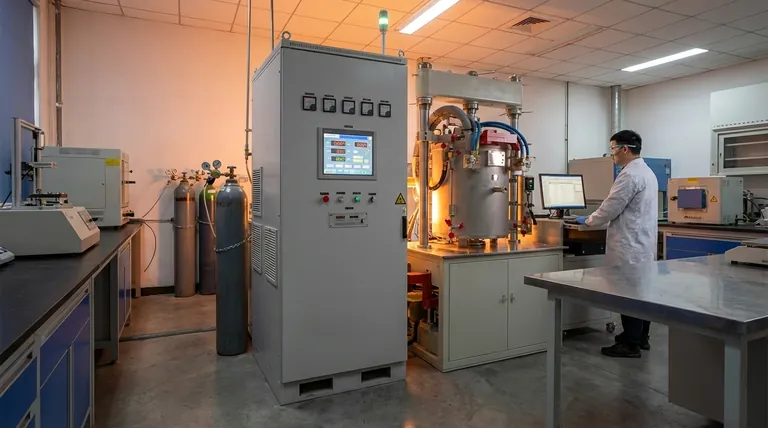
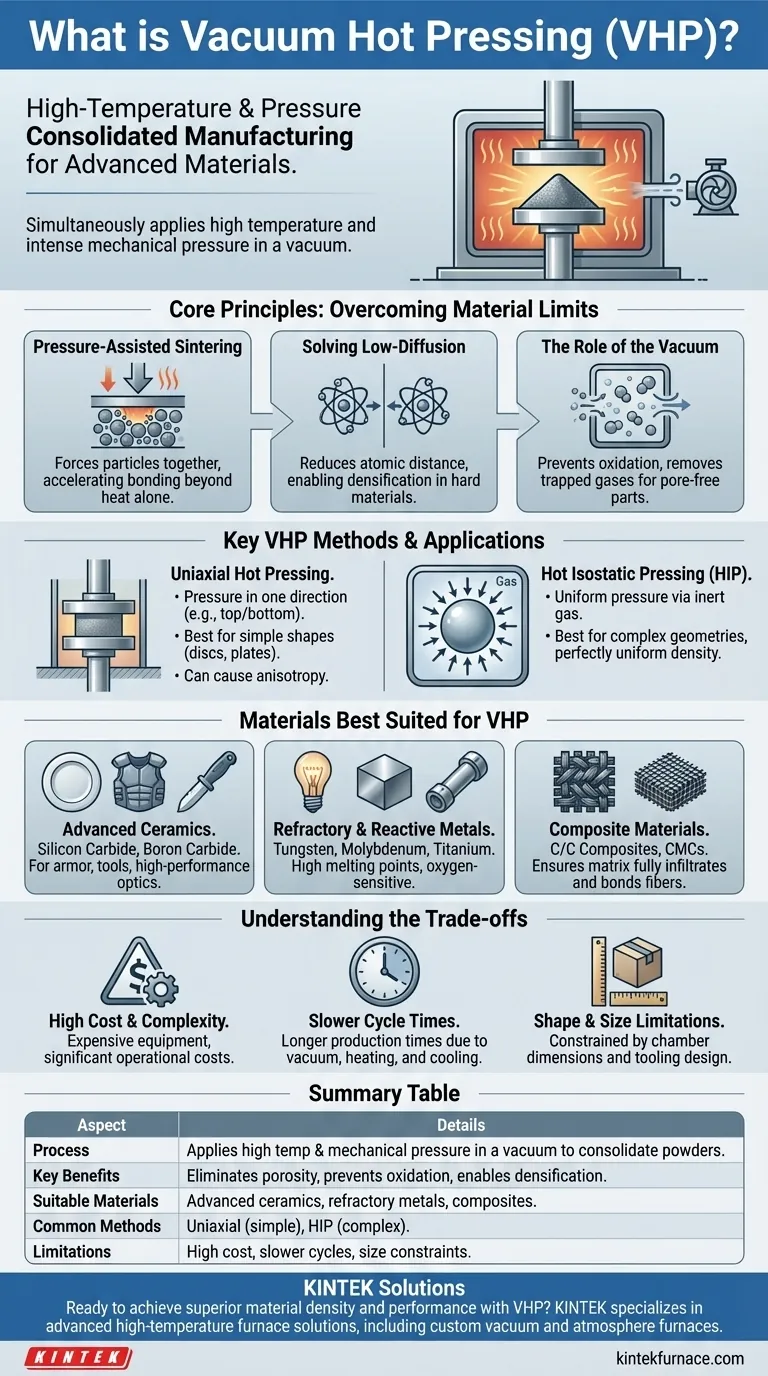
At its core, vacuum hot pressing (VHP) is a high-performance manufacturing process that simultaneously applies high temperature and intense mechanical pressure to a material inside a vacuum. This combination forces powder particles to consolidate and bond into a solid, exceptionally dense component. It is specifically designed for advanced materials that are difficult to process using conventional methods, such as certain ceramics, metals, and composites.
The central purpose of VHP is to overcome a material's natural resistance to densification. By using pressure to physically force atoms together while heat makes them more mobile, the process eliminates the internal voids (porosity) that weaken conventional materials.

