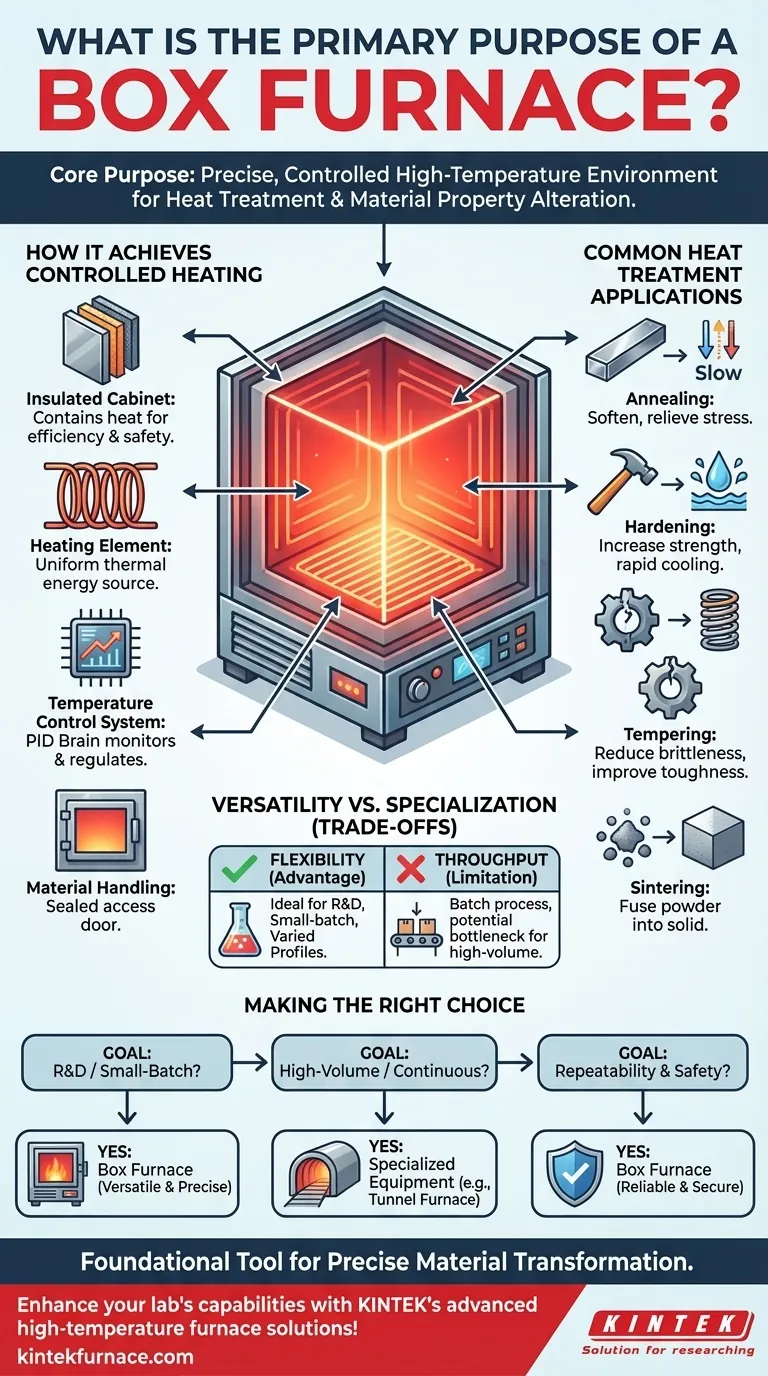
At its core, a box furnace is a highly versatile piece of equipment designed to create a precisely controlled, high-temperature environment. Its fundamental purpose is to perform heat treatment processes that intentionally alter the physical, and sometimes chemical, properties of materials to meet specific engineering, industrial, or scientific requirements.
The true value of a box furnace lies not just in its ability to generate high temperatures, but in its capacity to do so with exceptional uniformity and precision, enabling the repeatable transformation of materials.
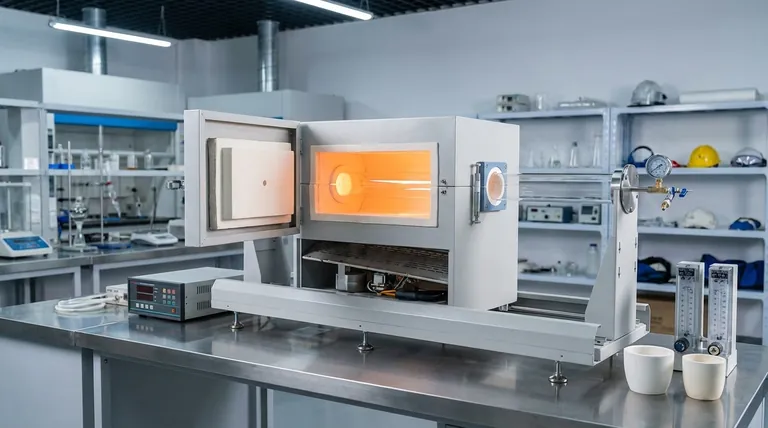

How a Box Furnace Achieves Controlled Heating
A box furnace's ability to deliver a stable thermal environment is the result of several key components working in concert. Understanding these parts clarifies how the furnace fulfills its primary purpose.
