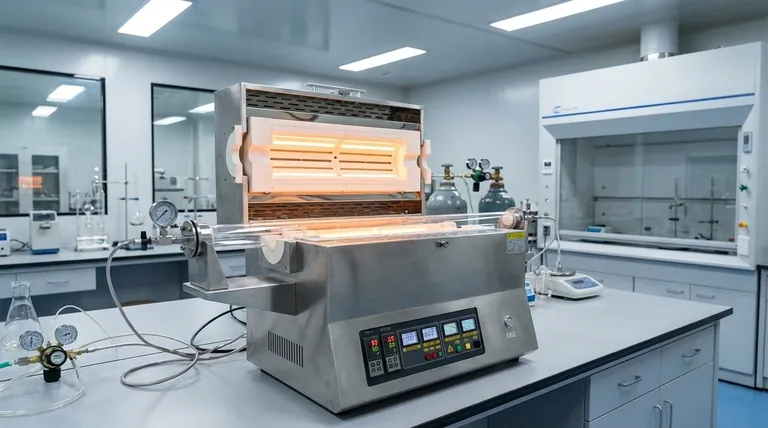
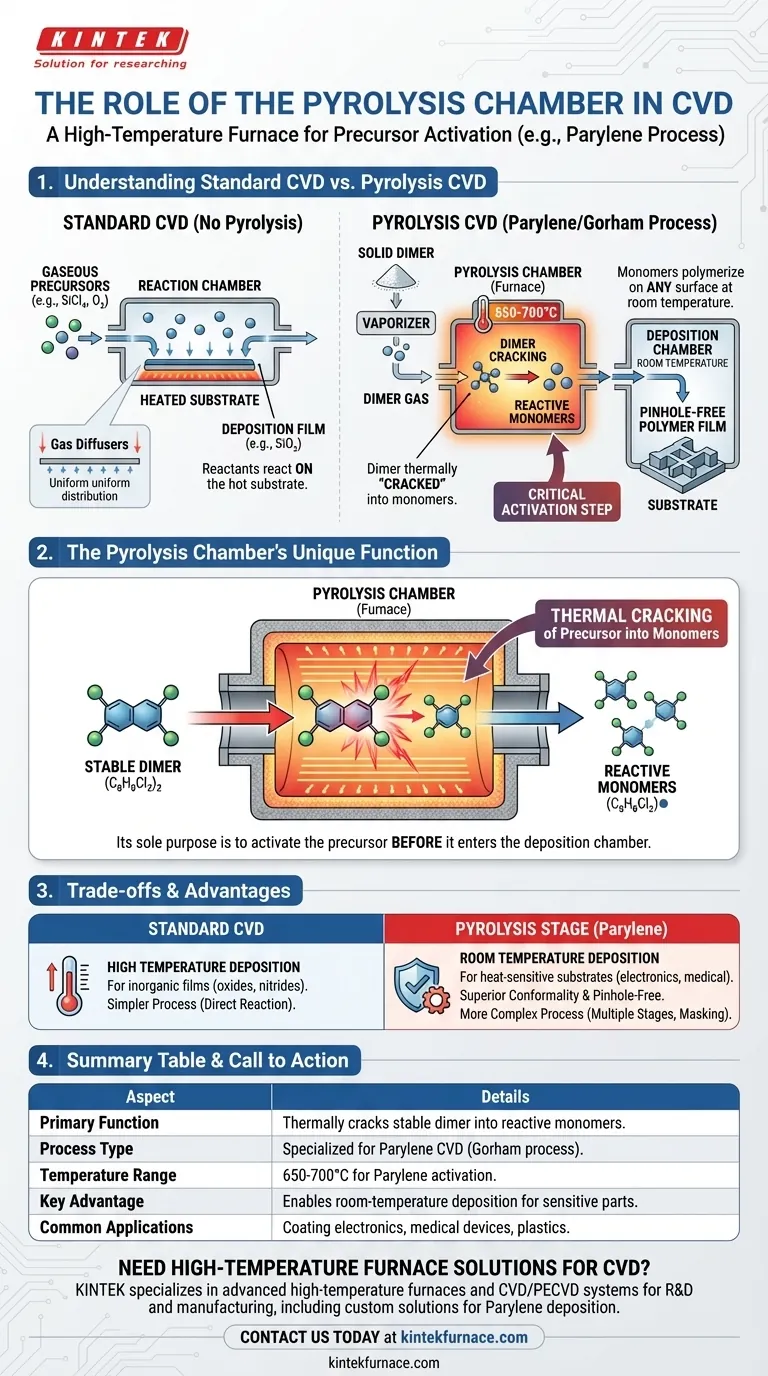
In short, the pyrolysis chamber acts as a high-temperature furnace within a specific type of Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) process. Its primary function is to thermally "crack" a stable precursor material, known as a dimer, into highly reactive molecules called monomers. These activated monomers are then ready for the subsequent deposition stage.
