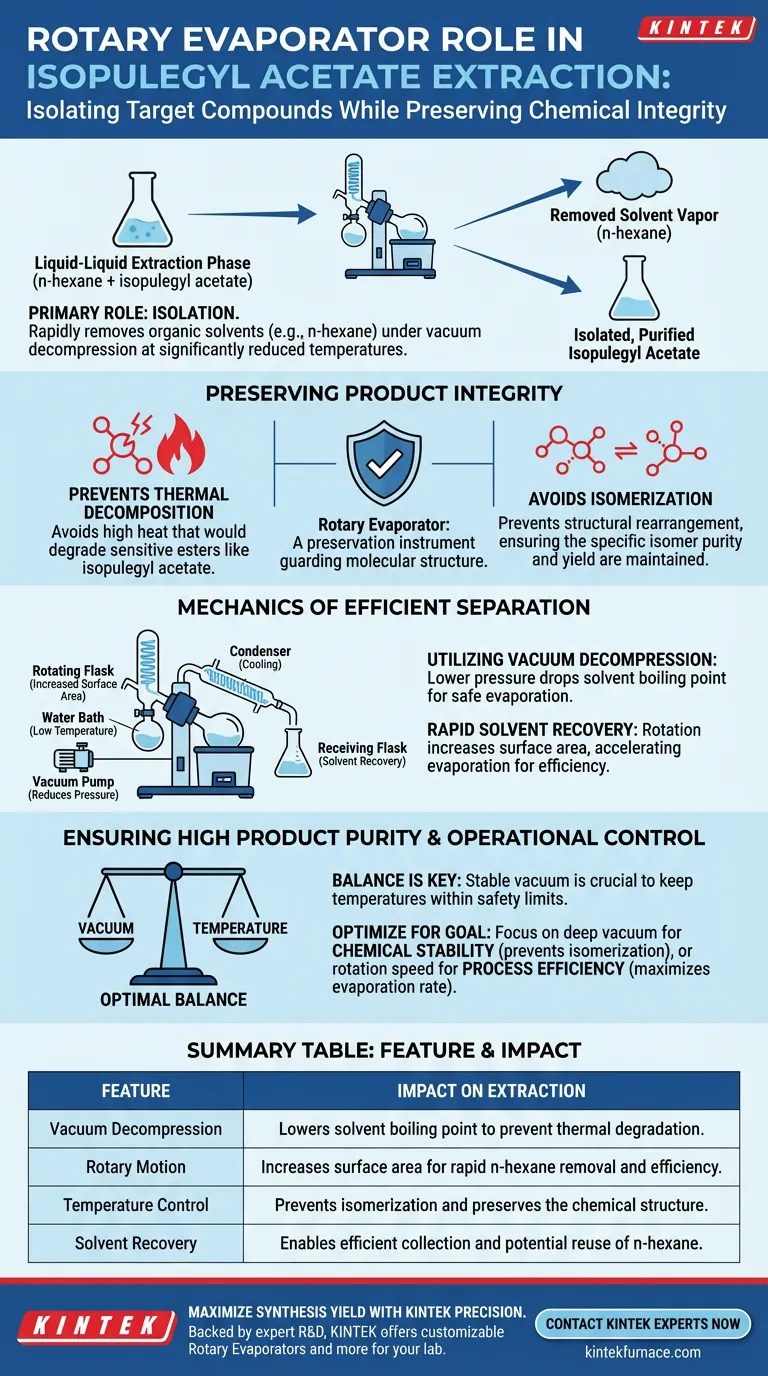
The primary role of a rotary evaporator in this synthesis is to isolate the target compound, isopulegyl acetate, from the organic solvent used during extraction. By applying vacuum decompression, the device rapidly removes solvents like n-hexane at significantly reduced temperatures. This step is critical for transitioning from the liquid-liquid extraction phase to a final, purified product without compromising chemical stability.
Thermal sensitivity is a major challenge in organic synthesis. A rotary evaporator addresses this by lowering the boiling point of the solvent, allowing for efficient removal without the high heat that would otherwise degrade the isopulegyl acetate.
