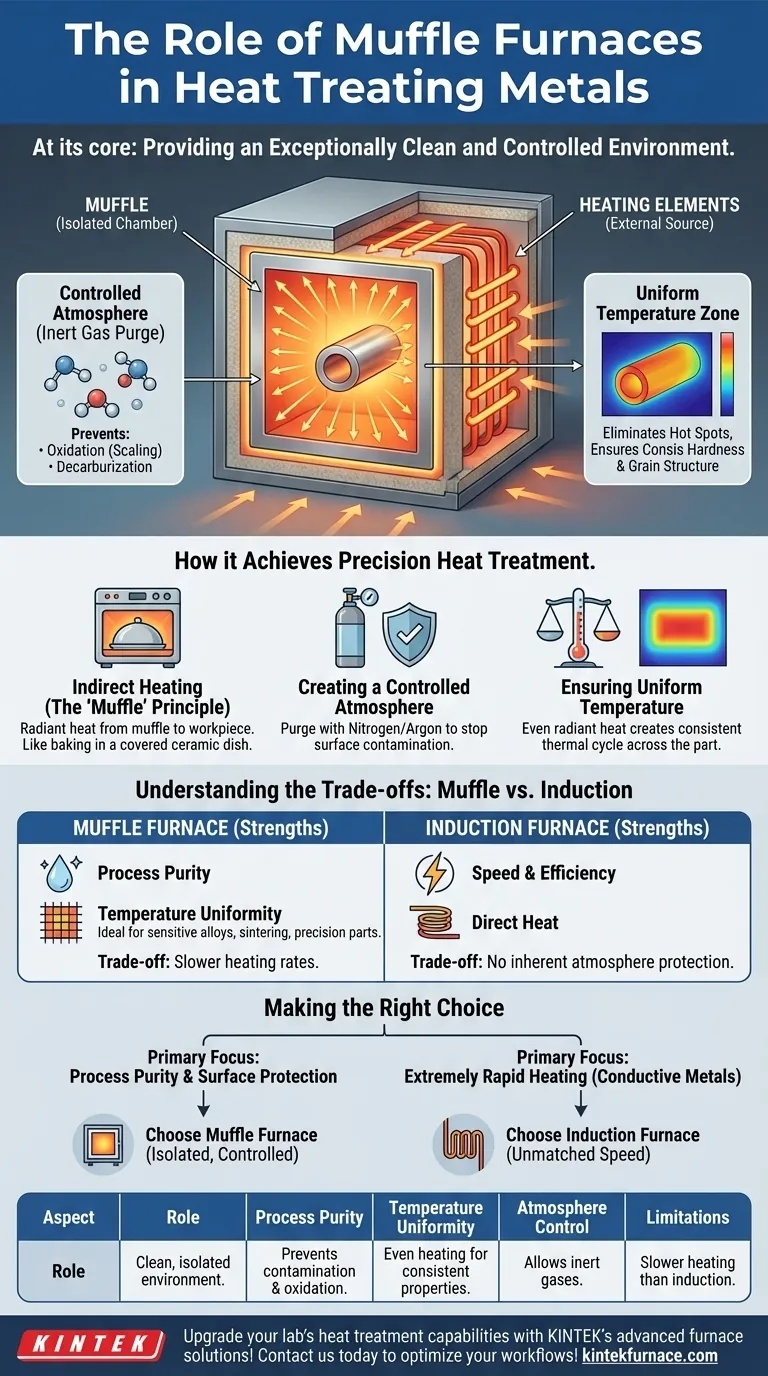
At its core, the role of a muffle furnace in heat treating is to provide an exceptionally clean and controlled environment. By physically separating the material being treated from the heating elements and their combustion byproducts, it ensures the process alters only the metal's internal structure, not its surface chemistry.
The critical function of a muffle furnace is not just to generate heat, but to create a highly uniform and inert thermal environment. This isolation is essential for high-precision applications where surface contamination or oxidation would compromise the final product.
