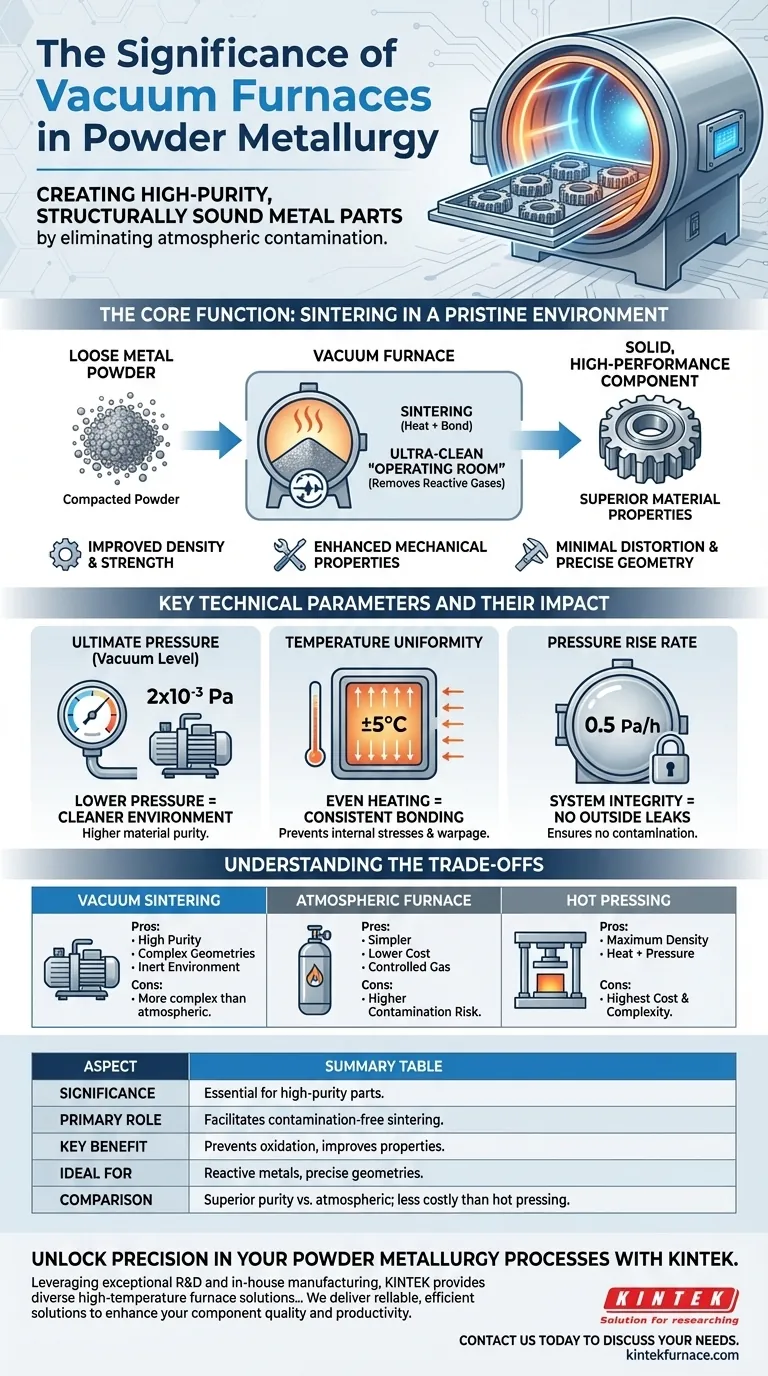
In powder metallurgy, the significance of a vacuum furnace is its unique ability to create high-purity, structurally sound metal parts by eliminating atmospheric contamination. This controlled environment allows metal powders to be sintered—heated and bonded together—without the risk of oxidation or other unwanted chemical reactions, resulting in superior density, strength, and dimensional accuracy.
The core challenge in powder metallurgy is transforming loose powder into a solid, high-performance component. A vacuum furnace solves this by creating an ultra-clean "operating room" that removes reactive gases, ensuring the metal bonds perfectly according to design without being compromised by its environment.
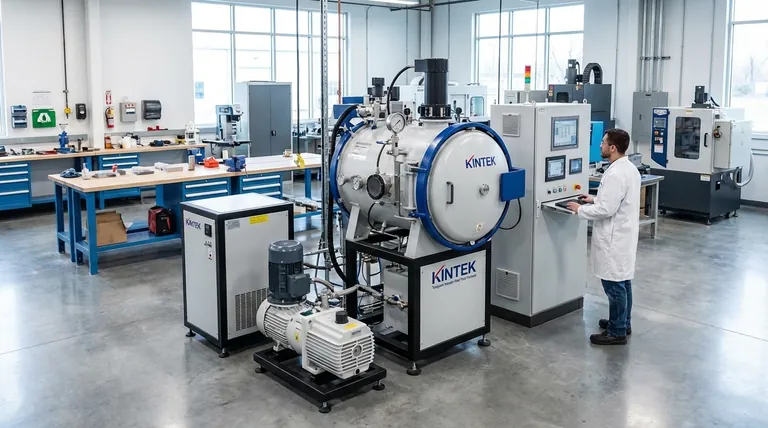

The Core Function: Sintering in a Pristine Environment
The primary role of a vacuum furnace in this field is to facilitate the sintering process under ideal conditions. This directly impacts the final quality of the component.
