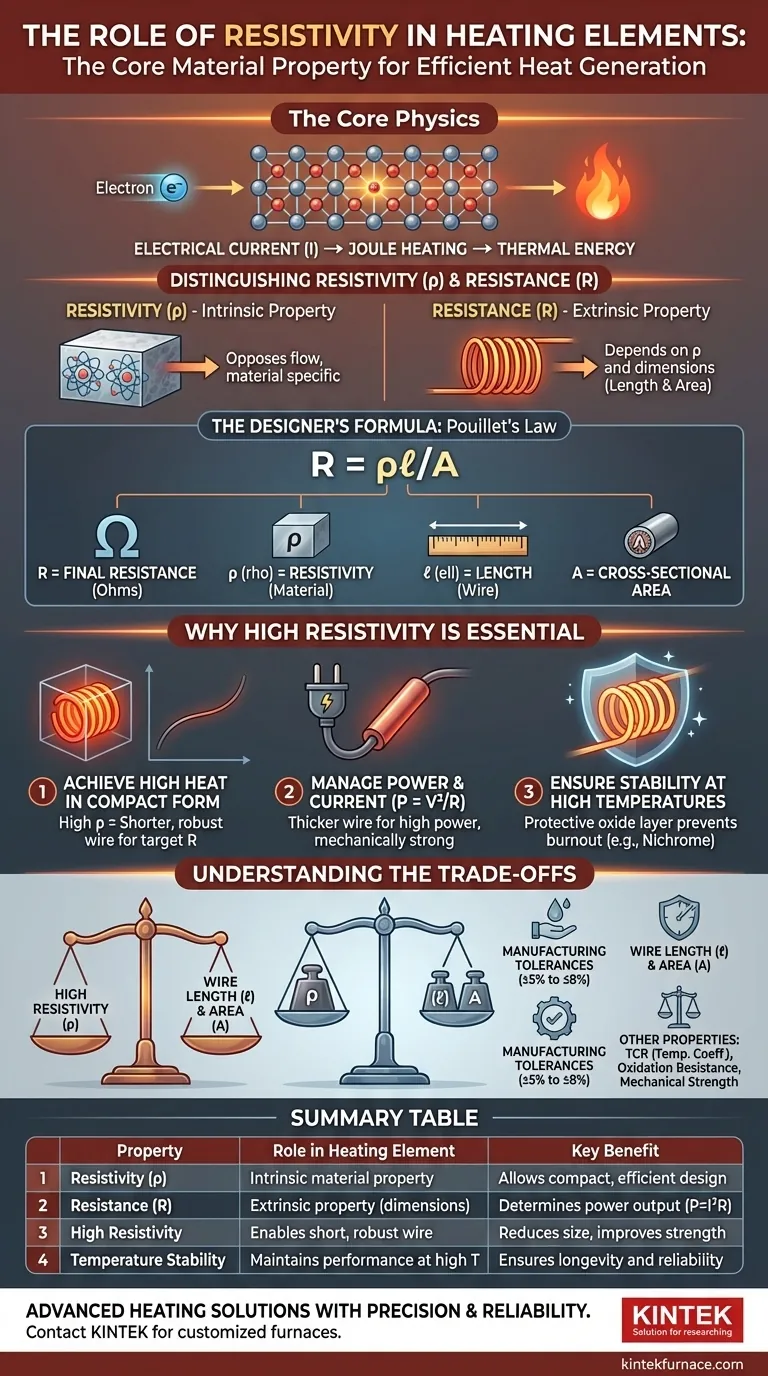
In a heating element, resistivity is the fundamental material property that governs the efficiency of converting electrical energy into thermal energy. Materials with high resistivity are deliberately selected because they generate substantial heat from a given electrical current while allowing for a compact and robust physical design.
The core challenge in heating element design is not merely generating heat, but generating a specific amount of heat controllably, reliably, and within a constrained physical space. High resistivity is the key material characteristic that makes this possible, allowing designers to achieve high resistance with a practical length and diameter of wire.

The Physics of Electrical Heating
To understand the role of resistivity, we must first distinguish it from resistance and see how they work together to produce heat.
From Current to Heat
All electrical conductors produce heat when a current passes through them. This phenomenon, known as Joule heating, is the principle behind any heating element.
