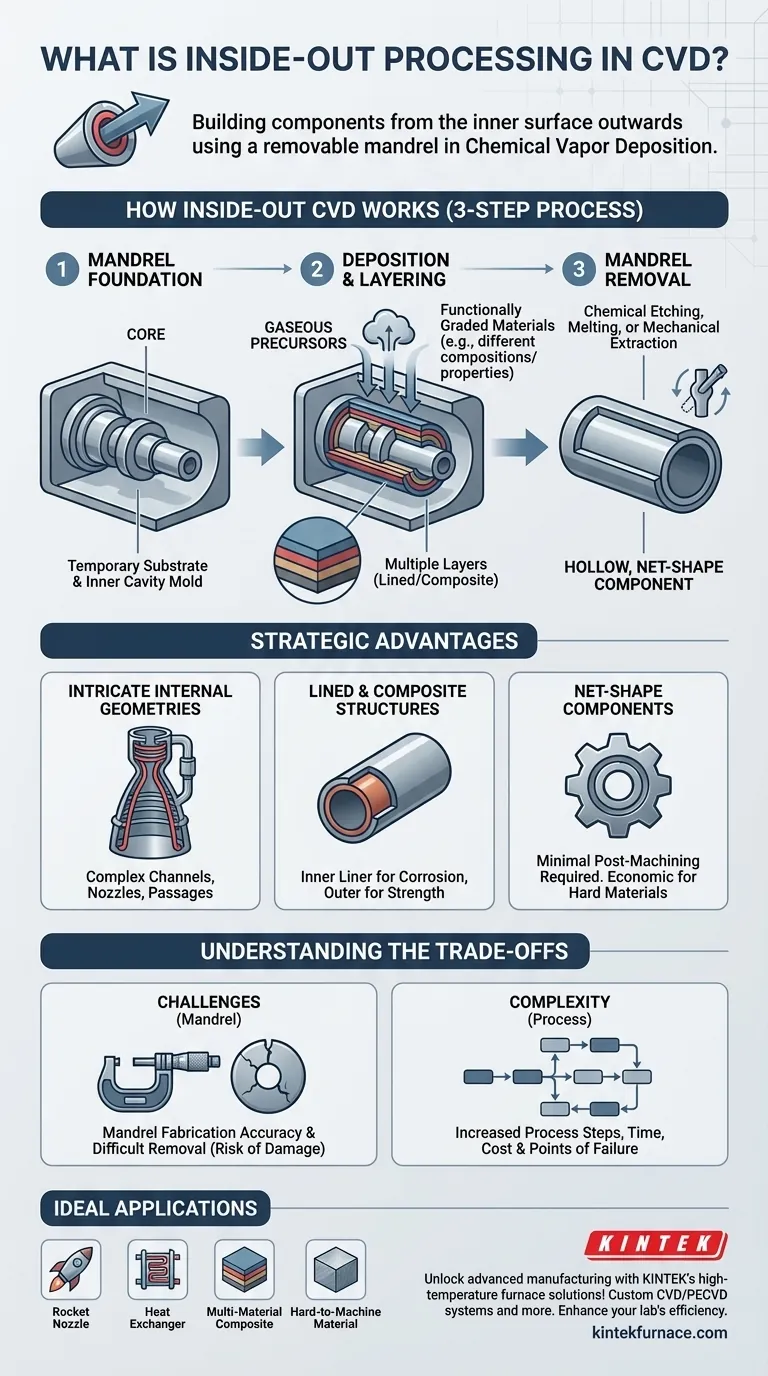
In essence, inside-out processing in Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a fabrication method where a component is built from its inner surface outwards. It starts by creating a removable mold, called a mandrel, that matches the exact internal dimensions of the desired part. Material is then deposited onto this mandrel, and once the deposition is complete, the mandrel is removed to leave behind a hollow, finished component.
This technique fundamentally shifts CVD from a surface coating process to a method for building complex, freestanding structures. Its primary purpose is to create parts with intricate internal geometries or layered material compositions that are impossible to achieve with traditional manufacturing.

How Inside-Out CVD Works
The process is a logical, step-by-step method for building a part around a temporary core. It rethinks the role of the substrate in a standard CVD process.