What is Sintering?
Sintering is a thermal process where compacted metal powder is heated to a temperature below its melting point. At this temperature, the individual particles bond together, reducing porosity and increasing the density of the material to form a solid, coherent mass.
The Critical Role of the Vacuum
The "vacuum" is the most important feature. By removing air and other gases, the furnace creates an inert environment that prevents oxygen and other reactive elements from contaminating the metal. This is essential for materials that readily oxidize, such as titanium and certain high-performance steel alloys.
The Outcome: Superior Material Properties
Sintering in a vacuum ensures that the bonds between metal particles are pure and strong. This process leads directly to improved density, enhanced mechanical properties like strength and durability, and minimal distortion, preserving the precise geometry of the part.
Key Technical Parameters and Their Impact
The performance of a vacuum furnace is defined by several technical parameters that dictate the quality of the final product.
Ultimate Pressure (Vacuum Level)
This measures how much air and gas is removed from the chamber. A lower pressure, such as 2x10⁻³ Pa, signifies a cleaner environment with fewer molecules to interfere with the sintering process, ensuring higher material purity.
Temperature Uniformity
This parameter, often controlled to within ±5°C, ensures that the entire component is heated evenly. Uniform temperature is critical for consistent particle bonding across the part, preventing internal stresses, weak spots, and warpage.
Pressure Rise Rate
A low pressure rise rate (e.g., 0.5 Pa/h) indicates how well the furnace chamber is sealed. It's a measure of system integrity, proving that no outside air is leaking in to contaminate the process.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a vacuum furnace is not the only option. Understanding its place among other thermal processes is key to making an informed decision.
Vacuum Sintering vs. Atmospheric Furnaces
Standard atmospheric furnaces are simpler and less expensive but operate in the presence of a controlled gas (like nitrogen or argon). This is sufficient for some materials, but it always carries a higher risk of contamination compared to the near-perfect inertness of a deep vacuum.
Vacuum Sintering vs. Hot Pressing
A hot press furnace applies both high temperature and immense mechanical pressure simultaneously. This combination achieves maximum density but is a more complex and costly process typically reserved for creating extremely high-performance components where any level of porosity is unacceptable.
Context for Other Furnace Types
Furnaces like rotary and tube furnaces are also used in metallurgy. However, they often serve different roles, such as producing the initial metal powders (rotary furnace) or for general heat treatments like annealing and tempering (tube furnace), rather than the specialized task of sintering high-precision final parts.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal thermal process depends entirely on the material requirements and performance targets of your component.
- If your primary focus is high purity and complex geometries for reactive metals: A vacuum sintering furnace is the definitive choice for eliminating contamination and ensuring dimensional stability.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness for non-reactive materials: A controlled atmosphere furnace may be sufficient, but you must accept the trade-off of potentially lower purity and performance.
- If your primary focus is achieving near-total theoretical density for extreme performance: A hot press furnace is necessary to apply both heat and pressure, though at a significantly higher cost and complexity.
Ultimately, controlling the processing environment is the most critical factor in determining the final quality of a powder metallurgy component.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Significance in Powder Metallurgy |
|---|---|
| Primary Role | Facilitates sintering in a contamination-free environment for high-purity parts. |
| Key Benefit | Prevents oxidation and unwanted reactions, improving material properties like density and strength. |
| Ideal For | Reactive metals (e.g., titanium, high-performance steels) requiring precise geometries. |
| Comparison | Superior to atmospheric furnaces for purity; less complex than hot pressing for cost-effectiveness. |
Unlock Precision in Your Powder Metallurgy Processes with KINTEK
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you need high-purity sintering for reactive metals or tailored thermal processes, we deliver reliable, efficient solutions to enhance your component quality and productivity.
Contact us today to discuss how our vacuum furnaces can transform your powder metallurgy outcomes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-vacuum environment necessary in copper slag impoverishment? Maximize Your Matte Separation Efficiency
- Why is a vacuum environment essential for sintering Titanium? Ensure High Purity and Eliminate Brittleness
- What is the mechanism of a vacuum sintering furnace for AlCoCrFeNi2.1 + Y2O3? Optimize Your High-Entropy Alloy Processing
- What is the function of a vacuum sintering furnace in the SAGBD process? Optimize Magnetic Coercivity and Performance
- What is the purpose of performing medium vacuum annealing on working ampoules? Ensure Pure High-Temp Diffusion



