The power dissipated as heat is determined by the element's total resistance (R) and the current (I) flowing through it, described by the formula P = I²R.
Resistance vs. Resistivity: The Critical Distinction
Though related, resistance and resistivity are not the same. This distinction is crucial for design.
- Resistivity (ρ) is an intrinsic property of a material. It measures how strongly a material opposes the flow of electric current, regardless of its shape or size.
- Resistance (R) is an extrinsic property of a specific object. It depends not only on the material's resistivity but also on its physical dimensions.
The Designer's Formula: Pouillet's Law
The relationship between these properties is defined by Pouillet's Law:
R = ρℓ/A
Here's what each variable represents:
- R is the final resistance of the wire (in Ohms).
- ρ (rho) is the material's resistivity.
- ℓ (ell) is the length of the wire.
- A is the cross-sectional area of the wire.
This formula gives an engineer three "dials"—resistivity, length, and area—to turn to achieve a target resistance and, therefore, a target heat output.
Why High Resistivity is Essential
Using a material with high resistivity provides significant practical advantages that a standard conductor like copper cannot offer.
Achieving High Heat in a Compact Form
The primary benefit of high resistivity is achieving the desired resistance with a much shorter length of wire.
Imagine trying to create a 1000-watt heater. Using a low-resistivity material would require an impractically long and thin wire to achieve the necessary resistance, making the final product fragile and enormous.
A high-resistivity material like nichrome can achieve that same resistance in a compact, durable coil, perfect for fitting inside an appliance.
Managing Power and Current
For a fixed voltage (like a wall outlet), power is determined by P = V²/R. To achieve high power (heat), you need a relatively low total resistance.
However, to create that resistance from a high-resistivity material, you can use a thicker, shorter wire. This makes the element mechanically strong and less prone to failure at high temperatures.
Ensuring Stability at High Temperatures
Heating element alloys are chosen not just for high resistivity but also for their ability to withstand high temperatures without degrading.
Materials like nichrome or Kanthal form a protective oxide layer on their surface when heated. This layer prevents the material from burning out or corroding, ensuring a long and reliable service life.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a material is not as simple as choosing the highest resistivity. It involves a balancing act of competing factors.
The Balancing Act of Design
An engineer must use the R = ρℓ/A formula to balance trade-offs. If a material with extremely high resistivity is chosen, a shorter or thicker wire is needed to hit the target resistance. This impacts how the element coil is wound and fits into the final product.
Manufacturing Tolerances
Heating element wire is manufactured to specific standards, such as ASTM or DIN, which allow for tolerances in resistance per unit length.
These tolerances, often between ±5% and ±8%, mean that two identical-looking elements can have slightly different power outputs. This variation must be accounted for in the overall product design to ensure safety and consistent performance.
Beyond Resistivity: Other Key Properties
Resistivity is critical, but it's only part of the story. Other properties are equally important for performance and longevity:
- Temperature Coefficient of Resistance (TCR): How much the resistivity changes as the element heats up.
- Oxidation Resistance: The material's ability to resist burning out at operating temperature.
- Mechanical Strength: The ability to hold its shape and resist vibration, especially when glowing hot.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The ideal approach depends entirely on the specific application and its primary design constraints.
- If your primary focus is maximum heat in a compact device: Prioritize a material with very high resistivity, as this allows for a shorter and more manageable wire length.
- If your primary focus is long-term durability and stability: Look beyond resistivity to materials with excellent oxidation resistance and a low temperature coefficient of resistance.
- If your primary focus is a simple, cost-effective heater: A material with moderate resistivity may be sufficient, especially if operating temperatures are not extreme.
Ultimately, understanding the central role of resistivity is the key to engineering a precise, efficient, and reliable heating solution.
Summary Table:
| Property | Role in Heating Element | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Resistivity (ρ) | Intrinsic material property for heat generation | Allows compact, efficient design with high resistance |
| Resistance (R) | Extrinsic property from dimensions and resistivity | Determines power output via P = I²R |
| High Resistivity | Enables short, robust wire for high heat | Reduces size and improves mechanical strength |
| Temperature Stability | Maintains performance at high temperatures | Ensures longevity and reliability |
Ready to enhance your heating solutions with precision and reliability? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your laboratory's efficiency and performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights



















