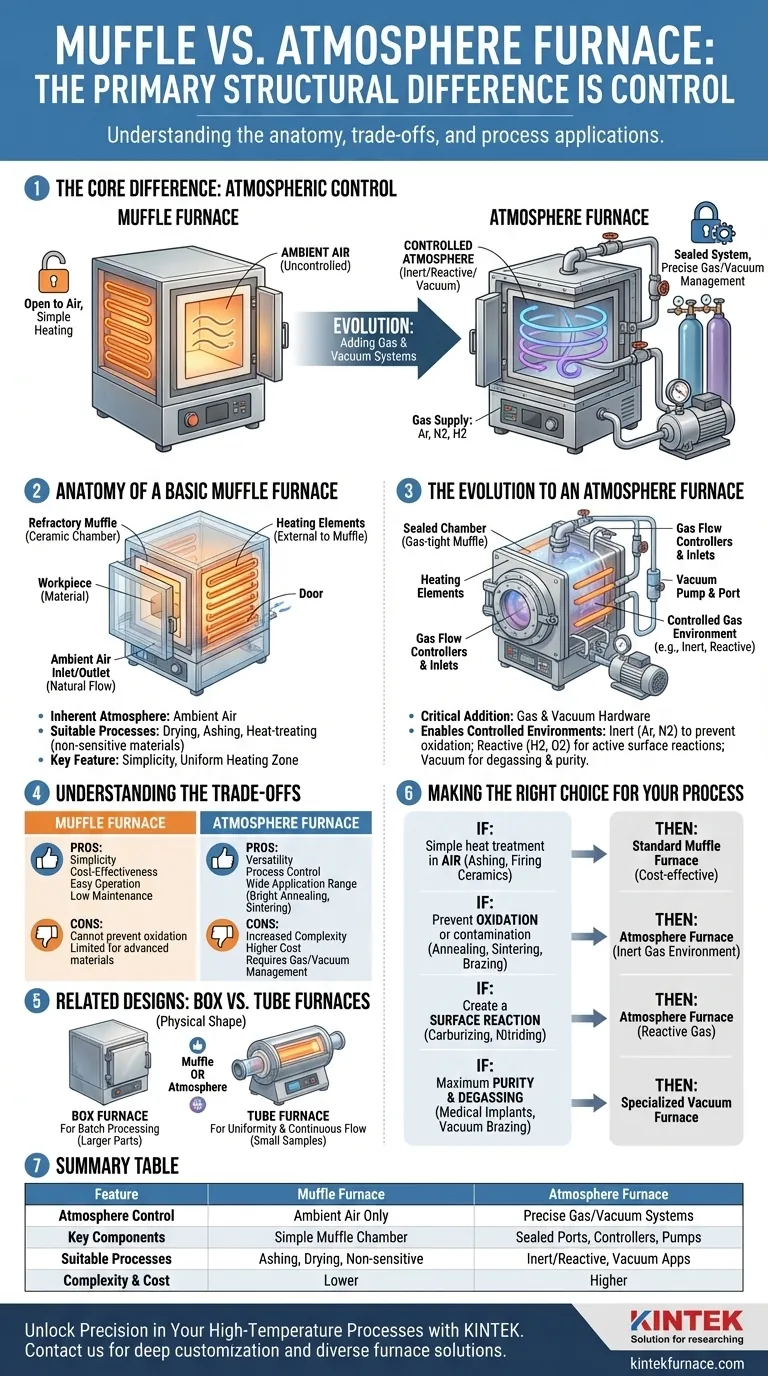
At its core, the primary structural difference is one of control. A standard muffle furnace contains a simple, enclosed heating chamber (the "muffle"), while an atmosphere furnace adds a gas delivery and/or vacuum system to precisely manage the gaseous environment within that chamber. This additional hardware is what allows for processing materials without exposure to air.
The choice between a muffle and an atmosphere furnace is not about temperature, but about chemistry. The fundamental difference is whether you need to control the atmosphere to prevent oxidation, remove impurities, or introduce a specific reaction during heating.

The Anatomy of a Basic Muffle Furnace
A muffle furnace is the foundational design for high-temperature laboratory and industrial heating. Its structure is defined by its simplicity.
The Core Component: The Muffle
The defining feature is the muffle itself—an isolated chamber made of a refractory ceramic material. This chamber separates the material being heated from the heating elements.
The primary purpose of the muffle is to provide a clean, uniform heating zone and protect the heating elements from any fumes or spatter from the workpiece.
The Inherent Atmosphere: Ambient Air
A standard muffle furnace operates with the air that is naturally trapped inside its chamber. It does not have systems for removing this air or introducing other gases.