How Vacuum Hot Pressing Overcomes Material Limits
The Core Principle: Pressure-Assisted Sintering
Sintering is the process of forming a solid mass of material by heat and pressure without melting it to the point of liquefaction.
For many advanced materials, heat alone is insufficient to create a fully dense part. VHP adds the critical element of mechanical pressure, which physically pushes the material's particles together, dramatically accelerating the bonding and consolidation process.
Solving the Low-Diffusion Problem
Some materials, particularly hard ceramics, have very low diffusion coefficients. This means their atoms do not move and bond easily, even at very high temperatures.
Pressure directly counteracts this by forcing particles into intimate contact, reducing the distance atoms need to travel to form strong bonds. This makes densification possible where it would otherwise fail.
The Role of the Vacuum
The vacuum environment is essential for two reasons. First, it prevents oxidation and other chemical reactions that would occur if reactive materials were heated in the open air.
Second, it removes trapped gases from between the powder particles. Without a vacuum, these gases would be trapped during consolidation, creating internal pores that compromise the final component's strength and performance.
Key VHP Methods and Their Applications
The way pressure is applied defines the specific VHP method and its ideal use case.
Uniaxial Hot Pressing
In this method, pressure is applied in a single direction, typically from the top and bottom, like a piston compressing powder in a die.
It is highly effective for producing simpler shapes such as discs, plates, and blocks. However, it can sometimes result in properties that vary depending on the direction of pressure (anisotropy).
Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP)
HIP is a more advanced form of VHP where pressure is applied uniformly from all directions. This is achieved by using a high-pressure inert gas (like Argon) to pressurize the entire chamber.
This is the preferred method for creating parts with complex geometries or when achieving perfectly uniform density and properties throughout the component is mission-critical.
Materials Best Suited for VHP
VHP is not a universal solution; it is a specialized process for materials where achieving maximum density is paramount.
Advanced Ceramics
Materials like silicon carbide, boron carbide, and transparent ceramics require VHP to reach their full potential. Their inherent hardness and low diffusion rates make them extremely difficult to consolidate without pressure. VHP is essential for applications like armor, cutting tools, and high-performance optics.
Refractory and Reactive Metals
Metals with very high melting points, such as tungsten and molybdenum, or those that react readily with oxygen, like titanium, benefit immensely from VHP. The vacuum prevents contamination, while the pressure aids in creating a fully dense, pore-free structure.
Composite Materials
VHP is crucial for consolidating carbon-carbon (C/C) composites and ceramic matrix composites (CMCs). The process ensures the matrix material (e.g., silicon carbide) fully infiltrates and bonds with the reinforcing fibers (e.g., carbon fiber), creating a unified, high-strength structure.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, VHP is a demanding process with clear limitations that must be considered.
High Cost and Complexity
Vacuum hot press furnaces are sophisticated and expensive pieces of equipment. The operational costs, including energy consumption and maintenance of the vacuum and pressure systems, are significant.
Slower Cycle Times
Compared to conventional furnace sintering, VHP is a much slower process. The need to create a vacuum, apply and control pressure, and execute controlled heating and cooling cycles results in longer production times per part.
Shape and Size Limitations
The final component's size is limited by the dimensions of the furnace's press chamber. Furthermore, the part's geometry is constrained by the design and material of the tooling (graphite dies are common) that must withstand the extreme temperature and pressure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice of consolidation technology depends entirely on your material and performance requirements.
- If your primary focus is producing simple shapes with maximum density: Uniaxial hot pressing is a direct and effective method for materials like ceramic plates or sputtering targets.
- If your primary focus is creating complex, mission-critical parts with perfectly uniform properties: Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) is the industry standard for eliminating all internal porosity in components like turbine blades or medical implants.
- If you are working with materials highly sensitive to oxygen: The vacuum or controlled atmosphere of any VHP process is non-negotiable to preserve material purity and prevent degradation.
By understanding the interplay of heat, pressure, and atmosphere, you can leverage VHP to engineer materials that achieve their ultimate performance potential.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Process | Applies high temperature and mechanical pressure in a vacuum to consolidate powders into dense solids. |
| Key Benefits | Eliminates porosity, prevents oxidation, and enables densification of low-diffusion materials. |
| Suitable Materials | Advanced ceramics (e.g., silicon carbide), refractory metals (e.g., tungsten), and composites (e.g., C/C composites). |
| Common Methods | Uniaxial hot pressing for simple shapes; Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) for complex geometries. |
| Limitations | High cost, slower cycle times, and size/geometry constraints. |
Ready to achieve superior material density and performance with vacuum hot pressing? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including custom vacuum and atmosphere furnaces tailored for VHP processes. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide precise, durable equipment to meet your unique experimental and production needs. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your lab's capabilities—Get in touch now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role do a laboratory pressure machine and a steel die-set play in the preparation of Mn2AlB2 compacts?
- What considerations guide the selection of heating elements and pressurization methods for a vacuum hot press furnace?
- What are the primary components of a vacuum hot press furnace? Master the Core Systems for Precise Material Processing
- Why are precision molds and laboratory presses critical for niobium-doped TiO2 ceramics? Achieve 94% Theoretical Density
- What role does a high-pressure press play in the preparation of zinc sample pellets? Optimize Carbothermic Reduction



















