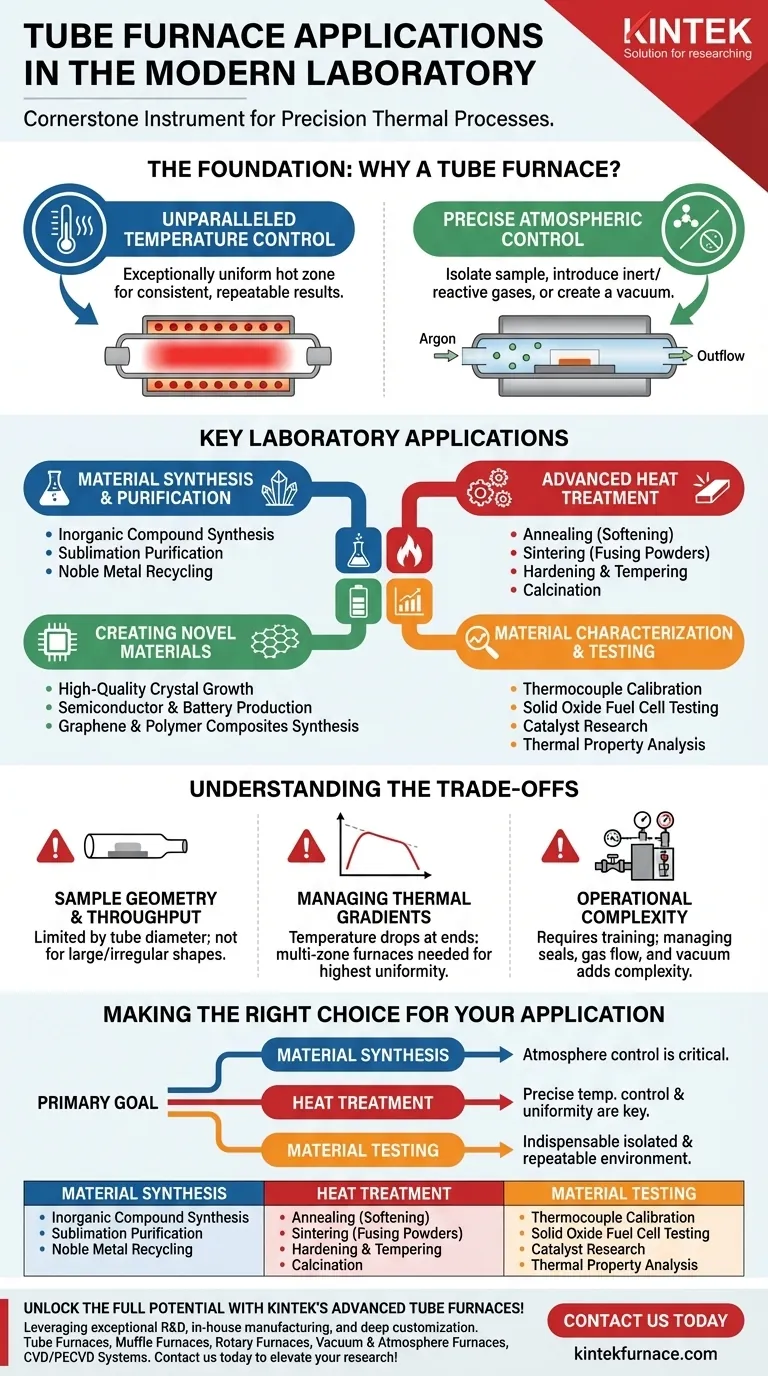
In the modern laboratory, a tube furnace is a cornerstone instrument for a vast range of thermal processes. Its primary applications involve the synthesis and purification of compounds, the heat treatment of materials to alter their properties, the creation of advanced materials like crystals and graphene, and the precise analysis of material behavior under controlled thermal and atmospheric conditions.
The core value of a tube furnace is not just its ability to get hot, but its capacity to create a highly uniform and precisely controlled environment. This control over both temperature and atmosphere is what makes it indispensable for sensitive processes in materials science, chemistry, and engineering.

The Foundation: Why a Tube Furnace?
