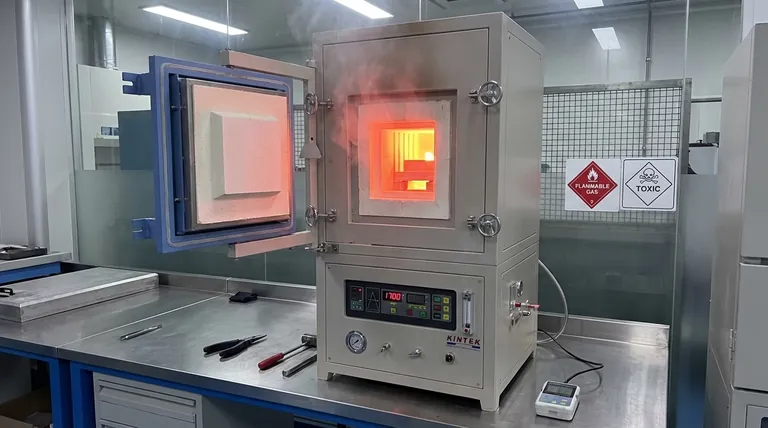
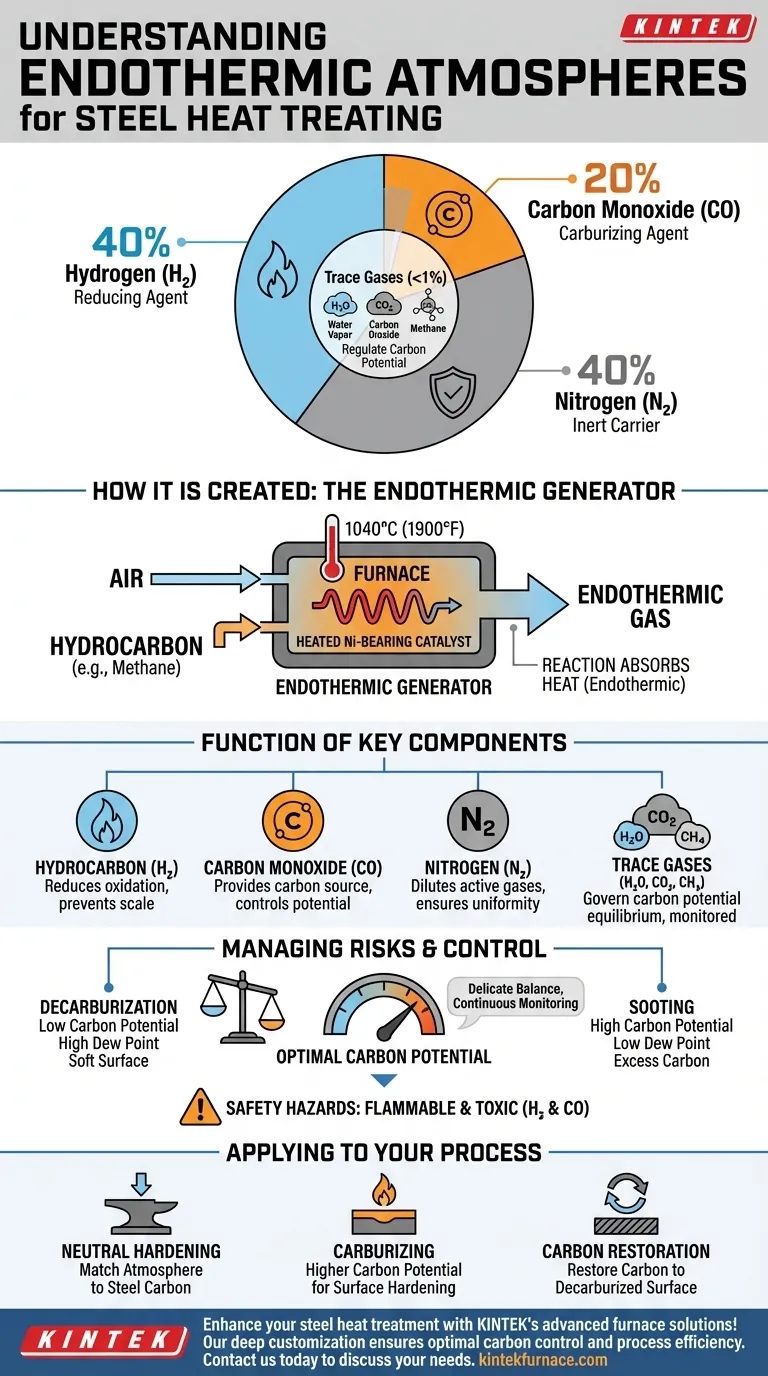
In its most basic form, a typical endothermic atmosphere is a precisely engineered gas mixture used to protect steel during high-temperature heat treatment. The nominal composition is approximately 40% hydrogen (H₂), 20% carbon monoxide (CO), and **40% nitrogen (N₂) **, with very small, controlled amounts of water vapor (H₂O), carbon dioxide (CO₂), and methane (CH₄).
