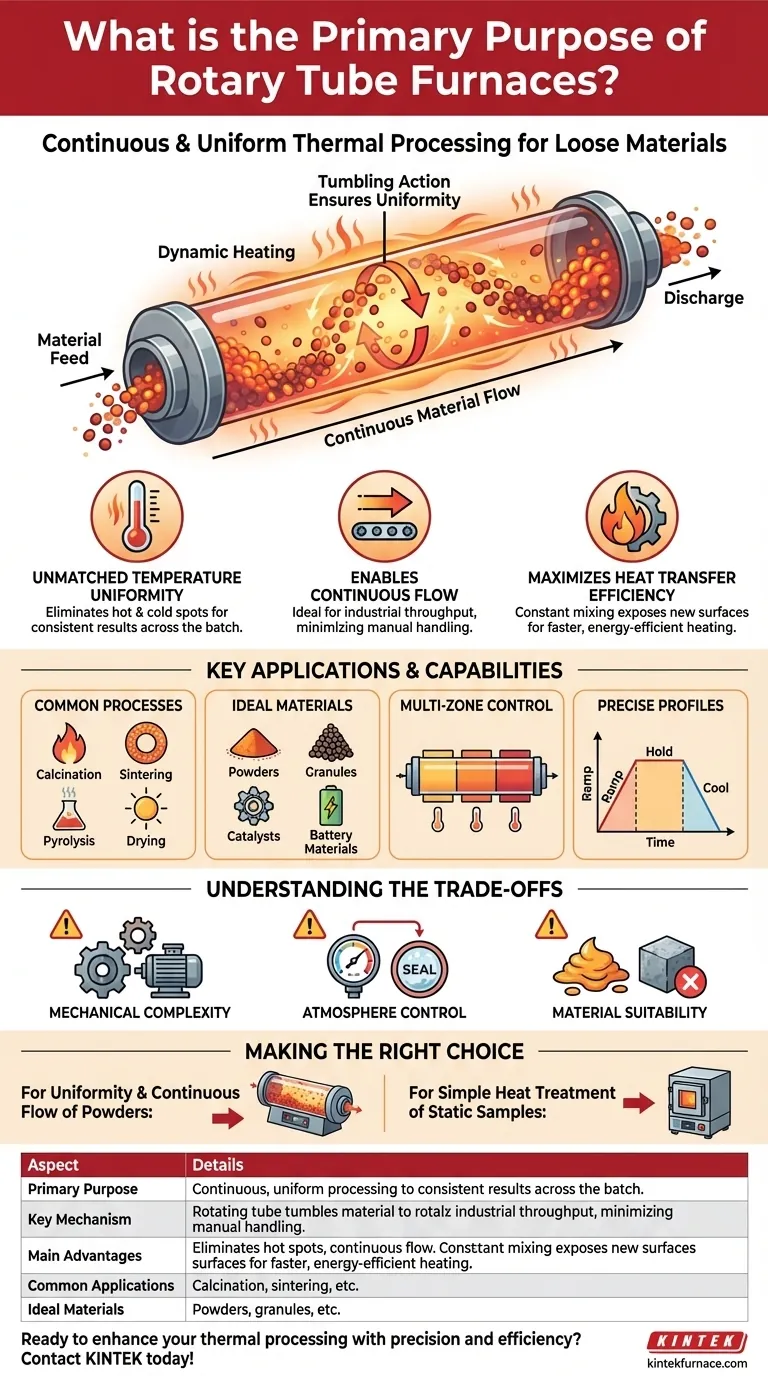
At their core, the primary purpose of rotary tube furnaces is the continuous and uniform thermal processing of loose, free-flowing materials like powders and granules. They use a rotating cylindrical tube to tumble the material, ensuring every particle is evenly exposed to heat for consistent physical or chemical changes.
The defining advantage of a rotary tube furnace is not just heating, but how it heats. The constant rotation is the key mechanism that guarantees superior temperature uniformity and efficient heat transfer, a feat difficult to achieve with static heating methods for bulk materials.

How Rotary Tube Furnaces Achieve Superior Processing
A rotary tube furnace operates on a principle of indirect, dynamic heating. This design choice is fundamental to its effectiveness for specific applications.
The Principle of Dynamic Heating
The furnace heats a cylindrical tube, which is rotated along its longitudinal axis. The material to be processed is placed inside this tube.