The Insulated Cabinet
The main body, or cabinet, is built from high-temperature, heat-resistant materials. This construction serves two critical functions: it contains the heat for maximum thermal efficiency and ensures the safety of the operator by keeping the exterior surfaces cool.
The Heating Element
Typically made from electric heating wire or similar resistive materials, the heating element is the source of the thermal energy. It is designed to provide stable, uniform heating throughout the chamber, eliminating hot spots and ensuring the entire workpiece experiences the same temperature profile.
The Temperature Control System
This is the brain of the furnace. A sophisticated control system, often a PID controller, constantly monitors the internal temperature and regulates power to the heating elements. It manages the rate of temperature rise, the duration at a specific temperature (the "soak"), and the cooling rate, which are all critical variables in heat treatment.
Material Handling
Simple but essential, the feeding and discharging device—the furnace door—provides access to the chamber. A well-designed door mechanism ensures a tight seal to maintain the internal atmosphere and temperature while allowing for the safe loading and unloading of materials.
Common Heat Treatment Applications
The controlled environment of a box furnace is essential for a range of processes that modify material properties. These are not simply about heating and cooling; they are precise thermal recipes.
Annealing
This process involves heating a material and then cooling it very slowly. The goal is to soften the material, relieve internal stresses created during manufacturing, and improve its ductility, making it easier to work with.
Hardening
Hardening increases the strength and wear resistance of metals like steel. It is achieved by heating the material to a critical temperature and then cooling it rapidly, a process known as quenching. This locks the material's crystal structure into a very hard state.
Tempering
Materials that have been hardened are often extremely brittle. Tempering is a secondary, lower-temperature heat treatment performed after hardening to reduce some of that brittleness and improve the material's toughness.
Sintering
In powder metallurgy, sintering uses heat to fuse fine particles together into a solid, coherent mass without melting them. Box furnaces provide the stable, controlled temperatures necessary for this diffusion process to occur effectively.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Versatility vs. Specialization
While incredibly useful, the box furnace is not the universal solution for all heating applications. Its design comes with inherent advantages and limitations.
The Advantage of Flexibility
The primary strength of a box furnace is its versatility. A single furnace can be programmed to run countless different thermal profiles, making it ideal for research labs, prototyping, tool rooms, and small-batch production where processes change frequently.
The Limitation of Throughput
The defining characteristic of a box furnace is that it processes materials in batches. For high-volume, continuous manufacturing, this start-and-stop workflow can be a significant bottleneck compared to specialized equipment like conveyor or tunnel furnaces.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct heating equipment depends entirely on your operational needs and production goals.
- If your primary focus is research, development, or small-batch production: A box furnace is an ideal choice due to its versatility and precise control over varying processes.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, continuous manufacturing: You should evaluate specialized equipment like a conveyor or tunnel furnace, as a box furnace's batch nature may create a bottleneck.
- If your primary focus is process repeatability and safety: The integrated temperature control systems and insulated construction of a modern box furnace make it a reliable and secure option.
Ultimately, the box furnace serves as a foundational tool for any operation that requires transforming materials through the precise and controlled application of heat.
Summary Table:
| Purpose | Key Components | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Create controlled high-temperature environments for material property alteration | Insulated cabinet, heating element, temperature control system, material handling door | Annealing, hardening, tempering, sintering |
Enhance your lab's capabilities with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with reliable box furnaces, muffle furnaces, tube furnaces, and more. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can precisely meet your unique experimental requirements for heat treatment processes. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can optimize your material transformation workflows!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What technical requirements affect the external thermal strength of furnace tubes? Optimize for High-Temp Performance
- What factors should be considered when purchasing a quartz tube furnace? Ensure Reliable High-Temperature Processing
- What is the difference between an alumina tube furnace and a quartz tube furnace? Choose the Right Tube Furnace for Your Lab
- What is a Quartz Tube Furnace and what is its primary function? Essential for Real-Time Material Observation
- How should a quartz tube furnace be cleaned? Essential Steps for Safe, Contamination-Free Maintenance



















