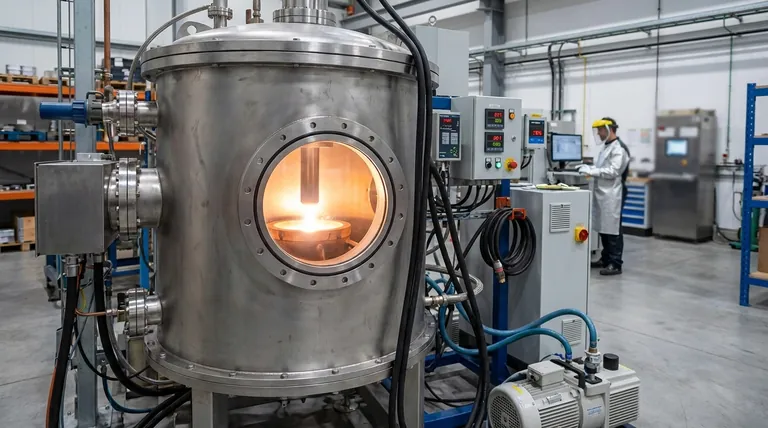
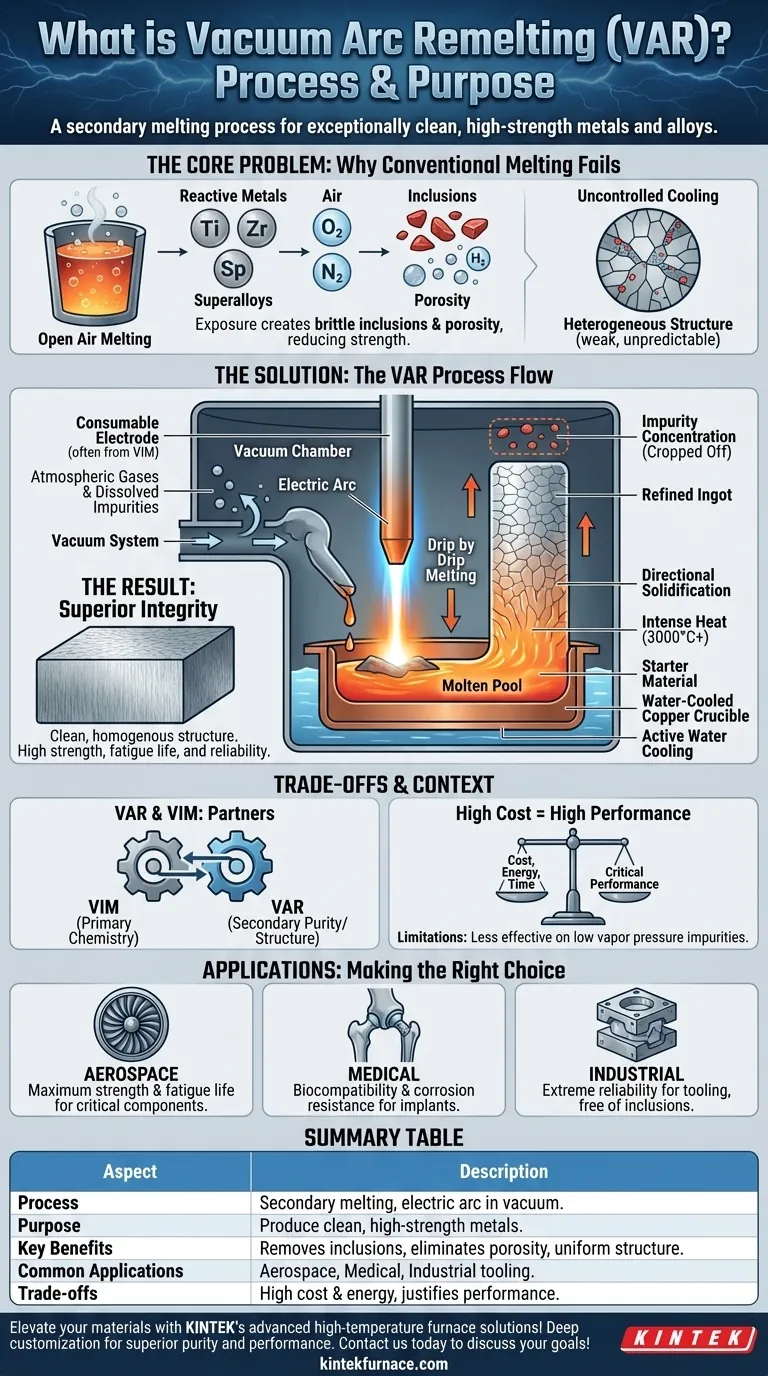
At its core, Vacuum Arc Remelting (VAR) is a secondary melting process designed to produce exceptionally clean, high-strength metals and alloys. It works by using a powerful electric arc to remelt a specially prepared metal bar, called a consumable electrode, inside a high-vacuum chamber. This environment purifies the metal by removing dissolved gases and unwanted impurities, resulting in a final ingot with superior structural integrity and mechanical properties.
The central challenge with high-performance metals like titanium and superalloys is their tendency to react with air and trap impurities during production. VAR solves this by creating a controlled vacuum environment that eliminates contamination and precisely manages solidification, yielding materials pure enough for the most demanding applications.