Before listing applications, it is crucial to understand why a tube furnace is selected over other heating methods. The choice is driven by two fundamental capabilities.
Unparalleled Temperature Control and Uniformity
A tube furnace works by surrounding a central ceramic or metal tube with heating elements. This design creates an exceptionally uniform hot zone along the length of the tube.
This uniformity is critical for processes where every part of the sample must experience the exact same temperature, ensuring consistent and repeatable results.
Precise Atmospheric Control
The enclosed tube is the furnace's defining feature. It allows you to completely isolate the sample from the outside air.
You can then introduce a vacuum to remove gases or flow a specific gas—such as an inert gas (like Argon) to prevent oxidation or a reactive gas to participate in a chemical reaction. This capability is impossible in a standard box furnace.
Key Laboratory Applications
The combination of precise thermal and atmospheric control unlocks a wide array of applications, which can be grouped into several key categories.
Material Synthesis and Purification
Tube furnaces are workhorses for creating and refining compounds. The controlled environment is perfect for air-sensitive or high-purity reactions.
Applications include the synthesis of inorganic compounds, purification of organic and inorganic materials through processes like sublimation, and even noble metal recycling.
Advanced Heat Treatment
Heat treatment modifies the microstructure and physical properties of a material. A tube furnace's ability to execute precise heating and cooling profiles is essential here.
Common processes include:
- Annealing: Softening materials and relieving internal stresses.
- Sintering: Fusing powders together to form a solid mass.
- Hardening & Tempering: Strengthening metals and ceramics.
- Calcination: Decomposing materials through heating.
Creating Novel Materials
The development of next-generation materials often relies on the precise conditions only a tube furnace can provide.
This includes the growth of high-quality single crystals for electronics, the production of semiconductors and batteries, and the synthesis of advanced materials like graphene and polymer composites.
Material Characterization and Testing
Researchers use tube furnaces to study how materials behave under specific conditions, providing critical data for development and quality control.
This includes thermocouple calibration, testing components for solid oxide fuel cells, catalyst research, and analyzing the thermal properties of polymers and aerospace ceramics.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly versatile, tube furnaces have practical limitations that are important to consider.
Sample Geometry and Throughput
The most obvious limitation is the diameter of the tube. This restricts the size and shape of the samples you can process. They are generally not suitable for treating large or irregularly shaped components.
Managing Thermal Gradients
While the central hot zone is highly uniform, the temperature naturally drops off toward the ends of the tube. For processes requiring the absolute highest uniformity, multi-zone furnaces with independent controllers for each section are used to extend and flatten this hot zone.
Operational Complexity
Compared to a simple box oven, operating a tube furnace—especially one with vacuum and gas flow systems—requires more training and setup. Ensuring a proper seal and managing gas flow adds layers of complexity to the experimental procedure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To determine if a tube furnace is the correct tool, consider your primary experimental goal.
- If your primary focus is material synthesis or chemical reaction: The ability to control the atmosphere to prevent side reactions or introduce reactive gases is the most critical feature.
- If your primary focus is heat treatment (annealing, sintering): The precise temperature control and uniform hot zone are the key benefits for achieving consistent material properties.
- If your primary focus is material testing and analysis: The furnace provides an indispensable, isolated, and repeatable environment to study material behavior under specific conditions.
Ultimately, a tube furnace is the instrument of choice whenever a process demands uncompromising control over its thermal and atmospheric environment.
Summary Table:
| Application Category | Key Uses |
|---|---|
| Material Synthesis & Purification | Inorganic compound synthesis, sublimation, noble metal recycling |
| Advanced Heat Treatment | Annealing, sintering, hardening, tempering, calcination |
| Novel Material Creation | Crystal growth, graphene synthesis, semiconductor and battery production |
| Material Characterization | Thermocouple calibration, fuel cell testing, catalyst research |
Unlock the full potential of your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced tube furnaces! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with high-temperature solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line, including Tube Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is enhanced by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you're focused on material synthesis, heat treatment, or analysis, KINTEK ensures superior performance and reliability. Contact us today to discuss how we can elevate your research and achieve consistent, high-quality results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing



















