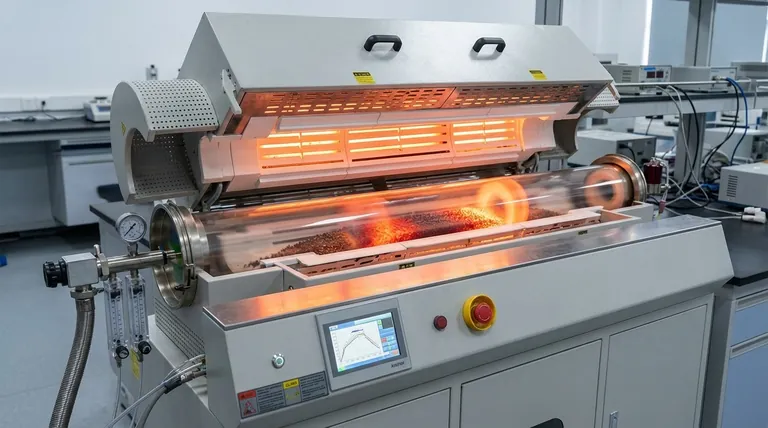
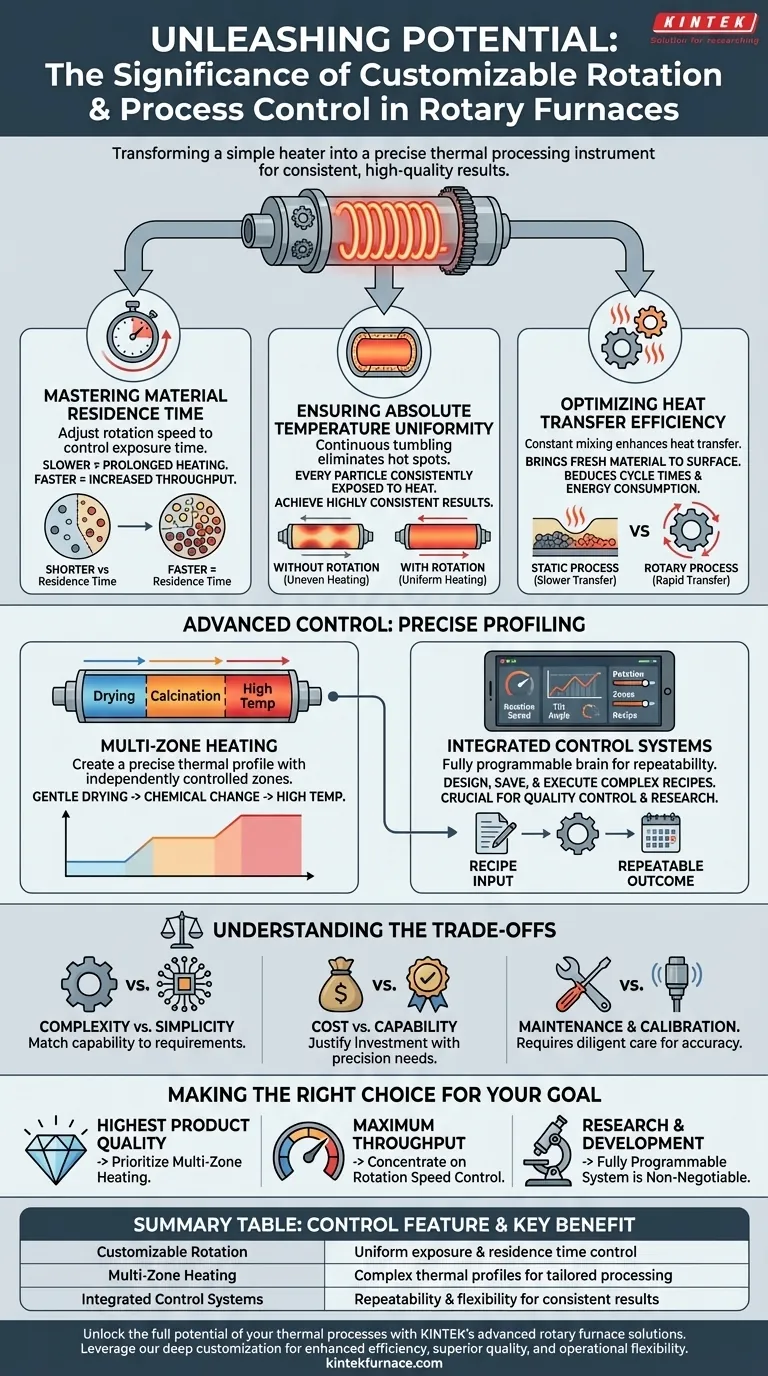
In short, customizable rotation and process control are significant because they transform a rotary furnace from a simple heater into a precise thermal processing instrument. These features give you direct command over material uniformity, processing time, and final product quality, ensuring consistent and efficient results.