As the tube rotates, the material inside gently tumbles. This constant motion ensures the material does not simply sit at the bottom but is continuously mixed and exposed to the hot inner surface of the tube.
Ensuring Unmatched Temperature Uniformity
In a static furnace, powders or granules can suffer from inconsistent heating. The material on the top may be at a different temperature than the material in contact with the hot surface at the bottom.
The tumbling action in a rotary furnace solves this problem. It eliminates hot spots and cold spots, guaranteeing that the entire batch of material experiences the same temperature profile.
Enabling Continuous Material Flow
Rotary tube furnaces are engineered for continuous or large-batch processing. Material can be fed into one end of the tilted, rotating tube and slowly travel to the other end as it is being heated.
This capability is ideal for industrial settings where a consistent throughput of processed material is required, minimizing the need for manual handling between batches.
Maximizing Heat Transfer Efficiency
The constant mixing action dramatically improves the efficiency of heat transfer. Every time a particle tumbles, it exposes a new surface to the radiant and conductive heat from the tube wall.
This leads to shorter processing times and lower energy consumption compared to heating a static pile of the same material.
Key Applications and Capabilities
The unique design of rotary tube furnaces makes them highly versatile for a range of thermal processes in both laboratory and industrial environments.
Common Thermal Processes
These furnaces excel at processes requiring precise temperature control and uniformity, such as calcination, pyrolysis, sintering, drying, and material synthesis.
Ideal Material Types
Their primary strength lies in processing any free-flowing solid. This includes metal powders, catalysts, battery materials, ceramics, and various chemicals.
Multi-Zone Temperature Control
Many advanced models feature multiple, independently controlled heating zones along the length of the tube. This allows for the creation of precise temperature profiles, where the material can be ramped up, held, and cooled down in a single pass.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, the design of a rotary tube furnace presents certain considerations that differentiate it from simpler furnace types.
Mechanical Complexity
The primary trade-off is increased mechanical complexity. The rotating seals, drive motor, and support system require more maintenance than a simple, static tube or box furnace.
Atmosphere Control
Maintaining a perfectly sealed, controlled atmosphere (e.g., inert gas) inside a rotating tube can be more challenging than in a static system. The seals at either end of the tube are critical components that must be properly maintained.
Material Suitability
These furnaces are not suitable for materials that are sticky, could melt and coat the tube, or are single, solid objects. Their design is exclusively for materials that can tumble freely.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct furnace technology depends entirely on your material and your processing objective.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible temperature uniformity for powders or granules: The dynamic heating of a rotary tube furnace is the superior choice.
- If your primary focus is scaling a process from the lab to continuous industrial production: The inherent design of a rotary tube furnace for material flow makes it the ideal platform for scale-up.
- If your primary focus is simple heat treatment of a small number of static samples or solid parts: A standard box furnace or static tube furnace is a more direct and cost-effective solution.
Ultimately, choosing a rotary tube furnace is a decision to prioritize process consistency and efficiency for bulk, free-flowing materials.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Continuous, uniform thermal processing of loose, free-flowing materials like powders and granules |
| Key Mechanism | Rotating tube tumbles material for even heat exposure and superior temperature uniformity |
| Main Advantages | Eliminates hot/cold spots, enables continuous flow, maximizes heat transfer efficiency |
| Common Applications | Calcination, pyrolysis, sintering, drying, material synthesis |
| Ideal Materials | Metal powders, catalysts, battery materials, ceramics, chemicals |
| Trade-offs | Higher mechanical complexity, challenging atmosphere control, not for sticky or solid objects |
Ready to enhance your thermal processing with precision and efficiency? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Rotary Tube Furnaces, designed for labs and industries handling powders and granules. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs—ensuring uniform heating, continuous flow, and optimal performance. Contact us today via our contact form to discuss how our tailored solutions can drive your success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How do rotary tube furnaces achieve precise temperature control? Master Uniform Heating for Dynamic Processes
- What factors should be considered when selecting a tube for a rotary tube furnace? Ensure Optimal Performance and Longevity
- What are the main structural components of a rotary furnace? Explore Key Parts for Efficient Material Processing
- What types of materials are suitable for processing in rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Free-Flowing Powders and Granules
- What supplementary features can enhance rotary tube furnace performance? Boost Efficiency with Precision Control



















