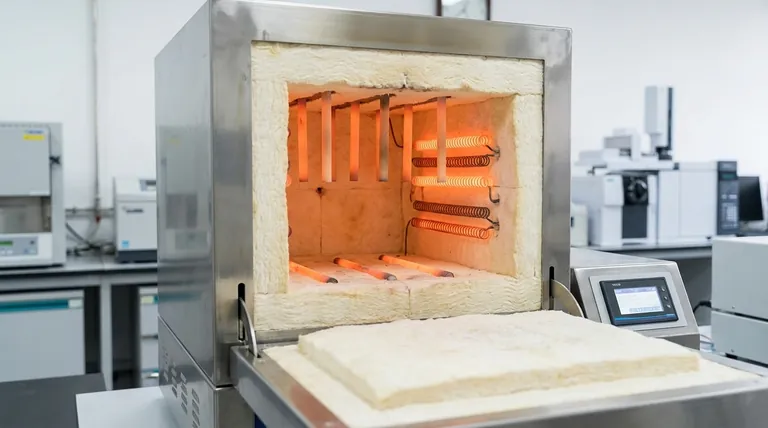
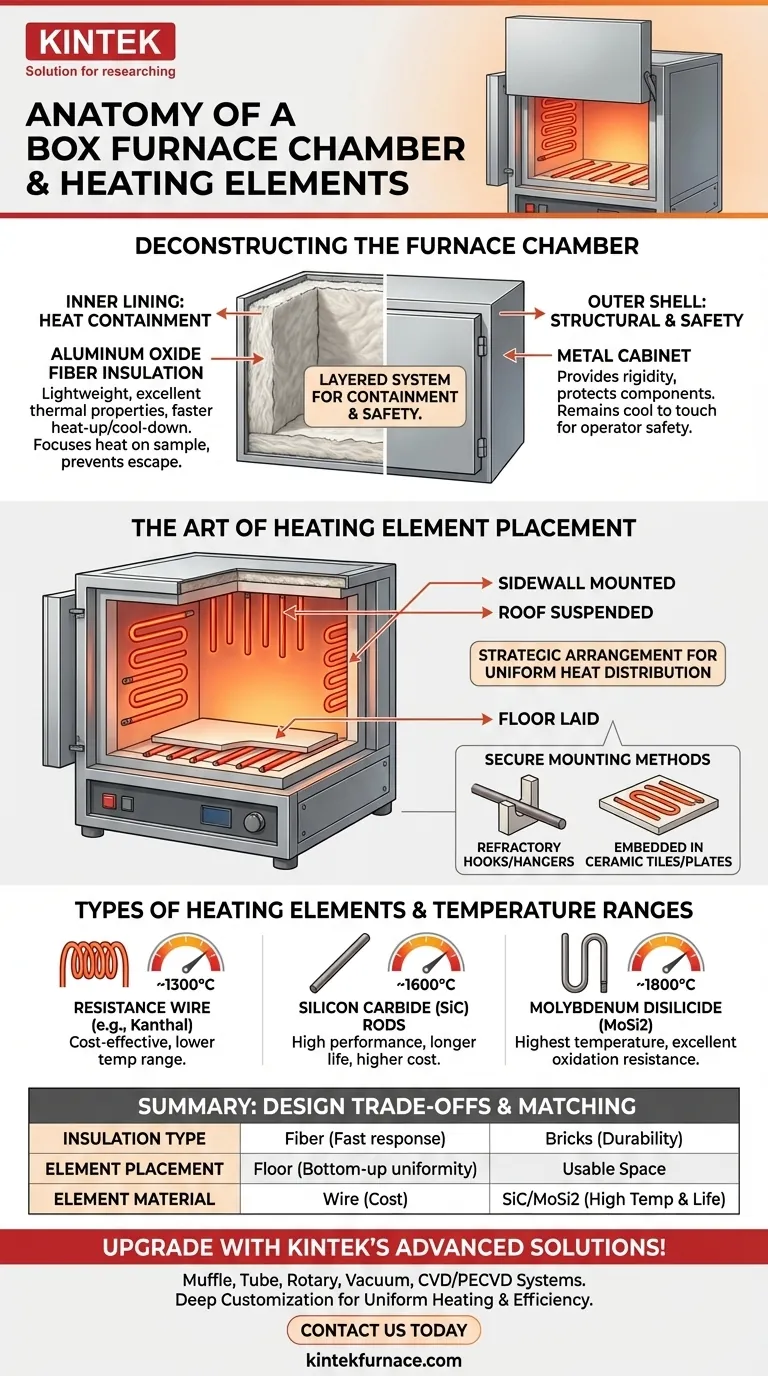
In a standard box furnace, the chamber is constructed from high-temperature refractory materials, with modern designs often using aluminum oxide fiber for insulation. The heating elements are strategically arranged within this chamber—they can be mounted on the sidewalls, suspended from the roof, or laid on the floor to ensure uniform heat distribution.