The pyrolysis chamber is not a component of every CVD system. It is a specialized module required for processes like Parylene deposition, where the precursor material must be activated before it enters the main deposition chamber, rather than reacting on the target substrate's surface.

Understanding the Standard CVD Process
To understand the unique role of the pyrolysis chamber, we must first look at a typical CVD setup.
The Conventional Mechanism
In a standard CVD process, gaseous reactants, called precursors, are introduced directly into a reaction chamber.
These gases flow over a heated substrate. The thermal energy at the substrate's surface drives chemical reactions, causing a solid material to deposit and form a thin film.
For example, silicon tetrachloride (SiCl₄) gas can react with oxygen (O₂) on a hot surface to deposit a film of silicon dioxide (SiO₂).
Ensuring Uniformity
In these systems, components like gas diffusers are often used. Their purpose is to ensure the reactant gases are distributed evenly throughout the chamber, which is critical for achieving a uniform coating across the entire substrate.
Where Pyrolysis Fits In: The Parylene Process
Some CVD processes, most notably the deposition of Parylene polymer, follow a different path that absolutely requires a pyrolysis stage. This is often called the Gorham process.
The Starting Material: A Solid Dimer
Unlike the gaseous precursors of standard CVD, the Parylene process begins with a solid, stable powder called a dimer. This material is not reactive enough on its own to form a film.
First, this solid dimer is heated in a vaporizer (a separate first step) until it turns into a gas.
The Critical Role of the Pyrolysis Chamber
This dimer gas then flows into the pyrolysis chamber, which is essentially a furnace heated to extreme temperatures (e.g., around 650-700°C for Parylene).
Inside this chamber, the intense heat breaks the chemical bonds of the dimer, cracking each molecule into two identical, highly reactive di-radical monomers. This activation step is the sole purpose of the pyrolysis chamber.
The Final Deposition Stage
These activated monomers then exit the pyrolysis chamber and enter the main deposition chamber, which is kept at room temperature.
Upon contact with any surface in this chamber, the reactive monomers spontaneously link together, or polymerize, forming a pinhole-free, highly conformal polymer film on the substrate.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The inclusion of a pyrolysis stage introduces a distinct set of advantages and disadvantages compared to standard CVD.
Advantage: Superior Conformality at Room Temperature
The Parylene process produces an exceptionally uniform and conformal coating that covers all features of a substrate, even complex, three-dimensional shapes.
Because deposition occurs at room temperature, it is ideal for coating sensitive substrates like electronics, plastics, or medical devices that cannot withstand the high heat of conventional CVD.
Disadvantage: Process Complexity
A system with a pyrolysis stage is inherently more complex. It involves three distinct stages: vaporization, pyrolysis, and deposition, each requiring precise control of temperature and pressure.
Furthermore, because the polymerization happens on every surface it touches, areas that must remain uncoated require careful and often difficult masking before the process begins.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The decision to use a process with a pyrolysis chamber depends entirely on the material you need to deposit and the nature of your substrate.
- If your primary focus is depositing inorganic films like oxides or nitrides at high temperatures: A standard CVD process without a pyrolysis chamber is the direct and appropriate method.
- If your primary focus is creating a highly conformal, protective polymer coating on a temperature-sensitive component: A process that uses a pyrolysis chamber, such as Parylene CVD, is the necessary solution.
Ultimately, understanding the function of each component allows you to select the precise deposition technology that aligns with your material and performance requirements.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Thermally cracks stable dimer precursors into reactive monomers for CVD deposition. |
| Process Type | Specialized for Parylene CVD (Gorham process), not standard CVD. |
| Temperature Range | Typically 650-700°C for Parylene activation. |
| Key Advantage | Enables room-temperature deposition, ideal for heat-sensitive substrates. |
| Common Applications | Coating electronics, medical devices, and plastics with conformal polymer films. |
Need a High-Temperature Furnace for Your CVD Process?
At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for diverse laboratory needs. Our expertise in R&D and in-house manufacturing ensures you get reliable equipment like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With strong deep customization capabilities, we can precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, whether you're working with Parylene deposition or other specialized processes.
Contact us today via our contact form to discuss how our solutions can enhance your lab's efficiency and performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab



















