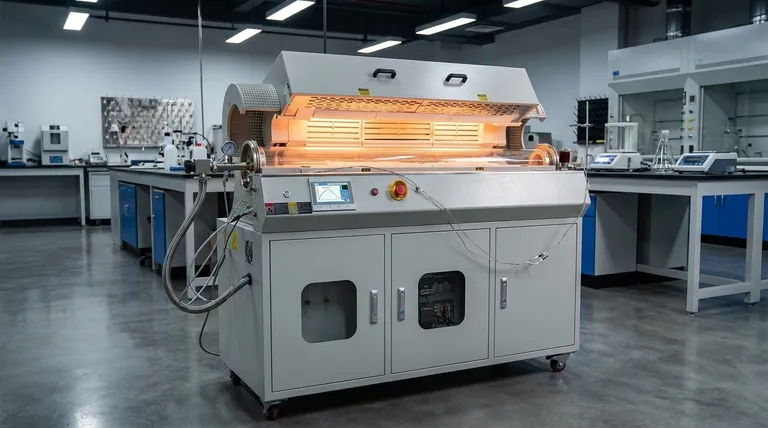
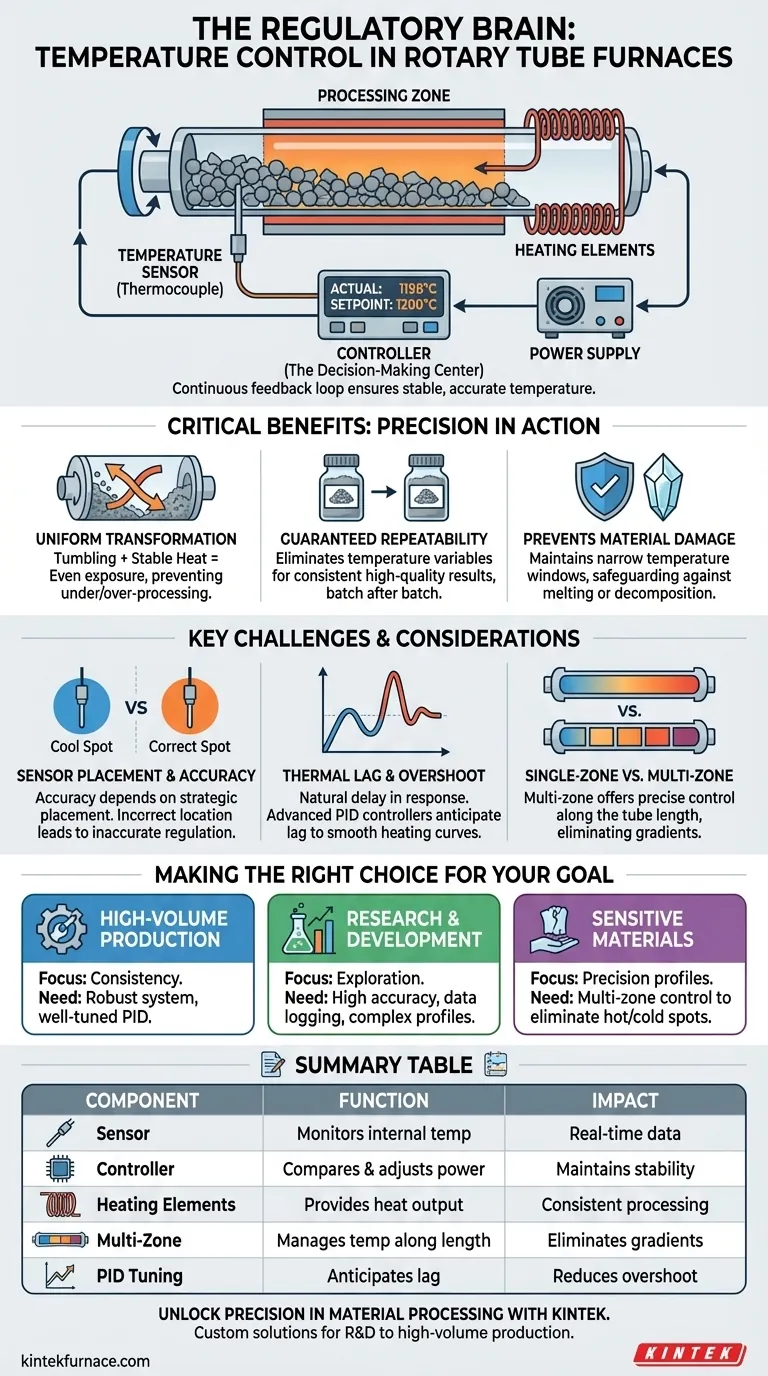
At its core, the temperature control system is the regulatory brain of a rotary tube furnace. It uses sensors, typically thermocouples, to constantly monitor the internal temperature and sends this information to a controller. The controller then compares this real-time data to the desired setpoint and precisely adjusts the power supplied to the heating elements, ensuring the furnace maintains a stable and accurate temperature.
In material processing, temperature is not just about being hot—it is about being precisely and consistently correct. The temperature control system is what guarantees this precision, transforming a furnace from a simple heat source into a reliable tool for repeatable, high-quality results.