The design of a box furnace is a deliberate system. The inner chamber uses specialized refractory insulation to contain extreme heat, while the precise placement of heating elements on multiple surfaces is the key to achieving a stable and uniform temperature environment for your process.

Deconstructing the Furnace Chamber
The furnace chamber is not a single component but a layered system designed for heat containment, structural integrity, and user safety.
The Inner Lining: Refractory Materials
The core of the chamber, the surface you see when you open the door, is lined with refractory materials. These are materials specifically engineered to withstand extreme temperatures without degrading.
A very common material in modern furnaces is aluminum oxide fiber. This lightweight insulation offers excellent thermal properties, allowing for faster heat-up and cool-down times compared to traditional refractory bricks.
The primary job of this inner lining is to insulate the chamber, keeping the heat focused on your sample and preventing it from escaping into the lab and damaging the furnace's external components.
The Outer Shell: Structural Integrity and Safety
The entire chamber assembly is housed within a sturdy metal shell or cabinet. This external structure provides the necessary rigidity and protection for the delicate internal components.
This cabinet is also a critical safety feature. It is built to remain cool to the touch (or at least at a safe temperature), protecting the operator from the extreme heat generated inside.
The Art of Heating Element Placement
The arrangement of heating elements is not arbitrary. It is engineered to create a consistent and uniform thermal environment, which is critical for repeatable scientific and industrial processes.
Common Arrangements for Uniform Heating
To avoid hot and cold spots, heating elements are distributed within the chamber. The three primary arrangements are:
- Supported from the furnace sidewalls
- Suspended from the roof
- Laid in grooves on the floor
Furnaces designed for high uniformity often use a combination of these placements, such as having elements on both sidewalls and the roof to fully envelop the workload in heat.
Secure Mounting Methods
Heating elements cannot simply be placed inside; they must be securely held. This is accomplished using components made from materials that can also withstand the heat.
Common methods include using refractory or ceramic hooks and hangers. Another effective technique is to embed the elements directly into pre-formed ceramic tiles or plates, which are then integrated into the chamber walls.
Types of Heating Elements
The elements themselves are typically made of materials with high electrical resistance. Common types include resistance wires (like Kanthal), silicon carbide (SiC) rods, and molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) elements, chosen based on the furnace's maximum required operating temperature.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The specific materials and design choices in a furnace involve trade-offs that affect performance, cost, and longevity.
Insulation Type vs. Thermal Response
Lightweight fiber insulation allows a furnace to heat up and cool down much faster than one lined with dense refractory bricks. However, fiber can be more susceptible to mechanical damage and chemical attack from certain process vapors.
Element Placement vs. Usable Space
Placing heating elements on the furnace floor (hearth) can improve bottom-up heat uniformity. However, this often requires a protective ceramic plate over the elements, which can slightly reduce the maximum vertical working height.
Element Material vs. Cost and Temperature
Simple resistance wire elements are cost-effective but are limited to temperatures typically below 1200-1300°C. High-performance SiC or MoSi2 elements can reach 1500-1800°C and offer a longer service life, but they significantly increase the initial cost of the furnace.
Matching Design to Your Application
Understanding these design principles allows you to select a furnace that is truly fit for your purpose.
- If your primary focus is rapid heating and cooling cycles: Prioritize a furnace built with lightweight ceramic fiber insulation.
- If your primary focus is maximum temperature uniformity: Seek a design that incorporates heating elements on multiple surfaces, such as both sidewalls and the roof.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature operation (above 1400°C): Ensure the furnace is equipped with high-grade heating elements like Silicon Carbide (SiC) or Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2).
By looking beyond the spec sheet and understanding how a furnace is built, you can make a more informed decision for your work.
Summary Table:
| Component | Key Details |
|---|---|
| Chamber Material | High-temperature refractory materials, often aluminum oxide fiber for insulation |
| Heating Element Arrangement | Mounted on sidewalls, suspended from roof, or laid on floor for uniform heat distribution |
| Common Element Types | Resistance wires (e.g., Kanthal), silicon carbide (SiC) rods, molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) |
| Key Trade-offs | Fiber insulation vs. bricks for thermal response; element placement vs. usable space; material choice vs. cost and temperature |
Upgrade your laboratory's capabilities with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer a diverse product line including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements for uniform heating, durability, and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can enhance your processes and deliver reliable results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis



