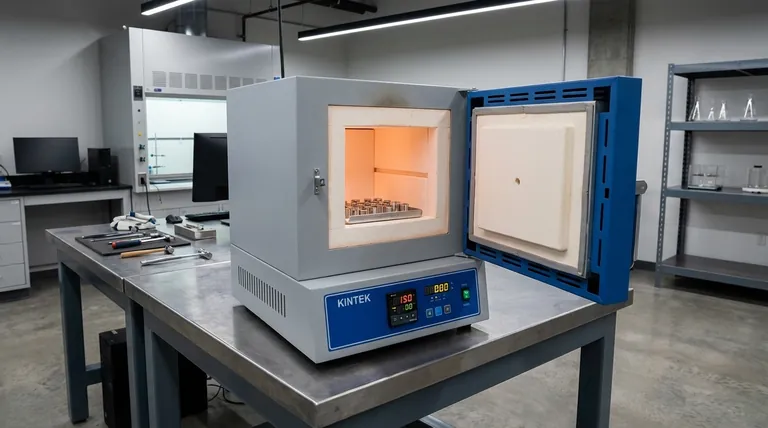

How a Muffle Furnace Achieves Precision Heat Treatment
The unique design of a muffle furnace is what enables its precise control over the heat treatment process. It operates on a principle of indirect heating, which is fundamental to its advantages.
The "Muffle" Principle: Indirect Heating
A muffle furnace contains an inner chamber, or "muffle," which is sealed off from the external heating elements.
The outer elements heat the muffle, which then radiates thermal energy uniformly into the sealed chamber. This is analogous to baking food in a covered ceramic dish inside an oven; the dish protects the food from direct flame and ensures even cooking.
Creating a Controlled Atmosphere
This separation is crucial because it allows for complete control over the atmosphere surrounding the workpiece.
By purging the chamber and introducing inert gases like nitrogen or argon, the furnace prevents oxidation (scaling) and decarburization (loss of carbon from the surface), which can occur in open-air heating.
This atmospheric control is non-negotiable for treating sensitive alloys or parts requiring a specific surface finish and hardness.
Ensuring Uniform Temperature
Because heat is radiated from the entire inner surface of the muffle, it creates a very uniform temperature zone.
This eliminates hot spots that can occur with direct heating methods, ensuring that the entire workpiece, regardless of its geometry, experiences the same thermal cycle. This uniformity is key to achieving consistent hardness, grain structure, and strength across the entire part.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Muffle vs. Other Furnaces
While powerful, a muffle furnace is not the universal solution for all heating tasks. Understanding its limitations compared to other technologies, like induction furnaces, is key to making the right choice.
Muffle Furnace Strengths
The primary strengths are process purity and temperature uniformity. For applications like annealing sensitive medical implants, sintering powdered metals, or hardening precision tool steels, the clean, controlled environment is a significant advantage.
Muffle Furnace Limitations
The main trade-off is speed and, in some cases, energy efficiency. Because the heat is transferred indirectly, heating rates are generally slower than direct methods. The furnace must first heat the muffle, which then heats the part.
Contrast with Induction Furnaces
Induction furnaces, by contrast, use electromagnetic fields to generate heat directly within the metal part itself. This process is extremely fast and energy-efficient for conductive materials.
However, induction heating offers little to no protection from the surrounding atmosphere unless conducted in a separate vacuum or inert chamber. It is better suited for bulk melting or rapid, localized surface hardening where atmospheric contamination is less of a concern.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The decision between a muffle furnace and another heating method depends entirely on the metallurgical outcome you need to achieve.
- If your primary focus is process purity and preventing surface contamination: A muffle furnace is the superior choice due to its isolated, controlled atmosphere.
- If your primary focus is achieving consistent, uniform material properties: The radiant, even heating of a muffle furnace ensures predictable results across the entire workpiece.
- If your primary focus is extremely rapid heating of conductive metals: An induction furnace offers unmatched speed and efficiency for tasks like bulk melting or localized hardening.
Ultimately, selecting the correct furnace is about matching the tool's inherent capabilities to your specific material and process requirements.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Role in Heat Treating Metals |
|---|---|
| Process Purity | Provides a clean, isolated environment to prevent surface contamination and oxidation. |
| Temperature Uniformity | Ensures even heating for consistent hardness and grain structure across the workpiece. |
| Atmosphere Control | Allows use of inert gases to avoid decarburization and scaling. |
| Limitations | Slower heating rates compared to direct methods like induction furnaces. |
Upgrade your lab's heat treatment capabilities with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise matching to your unique experimental needs, delivering superior process purity and uniform results. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your metal processing workflows!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production



















