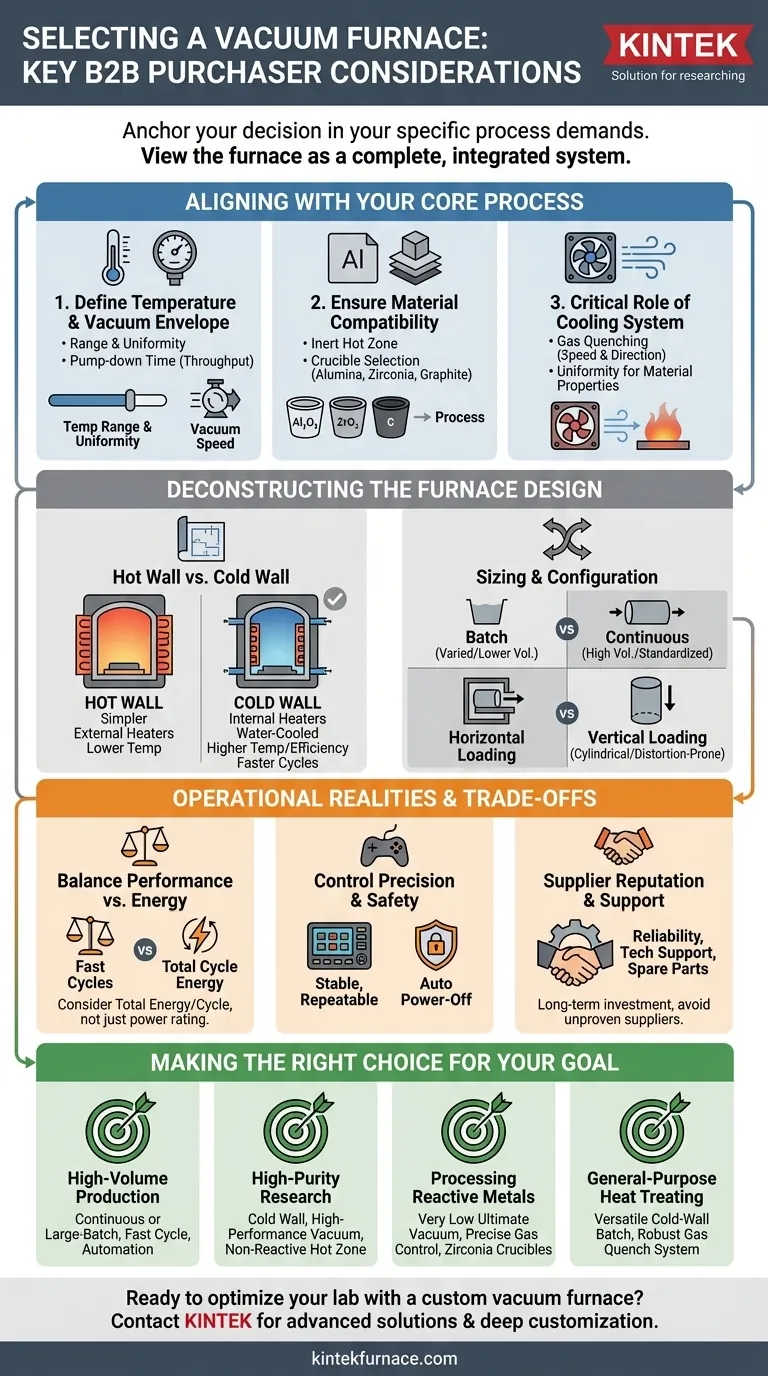
When selecting a vacuum furnace, your decision must be anchored in the specific demands of your application. The key is to evaluate the furnace as a complete system, focusing on its ability to achieve the required temperature range and vacuum level, its compatibility with your materials, and the capabilities of its cooling system. These core parameters dictate the furnace's suitability for your process, from basic annealing to complex brazing or sintering.
The most common mistake is focusing on a single specification, like maximum temperature. A vacuum furnace is an integrated system where the heating elements, vacuum pumps, chamber design, and cooling process must work in concert to deliver consistent, high-quality results for your specific workload.
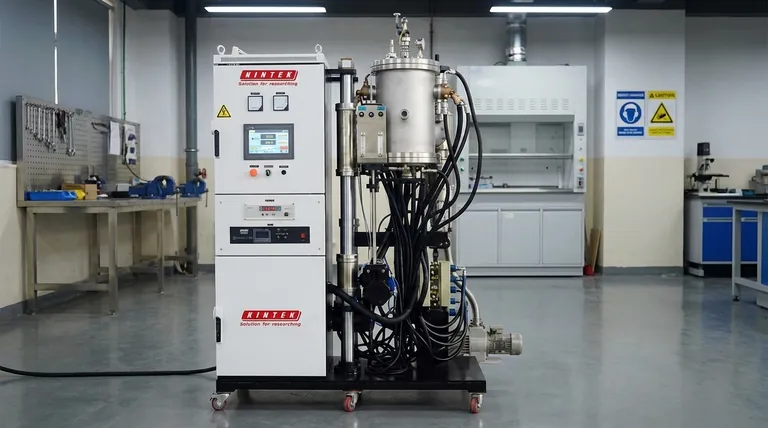

Aligning the Furnace with Your Core Process
Before examining hardware, you must define your non-negotiable process requirements. The furnace's primary function is to create a specific, repeatable environment.