How the Temperature Control System Achieves Precision
A rotary tube furnace's effectiveness hinges on a closed-loop feedback system. This system continuously measures, compares, and corrects the temperature to keep the process within strict parameters.
The Role of Temperature Sensors
The process begins with a temperature sensor, most commonly a thermocouple. This device acts as the furnace's nerve ending, placed strategically to measure the heat in the processing zone.
It converts the detected thermal energy into a small electrical signal. This signal is a direct, real-time representation of the temperature your material is experiencing.
The Function of the Controller
The electrical signal from the thermocouple is sent to the temperature controller, which is the system's decision-making center.
The controller's primary job is to constantly compare the incoming signal (actual temperature) with the setpoint temperature that you have programmed.
Regulating the Heating Elements
Based on the difference between the actual temperature and the setpoint, the controller adjusts the power output to the heating elements.
If the temperature is too low, the controller increases power. If it's too high, it decreases or cuts off power. This constant cycle of adjustment ensures the temperature remains exceptionally stable around the desired point.
Why This Control is Critical for Rotary Furnaces
The combination of rotation and precise temperature control is what makes a rotary tube furnace so effective. One cannot function optimally without the other.
Ensuring Uniform Material Transformation
The rotating tube is designed to tumble the material, ensuring every particle is exposed to the heat source evenly.
However, this is only effective if the heat source itself is stable. The temperature control system guarantees that the heat the material is being uniformly exposed to is the correct and unwavering temperature, preventing under-processed or over-processed spots in the batch.
Guaranteeing Process Repeatability
For any industrial or research application, achieving the same result every time is paramount. Minor temperature deviations can lead to significant variations in product quality, from chemical composition to physical structure.
A precise control system eliminates temperature as a variable, ensuring that batch #1 and batch #100 are processed under identical thermal conditions.
Preventing Material Damage
Many advanced material processes, like sintering, calcination, or pyrolysis, occur within very narrow temperature windows.
Exceeding the target temperature can melt, decompose, or otherwise ruin the material. Falling short can mean the desired chemical or physical transformation simply fails to happen. The control system is the primary safeguard against this kind of process failure.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While essential, a temperature control system is not without its own inherent challenges that require consideration.
Sensor Placement and Accuracy
The system's accuracy is entirely dependent on its sensor. A thermocouple reading is only valid for the exact spot where it is placed. If it's too close to a heating element or in a cooler zone, the controller will be regulating the wrong temperature, leading to inaccurate processing.
Thermal Lag and Overshoot
There is a natural delay between the controller adjusting power and the furnace's internal temperature actually changing. This is known as thermal lag.
A simplistic controller can easily overshoot the target temperature by applying too much heat before the sensor registers the change. Advanced PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) controllers are specifically designed to anticipate this lag and smooth out the heating curve, but they require proper tuning.
Single-Zone vs. Multi-Zone Control
A standard furnace has a single heating zone with one controller. While effective, it can create a temperature gradient where the center of the tube is hottest. For longer tubes or highly sensitive processes, multi-zone furnaces with independent controllers for each section offer far more precise control over the temperature profile along the entire length of the tube.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The ideal temperature control setup depends entirely on your specific application.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, continuous production: Prioritize a robust system with a well-tuned PID controller to ensure consistency across large batches and prevent costly spoilage.
- If your primary focus is research and development: You need a system with high accuracy, data logging capabilities, and the ability to program complex temperature profiles to explore different process parameters.
- If your primary focus is processing highly sensitive materials: A multi-zone control system is critical for creating precise and uniform temperature profiles along the tube, eliminating hot or cold spots.
Ultimately, an effective temperature control system is what elevates a rotary furnace from a basic oven to a precision instrument for modern material science and production.
Summary Table:
| Component | Function | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Sensor | Monitors internal temperature via thermocouples | Provides real-time data for accurate regulation |
| Controller | Compares actual temperature to setpoint and adjusts power | Maintains stable temperature, preventing deviations |
| Heating Elements | Receive power adjustments from the controller | Ensures consistent heat output for uniform processing |
| Multi-Zone Control | Manages temperature along the tube length | Eliminates gradients for sensitive materials |
| PID Tuning | Anticipates thermal lag and smooths heating curves | Reduces overshoot and improves process reliability |
Unlock Precision in Your Material Processing with KINTEK
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you're focused on high-volume production, R&D, or processing sensitive materials, our temperature control systems ensure accuracy, uniformity, and repeatability. Contact us today to discuss how we can tailor a solution for your needs and enhance your lab's efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What materials can be used to make the rotating tube assembly of these furnaces? Choose the Best for Your High-Temp Needs
- What factors should be considered when selecting a tube for a rotary tube furnace? Ensure Optimal Performance and Longevity
- What are the common approaches to mixing in rotary furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- What are the main structural components of a rotary furnace? Explore Key Parts for Efficient Material Processing
- What supplementary features can enhance rotary tube furnace performance? Boost Efficiency with Precision Control



