The Mandrel as the Foundation
The entire process begins with the mandrel. This is a precisely machined form that serves as the temporary substrate for deposition.
Unlike a typical wafer, the mandrel's shape defines the inner cavity of the final component. It is the positive mold for the negative space inside the part.
Deposition and Layering
With the mandrel in the reaction chamber, the CVD process begins. Gaseous precursors are introduced, reacting on the mandrel's surface to deposit a solid material layer by layer.
A key advantage here is the ability to change the precursor gases during deposition. This allows for the creation of functionally graded materials, where each layer has a different composition and set of properties, such as thermal resistance or structural strength.
Mandrel Removal
Once the desired thickness and material layers have been deposited, the process is stopped. The final, critical step is to remove the original mandrel from the newly formed structure.
This is typically done through chemical etching, melting, or mechanical extraction, depending on the mandrel material. This leaves behind a hollow, net-shape component with the intended internal features.
The Strategic Advantages of Inside-Out Processing
Engineers choose this method not because it is simple, but because it unlocks capabilities that other methods cannot offer. It solves specific, high-value manufacturing challenges.
Fabricating Intricate Internal Geometries
This is the primary driver for using inside-out CVD. It allows for the creation of components with complex internal channels, nozzles, or cooling passages that cannot be machined or cast conventionally.
Creating Lined or Composite Structures
The ability to deposit multiple, distinct materials in sequence is a powerful tool. You can create a structure with an inner liner for corrosion resistance and an outer body for structural integrity, all within a single, integrated process.
Achieving Net-Shape Components
The process yields a part that is very close to its final dimensions, requiring little to no subsequent machining. This is a massive economic advantage when working with extremely hard or brittle materials, such as ceramics or refractory metals, where machining is difficult and expensive.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, inside-out processing introduces its own set of complexities that must be managed for a successful outcome.
The Challenge of Mandrel Fabrication
The accuracy of the final part is entirely dependent on the accuracy of the mandrel. Creating a precise, smooth mandrel can be a complex and costly process in itself.
The Difficulty of Mandrel Removal
Removing the mandrel without damaging the thin-walled or delicate deposited structure is a significant technical hurdle. The removal process must be carefully controlled to avoid cracking or deforming the final component.
Increased Process Complexity
Compared to standard CVD, this method adds two major steps: mandrel creation and mandrel removal. This increases the overall time, cost, and potential points of failure in the manufacturing workflow.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Deciding to use inside-out CVD depends entirely on whether the final component's requirements justify the process complexity.
- If your primary focus is creating complex internal shapes: This method is ideal for components like rocket nozzles or advanced heat exchangers where internal geometry is the critical design feature.
- If your primary focus is building multi-material structures: Use this to create layered composites with tailored properties, such as a wear-resistant inner layer and a tough outer shell.
- If your primary focus is minimizing post-processing on difficult materials: This technique produces net-shape ceramic or metal matrix composites, avoiding costly and time-consuming machining.
Ultimately, inside-out CVD provides a unique pathway to manufacture components that were previously considered impossible to build.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Details |
|---|---|
| Process Definition | Builds components from inner surface outwards using a removable mandrel in CVD. |
| Key Steps | Mandrel fabrication, material deposition, mandrel removal. |
| Primary Advantages | Fabricates intricate internal geometries, creates lined/composite structures, achieves net-shape components. |
| Main Challenges | Mandrel fabrication accuracy, difficulty in removal, increased process complexity. |
| Ideal Applications | Rocket nozzles, heat exchangers, multi-material composites, hard-to-machine materials. |
Unlock advanced manufacturing with KINTEK's high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with advanced systems like CVD/PECVD, Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces. Our strong deep customization capability precisely meets your unique experimental needs for inside-out processing and beyond. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your lab's efficiency and innovation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- What is PECVD and how does it differ from traditional CVD? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- How is silicon dioxide (SiO2) used in PECVD applications? Key Roles in Microfabrication
- How does plasma vapor deposition work? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- What is PECVD equipment? A Guide to Low-Temperature Thin-Film Deposition
- How does plasma enhanced CVD work? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition



