Customizable control is not merely a feature—it is the core mechanism that dictates process outcomes. It allows you to tailor the thermal environment to the specific needs of your material, moving beyond brute-force heating to achieve predictable quality, higher efficiency, and greater operational flexibility.

The Core Pillars of Process Control
Understanding how each control element functions is key to leveraging the full power of a rotary furnace. These controls work in concert to manage the material's entire journey through the thermal process.
Mastering Material Residence Time
The speed at which the furnace tube rotates directly influences how quickly material moves through it. This is known as residence time.
By precisely adjusting the rotation speed, you can control exactly how long every particle is exposed to the heat. Slower rotation increases residence time for processes that require prolonged heating, while faster rotation increases throughput.
Ensuring Absolute Temperature Uniformity
Without rotation, material would simply settle at the bottom of the tube, leading to uneven heating. The top of the material bed would be over-processed while the bottom remains under-processed.
The continuous tumbling motion created by rotation ensures every particle is consistently exposed to the heat source and the tube walls. This eliminates hot spots and guarantees a uniform temperature distribution throughout the material bed, leading to highly consistent results.
Optimizing Heat Transfer Efficiency
The constant mixing action of a rotary furnace dramatically enhances heat transfer. It brings fresh material to the surface to absorb radiant heat and ensures contact with the hot tube walls.
This efficiency means the material reaches the target temperature faster and more uniformly, reducing overall cycle times and lowering energy consumption compared to a static process.
Advanced Control: From Simple Heating to Precise Profiling
Modern rotary furnaces offer layers of control that go far beyond simple rotation, enabling complex, multi-stage processes within a single piece of equipment.
The Power of Multi-Zone Heating
Many advanced furnaces feature multi-zone heating, where the length of the tube is divided into separate, independently controlled temperature zones. This allows you to create a precise thermal profile.
For example, in a calcination process, an initial zone can be set to a low temperature to gently drive off moisture. Subsequent zones can then ramp up to much higher temperatures to induce chemical or phase changes. This level of control is critical for creating high-quality, specialized materials.
The Role of Integrated Control Systems
These individual parameters—rotation speed, tilt angle, and multiple temperature zones—are managed by a fully programmable, integrated control system.
This central brain allows operators to design, save, and execute complex recipes with perfect repeatability. It ensures that every batch is processed under the exact same conditions, which is crucial for quality control, process validation, and scientific research.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While advanced control offers significant advantages, it's important to weigh them against practical considerations.
Complexity vs. Simplicity
A highly controllable system has more variables to manage. For a straightforward, single-stage process, a furnace with multi-zone heating may introduce unnecessary operational complexity. You must match the furnace's capability to your actual process requirements.
Cost vs. Capability
Advanced features like multi-zone heating and fully programmable logic controllers (PLCs) increase the initial capital cost of the furnace. It is critical to justify this investment with the need for process precision, product quality, or the flexibility required for research and development.
Maintenance and Calibration
More sophisticated systems, with multiple heating elements, thermocouples, and control interfaces, require more diligent maintenance and calibration to ensure accuracy. While modern designs are durable, the control systems themselves add a layer of electronic and sensor maintenance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The level of control you need depends entirely on your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is the highest possible product quality: Prioritize a system with multi-zone heating to create the perfect thermal profile for your material.
- If your primary focus is maximum throughput and efficiency: Concentrate on precise rotation speed control and furnace design that promotes rapid heat transfer to minimize residence time.
- If your primary focus is research and process development: A fully programmable system with control over rotation, tilt, and multi-zone heating is non-negotiable for its operational flexibility.
Ultimately, these control features empower you to dictate the exact outcome of your thermal process, turning potential variability into predictable quality.
Summary Table:
| Control Feature | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Customizable Rotation | Ensures uniform material exposure and precise residence time control |
| Multi-Zone Heating | Enables complex thermal profiles for tailored material processing |
| Integrated Control Systems | Provides repeatability and flexibility for consistent, high-quality results |
Unlock the full potential of your thermal processes with KINTEK's advanced rotary furnace solutions. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer a diverse product line including Rotary Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Tube Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, delivering enhanced efficiency, superior product quality, and operational flexibility. Contact us today to discuss how we can tailor a solution for your laboratory!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the common approaches to mixing in rotary furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- How do rotary tube furnaces achieve precise temperature control? Master Uniform Heating for Dynamic Processes
- What is the purpose of the rotation mechanism in a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating and Enhanced Process Control
- What types of materials are suitable for processing in rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Free-Flowing Powders and Granules
- What factors should be considered when selecting a tube for a rotary tube furnace? Ensure Optimal Performance and Longevity



















