengths effectively.
Summary Table:
| Limitation | Explanation | Impact on Use |
|---|---|---|
| Limited Refining Capacity | Cannot efficiently process raw, impure materials; best for secondary processing | Requires clean, pre-processed charge of known composition |
| Not Suitable for Primary Smelting | Lacks mechanisms to handle large slag volumes or aggressive purification | Inefficient for refining raw ore or dirty scrap |
| Shared Weakness | Both are finishing tools, not starters, due to design and heating methods | Must be paired with primary refining furnaces like EAF or BOF |
Struggling with material processing limitations? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique needs. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all with deep customization capabilities. Whether you're in a lab requiring precise heat treatment or need reliable secondary processing, our expertise ensures optimal performance and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your operations with the right furnace solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What supplementary features can enhance rotary tube furnace performance? Boost Efficiency with Precision Control
- What are the main structural components of a rotary furnace? Explore Key Parts for Efficient Material Processing
- What types of materials are suitable for processing in rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Free-Flowing Powders and Granules
- What factors should be considered when selecting a tube for a rotary tube furnace? Ensure Optimal Performance and Longevity
- How do rotary tube furnaces achieve precise temperature control? Master Uniform Heating for Dynamic Processes



