The Core Problem: Why Conventional Melting Fails
To understand the value of VAR, you must first understand the limitations it overcomes. Standard melting techniques performed in open air are unsuitable for high-performance, reactive alloys.
The Challenge of Reactive Metals
Metals like titanium, zirconium, and nickel-based superalloys are highly reactive at their melting temperatures. When exposed to the atmosphere, they readily combine with oxygen and nitrogen, forming brittle ceramic-like compounds called inclusions. These inclusions act as internal stress points, compromising the metal's strength and fatigue life.
The Issue of Dissolved Gases
During initial melting, gases like hydrogen can dissolve into the molten metal. As the metal cools and solidifies, the solubility of these gases decreases, causing them to emerge from the solution and form microscopic voids or bubbles. This defect, known as porosity, significantly reduces the material's density and load-bearing capacity.
The Need for Structural Control
The way a metal solidifies dictates its final crystal structure, or grain. Uncontrolled cooling leads to a non-uniform, coarse-grained structure with segregated impurities. This heterogeneous structure results in unpredictable and inferior mechanical properties, such as low ductility and poor fatigue resistance.
How Vacuum Arc Remelting Solves the Problem
VAR is a systematic process engineered to directly counteract each of these failure points. It is not about melting raw ore; it is about refining an already-formed alloy.
The Consumable Electrode
The process begins with the material that needs refining, which has already been melted and cast into a large cylindrical bar—the consumable electrode. This initial melt is often performed in a vacuum as well, using a process like Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM).
The Role of the Vacuum
The electrode is suspended inside a sealed, water-cooled copper crucible, and a powerful vacuum is drawn. This crucial step removes virtually all atmospheric oxygen and nitrogen, preventing the formation of new inclusions. The vacuum also helps pull dissolved gases like hydrogen out of the molten metal.
The Arc and Controlled Solidification
An electric arc is struck between the bottom of the electrode and a small amount of starter material in the crucible. The intense heat of the arc (exceeding 3000°C) progressively melts the tip of the electrode, which falls drip by drip into the crucible below.
Because the copper crucible is actively water-cooled, the molten metal solidifies almost as soon as it arrives. This creates a highly controlled, directional solidification from the bottom up. As the ingot solidifies, impurities with lower melting points are pushed ahead of the solidification front, concentrating them at the very top of the final ingot, which is later cropped off. This results in an exceptionally clean and uniform crystal structure throughout the usable portion of the ingot.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Context
VAR is a powerful tool, but its application is specific and comes with clear trade-offs.
VAR vs. VIM: A Necessary Partnership
It's common to see VAR mentioned alongside Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM). They are not competitors but partners. VIM is often the primary melting process used to create the initial alloy chemistry and form the consumable electrode. VAR is the secondary remelting step used to achieve the ultimate level of purity and structural refinement.
High Cost, High Performance
The VAR process is slow, requires complex equipment, and consumes a significant amount of energy. This makes it far more expensive than conventional melting. Its use is therefore reserved for applications where material integrity is non-negotiable and performance justifies the cost.
Limitations of the Process
VAR is highly effective at removing dissolved gases and oxides. However, it is less effective at removing certain non-metallic impurities or metallic elements that have a very low vapor pressure, as they are not easily drawn out by the vacuum.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Specifying a VAR-processed material is a deliberate engineering decision driven by the need for ultimate performance and reliability.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and fatigue life: VAR is essential for creating the clean, homogenous superalloys required for jet engine turbine disks and critical structural airframe components.
- If your primary focus is biocompatibility and corrosion resistance: VAR is the standard for producing the high-purity titanium needed for medical implants, where impurities could cause adverse reactions in the body.
- If your primary focus is extreme reliability in tooling: VAR is used to produce specialty steels and alloys for high-performance molds and dies, ensuring the absence of inclusions that could lead to premature failure.
Ultimately, choosing a VAR material is an investment in eliminating the metallurgical variables that lead to unpredictable failures.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Process | Secondary melting using an electric arc in a vacuum chamber to remelt a consumable electrode. |
| Primary Purpose | Produce exceptionally clean, high-strength metals by removing dissolved gases and impurities, ensuring superior structural integrity. |
| Key Benefits | Removes inclusions, eliminates porosity, enables controlled directional solidification for uniform crystal structure. |
| Common Applications | Aerospace (jet engine components), medical (implants), industrial (high-performance tooling). |
| Trade-offs | High cost and energy consumption, limited effectiveness on certain non-metallic impurities; used where performance justifies expense. |
Elevate your materials with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored systems like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, helping you achieve superior purity and performance in metal processing. Ready to optimize your processes? Contact us today to discuss how we can support your goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does the Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) process work? Achieve Superior Metal Purity and Control
- What role does a vacuum induction melting furnace play in Fe-5%Mn-C alloys? Ensure Chemical Integrity and High Purity
- What are the core functions of the High Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace? Optimize DD5 Superalloy Purification
- What are some common applications of vacuum induction melting and casting (VIM&C)? Essential for Aerospace, Medical, and Nuclear Industries
- Why is a Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace essential? Unlock Purity for Aerospace and Semiconductors



