The true purpose of an endothermic atmosphere is not merely to be a protective blanket, but to create a chemically active environment. It is designed to be in equilibrium with the carbon content of the steel, preventing both the loss and unwanted gain of carbon at the surface.

How an Endothermic Atmosphere is Created
The specific composition of an endothermic atmosphere is a direct result of how it is generated. It is not created by simply mixing bottled gases.
The Generator Reaction
The gas is produced in a device called an endothermic generator. Inside, a controlled ratio of air and a hydrocarbon gas (typically natural gas, which is mostly methane) is reacted at high temperatures (around 1040°C or 1900°F).
The Role of the Catalyst
This reaction takes place over a heated nickel-bearing catalyst. The catalyst facilitates the breakdown and reformation of the molecules into the desired atmospheric composition.
Why "Endothermic"
The process is called "endothermic" because the chemical reaction absorbs heat from its surroundings to proceed. This is why the generator must be continuously heated to sustain the reaction and produce a stable gas mixture.
The Function of Each Gas Component
Each component of the atmosphere plays a distinct and critical role in the heat treatment process. Understanding these roles is key to controlling the outcome for your steel parts.
Hydrogen (H₂) - The Reducing Agent
Hydrogen is a powerful reducing agent. Its primary job is to seek out and react with any oxygen present in the furnace. This prevents the formation of iron oxide (scale) on the steel's surface, keeping it clean and bright.
Carbon Monoxide (CO) - The Carbon Carrier
Carbon monoxide is the main active carburizing gas. It is the source of carbon that can be transferred to the steel. The concentration of CO, in balance with other gases, determines the "carbon potential" of the atmosphere.
Nitrogen (N₂) - The Inert Carrier
Nitrogen is largely inert at typical hardening temperatures. It functions as a carrier gas, diluting the active components (H₂ and CO) and transporting them throughout the furnace to ensure a consistent environment around the parts.
The Critical Trace Gases (H₂O, CO₂, CH₄)
Though present in small amounts (often <1%), these gases are crucial. The equilibrium between CO/CO₂ and H₂/H₂O is what ultimately governs the carbon potential. These trace amounts are continuously monitored via dew point analyzers or oxygen probes to precisely control whether the atmosphere adds, removes, or maintains the carbon on the steel's surface.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
Improperly controlled endothermic gas is one of the most common sources of heat-treating defects. The balance is delicate and requires constant monitoring.
The Risk of Decarburization
If the atmosphere's carbon potential is too low for the steel being treated (often indicated by a high dew point or high CO₂), it will actively pull carbon out of the steel's surface. This creates a soft, weak surface layer known as decarburization, which can lead to part failure.
The Risk of Sooting
Conversely, if the carbon potential is too high (indicated by a low dew point or high CH₄), the atmosphere will deposit excess carbon in the form of soot onto the parts and the furnace interior. This creates significant cleaning challenges and can interfere with the process.
Critical Safety Hazards
It is essential to recognize that this atmosphere is both flammable and toxic. Hydrogen is highly explosive when mixed with air, and carbon monoxide is a lethal poison. Proper furnace maintenance, ventilation, and safety protocols are non-negotiable.
Applying This to Your Process
Your goal dictates how you control the atmosphere. The "nominal" composition is just the starting point; the real control comes from adjusting the air/gas ratio to fine-tune the trace elements.
- If your primary focus is neutral hardening: You must precisely match the atmosphere's carbon potential to the carbon content of the steel alloy to neither add nor remove carbon.
- If your primary focus is carburizing: You will operate with a higher carbon potential to intentionally diffuse carbon into the surface of a low-carbon steel, creating a hard, wear-resistant case.
- If your primary focus is carbon restoration: You will set a carbon potential to match the steel's core carbon level, allowing carbon to diffuse back into a previously decarburized surface layer.
Ultimately, mastering an endothermic atmosphere is about achieving a precise chemical equilibrium between the gas and the steel.
Summary Table:
| Component | Typical Percentage | Key Function |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen (H₂) | 40% | Acts as a reducing agent to prevent oxidation and scale formation on steel surfaces. |
| Carbon Monoxide (CO) | 20% | Serves as the primary carburizing agent, transferring carbon to the steel to control carbon potential. |
| Nitrogen (N₂) | 40% | Functions as an inert carrier gas, diluting active components for uniform distribution in the furnace. |
| Trace Gases (H₂O, CO₂, CH₄) | <1% | Regulate carbon potential through equilibrium; monitored for precise control to prevent defects like decarburization or sooting. |
Enhance your steel heat treatment with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs, helping you achieve optimal carbon control and process efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can benefit your operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the development prospects of atmosphere box furnaces in the aerospace industry? Unlock Advanced Material Processing for Aerospace Innovation
- How do argon and nitrogen protect samples in vacuum furnaces? Optimize Your Thermal Process with the Right Gas
- What are the primary inert gases used in vacuum furnaces? Optimize Your Heat Treatment Process
- What are some specific applications of atmosphere furnaces in the ceramics industry? Enhance Purity and Performance
- What is inert gas technology used for in high-temperature atmosphere vacuum furnaces? Protect Materials and Speed Up Cooling



