Defining Your Temperature and Vacuum Envelope
The required temperature range and vacuum level form the fundamental operating window for your process. This is the first filter in your selection process.
Ensure the furnace can not only reach your target temperature but also maintain it with high uniformity across the entire hot zone. Poor uniformity leads to inconsistent material properties.
Similarly, evaluate the vacuum system's performance, not just its ultimate pressure rating. Consider the pump-down time—how quickly the system can evacuate the chamber—as this directly impacts cycle time and throughput.
Ensuring Material and Process Compatibility
The materials used to construct the furnace's hot zone must not react with or contaminate your workload at high temperatures. This is a critical consideration for high-purity applications.
Crucible selection is a key part of this. The crucible must be chemically inert with the metals you are processing at the target temperature.
- Alumina is common for steels and nickel-based alloys.
- Zirconia is often required for high-temperature, reactive metals.
- Graphite is useful for some alloys but can form unwanted carbides with others.
The Critical Role of the Cooling System
The cooling stage is just as important as the heating stage for determining final material properties. The furnace's cooling system dictates how quickly and uniformly the part can be brought back to a safe temperature.
Evaluate the cooling options, such as high-pressure gas quenching. The speed and direction of the cooling gas can significantly influence the hardness, microstructure, and residual stress in the finished part.
Deconstructing the Furnace Design
Once your process needs are clear, you can evaluate how different furnace designs meet those needs.
Hot Wall vs. Cold Wall: A Fundamental Choice
This is one of the most significant design decisions.
- Hot wall furnaces feature heating elements outside the vacuum chamber. They are typically simpler and less expensive but are limited to lower temperatures.
- Cold wall furnaces have internal heating elements and a water-cooled chamber. They offer much higher operating temperatures, faster heating and cooling cycles, and superior temperature uniformity.
For most high-performance applications, a cold wall design is the standard choice. The low thermal mass of the internal insulation allows for significant energy savings and rapid temperature changes.
Sizing and Configuration
The furnace's physical size and loading orientation must match your workload and production volume.
- Batch vs. Continuous: Batch furnaces process one load at a time, ideal for varied jobs or lower volumes. Continuous furnaces move parts through heating and cooling zones, suited for high-volume, standardized production.
- Horizontal vs. Vertical Loading: Horizontal loading is most common. Vertical loading is often preferred for long, cylindrical parts to prevent distortion or for specific processes like vacuum carburizing.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Operational Realities
An effective choice requires balancing performance with long-term operational costs and risks.
Performance vs. Energy Efficiency
A furnace capable of extremely fast heating and cooling cycles will naturally have higher peak energy consumption. However, modern designs with low thermal mass can be more energy-efficient overall compared to older refractory-lined furnaces.
Always consider the total energy consumption per cycle, not just the power rating of the heating elements.
Control Precision and Safety
The quality of your output depends on the precision of the control system. A stable, reliable controller that is easy to program and adjust is essential for process repeatability.
Modern safety features are non-negotiable. An automatic power-off function when the furnace door is opened is a critical feature that protects operators from high temperatures and electrical hazards.
Supplier Reputation and Support
A vacuum furnace is a significant capital investment with a long service life. The supplier's reputation for reliability, technical support, and availability of spare parts is just as important as the furnace's initial specifications. A cheaper furnace from an unproven supplier can become a major liability.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Select a furnace that is not just capable, but optimized for your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production: Prioritize a continuous or large-batch furnace with fast cycle times and automation features to maximize throughput.
- If your primary focus is high-purity research: Select a cold wall furnace with a high-performance vacuum system and non-reactive hot zone materials to prevent contamination.
- If your primary focus is processing reactive metals: A furnace with a very low ultimate vacuum level and precise gas control, likely using zirconia crucibles, is essential.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose heat treating: A versatile, cold-wall batch furnace with a robust gas quench system offers the best balance of performance and flexibility.
Ultimately, choosing the right vacuum furnace is about ensuring the equipment can flawlessly execute your process day after day.
Summary Table:
| Consideration | Key Points |
|---|---|
| Temperature & Vacuum | Ensure range, uniformity, and pump-down time match process needs |
| Material Compatibility | Select inert hot zone materials and crucibles (e.g., alumina, zirconia) to prevent contamination |
| Cooling System | Evaluate options like gas quenching for uniform cooling and material properties |
| Design Type | Choose between hot wall (lower temp) and cold wall (higher temp, efficiency) |
| Size & Configuration | Match batch/continuous and horizontal/vertical loading to workload and volume |
| Operational Factors | Balance energy efficiency, control precision, safety, and supplier support |
Ready to optimize your lab with a custom vacuum furnace? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure your unique experimental requirements are met precisely. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your processes with reliable, high-performance equipment!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a vacuum sintering furnace play in the formation of the 'core-rim' structure in Ti(C,N)-FeCr cermets?
- How are parts loaded into a vacuum furnace? Ensure Precision and Efficiency in Your Process
- How does vacuum heat treatment reduce workpiece deformation? Achieve Superior Dimensional Stability
- How do vacuum sintering and annealing furnaces contribute to the densification of NdFeB magnets?
- What technological features enhance the efficiency of vacuum furnaces? Boost Performance with Advanced Control & Energy Savings



