Preserving Product Integrity
Preventing Thermal Decomposition
The synthesis of esters like isopulegyl acetate often results in a product that is sensitive to high temperatures.
Standard distillation methods typically require heating a mixture to the solvent's boiling point at atmospheric pressure.
The rotary evaporator uses a vacuum to mitigate this, ensuring the product does not undergo thermal decomposition due to excessive heat exposure.
Avoiding Isomerization
Beyond simple degradation, there is a specific risk of the molecule rearranging itself.
The primary reference notes that high heat can cause isomerization, where the isopulegyl acetate changes its structural configuration.
This would result in a different chemical compound entirely, lowering the purity and yield of the desired specific isomer.
Mechanics of Efficient Separation
Utilizing Vacuum Decompression
The core mechanism at work is the reduction of pressure inside the system.
By lowering the pressure, the boiling point of the organic solvent (specifically n-hexane in this context) drops well below its standard level.
This allows the solvent to transition into a vapor phase while the isopulegyl acetate remains in the liquid phase at a safe, low temperature.
Rapid Solvent Recovery
Speed is a critical factor in efficient chemical processing.
The rotary motion increases the surface area of the liquid, which, combined with the vacuum, facilitates rapid evaporation.
This improves the overall efficiency of solvent recovery, allowing the n-hexane to be collected and potentially reused while isolating the product quickly.
Understanding the Operational Requirements
The Necessity of Parameter Control
While the rotary evaporator protects the product, it relies entirely on the correct balance of vacuum and temperature.
If the vacuum level is insufficient, the bath temperature must be raised to evaporate the n-hexane, which re-introduces the risk of thermal damage.
Therefore, the operator must prioritize establishing a stable vacuum to ensure the process remains within the thermal safety limits of isopulegyl acetate.
Ensuring High Product Purity
Optimizing for the End Goal
The ultimate objective of using this equipment is to ensure high product purity.
By effectively removing the solvent without triggering chemical changes, the final substance matches the desired theoretical structure of the synthesis.
If your primary focus is Chemical Stability: Prioritize deep vacuum levels to keep the bath temperature as low as possible, specifically to prevent isomerization.
If your primary focus is Process Efficiency: Focus on the rotation speed and surface area to maximize the evaporation rate of the n-hexane solvent.
The rotary evaporator is not just a drying tool; it is a preservation instrument that safeguards the molecular structure of isopulegyl acetate during isolation.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Impact on Isopulegyl Acetate Extraction |
|---|---|
| Vacuum Decompression | Lowers solvent boiling point to prevent thermal degradation. |
| Rotary Motion | Increases surface area for rapid n-hexane removal and efficiency. |
| Temperature Control | Prevents isomerization and preserves the chemical structure. |
| Solvent Recovery | Enables efficient collection and potential reuse of n-hexane. |
Maximize Your Synthesis Yield with KINTEK Precision
Preserving the integrity of sensitive compounds like isopulegyl acetate requires precise control over pressure and temperature. KINTEK provides industry-leading laboratory solutions tailored for high-performance extraction and purification.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers Rotary Evaporators, Vacuum systems, Muffle, Tube, and CVD furnaces, all customizable for your unique lab needs. Don't compromise your product purity with inconsistent equipment—leverage our engineering expertise to optimize your solvent recovery today.
Visual Guide
References
- Citronellal Acetylation Using Ni-Co Metal Impregnated Hierarchical Zeolite Catalysis and Its Potential as an Antibacterial, Antifungal and Antioxidants. DOI: 10.1051/e3sconf/202562202002
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station CVD Machine
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Ultra Vacuum Electrode Feedthrough Connector Flange Power Lead for High Precision Applications
People Also Ask
- What are some common applications of rotary tube furnaces? Unlock Efficient Bulk Material Processing
- How is heat transferred to the furnace tubes in a rotary tube furnace? Master Uniform Heating for Your Materials
- How is the structure of a rotary tube furnace characterized? Discover Its Key Components and Benefits
- How does a rotary tube furnace operate? Master Continuous Heating for Uniform Results
- What are the key features of a rotary furnace? Achieve Superior Uniformity and Control



