This makes it suitable for processes like drying, ashing, or heat-treating materials that are not sensitive to oxidation.
The Evolution to an Atmosphere Furnace
An atmosphere furnace is not a completely different type of furnace; rather, it is an advanced version of a muffle or chamber furnace, engineered for atmospheric control.
The Critical Addition: Gas and Vacuum Systems
The key structural difference is the addition of gas and vacuum hardware. This includes sealed ports, gas flow controllers, and often a vacuum pump.
These systems allow an operator to first remove the ambient air from the chamber and then backfill it with a specific gas or gas mixture.
Enabling Controlled Environments
This structural addition allows for several processing environments not possible in a basic muffle furnace:
- Inert Atmosphere: Using gases like Argon or Nitrogen to prevent oxidation when heating reactive metals.
- Reactive Atmosphere: Introducing gases like Hydrogen or Oxygen to actively participate in a chemical reaction on the material's surface.
- Vacuum: Processing materials under low pressure to remove trapped gases and prevent any atmospheric contamination, which is the domain of a specialized atmosphere furnace known as a vacuum furnace.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right furnace requires understanding the functional consequences of these structural differences.
Muffle Furnace: Simplicity and Cost-Effectiveness
The primary advantage of a muffle furnace is its simplicity. With fewer systems, it is generally less expensive, easier to operate, and requires less maintenance.
Its major limitation is its inability to prevent oxidation. For many metals and advanced materials, heating in air is simply not an option.
Atmosphere Furnace: Versatility and Process Control
The ability to control the atmosphere unlocks a vast range of material processing applications, from bright annealing of steel to sintering advanced ceramics.
This versatility comes at the cost of increased complexity and expense. Operating an atmosphere furnace requires managing gas supplies, flow rates, and ensuring the chamber is properly sealed.
Related Designs: Box vs. Tube Furnaces
The terms "muffle" and "atmosphere" describe the furnace's gas-handling capability. "Box" and "tube" describe its physical shape and are independent of atmospheric control.
Box Furnaces: For Batch Processing
Box furnaces feature a large, cubic chamber, making them ideal for heating larger parts or batches of smaller parts simultaneously. A box furnace can be a simple muffle furnace or a fully capable atmosphere furnace.
Tube Furnaces: For Uniformity and Continuous Flow
Tube furnaces use a cylindrical heating chamber. This design provides excellent temperature uniformity along the tube's length and is well-suited for processing small samples or materials that can be passed continuously through the heated zone. Like box furnaces, they can be either simple air-atmosphere or controlled-atmosphere models.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your decision should be driven entirely by the chemical requirements of your heating process.
- If your primary focus is simple heat treatment in air (e.g., ashing, hardening non-reactive tools, firing some ceramics): A standard muffle furnace is the most direct and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is preventing oxidation or contamination (e.g., annealing copper, sintering powders, brazing): You need an atmosphere furnace capable of providing an inert gas environment.
- If your primary focus is creating a surface reaction (e.g., carburizing, nitriding): You require an atmosphere furnace designed to handle specific reactive gases.
- If your primary focus is maximum purity and degassing (e.g., medical implant processing, vacuum brazing): A specialized vacuum furnace is necessary.
By understanding that the furnace's structure dictates its function, you can confidently select the precise tool your process requires.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Muffle Furnace | Atmosphere Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Atmosphere Control | Operates with ambient air only | Includes gas delivery and/or vacuum systems for precise control |
| Key Components | Simple enclosed muffle chamber | Sealed ports, gas flow controllers, vacuum pumps |
| Suitable Processes | Ashing, drying, heat-treating non-sensitive materials | Inert/reactive gas processing, vacuum applications |
| Complexity & Cost | Lower cost, simpler operation | Higher cost, more complex due to added systems |
Unlock Precision in Your High-Temperature Processes with KINTEK
Struggling to choose the right furnace for your lab's unique needs? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for diverse laboratories. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your experimental requirements—whether you need simple heating or complex atmospheric control.
Don't let furnace limitations hold back your research or production. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your efficiency, ensure material purity, and drive innovation in your projects!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a batch type controlled atmosphere furnace operate? Master Precision Heat Treatment for Superior Materials
- What are the primary inert gases used in vacuum furnaces? Optimize Your Heat Treatment Process
- How do atmosphere furnaces contribute to ceramic manufacturing? Enhance Purity and Performance
- How do argon and nitrogen protect samples in vacuum furnaces? Optimize Your Thermal Process with the Right Gas
- What are the development prospects of atmosphere box furnaces in the aerospace industry? Unlock Advanced Material Processing for Aerospace Innovation



















