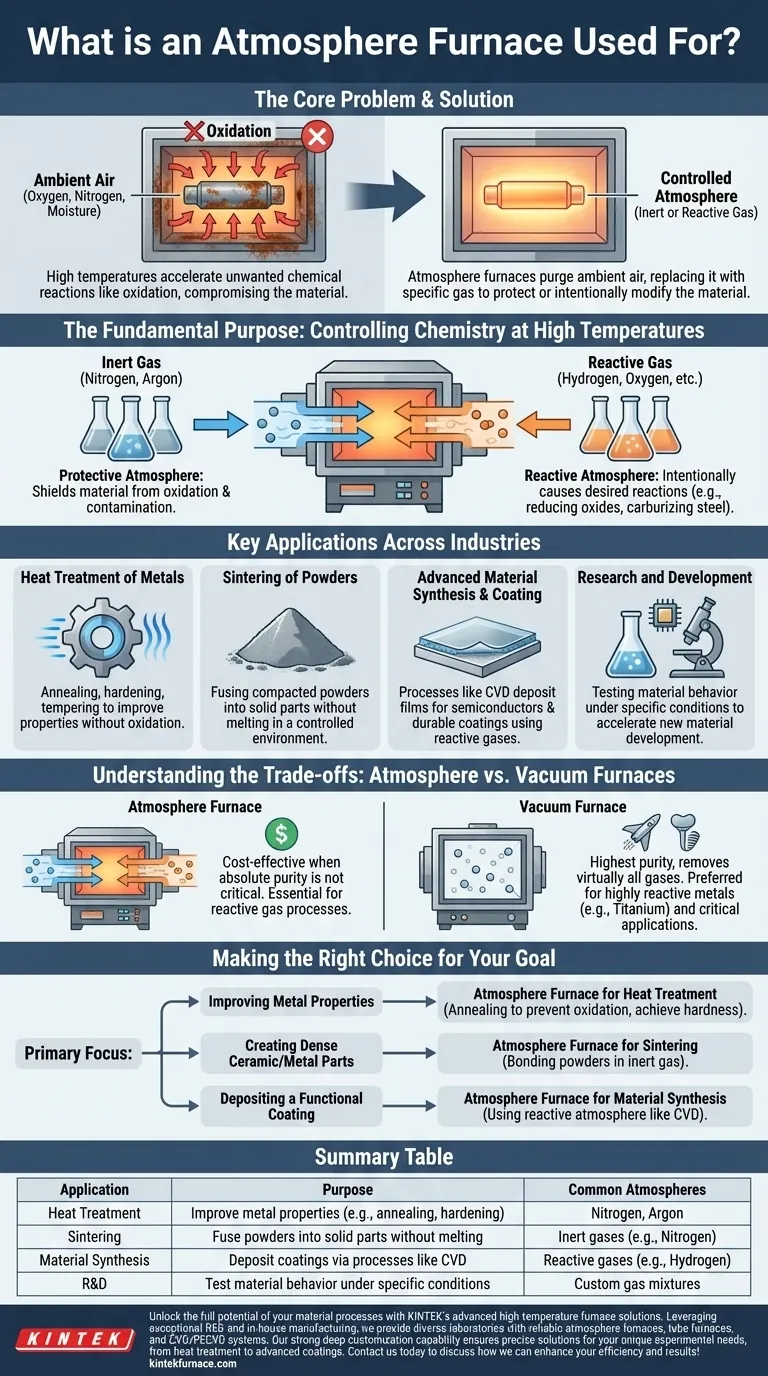
In essence, an atmosphere furnace is a specialized high-temperature oven used for processes that require a precisely controlled gaseous environment. It is a critical tool for heat treating metals, sintering ceramics, and synthesizing advanced materials, where exposure to ambient air would compromise the final product's integrity and properties.
The core problem with high-temperature processing is that heat accelerates unwanted chemical reactions, like oxidation (rust). An atmosphere furnace solves this by replacing the air inside with a specific gas—either inert to protect the material or reactive to intentionally modify it.
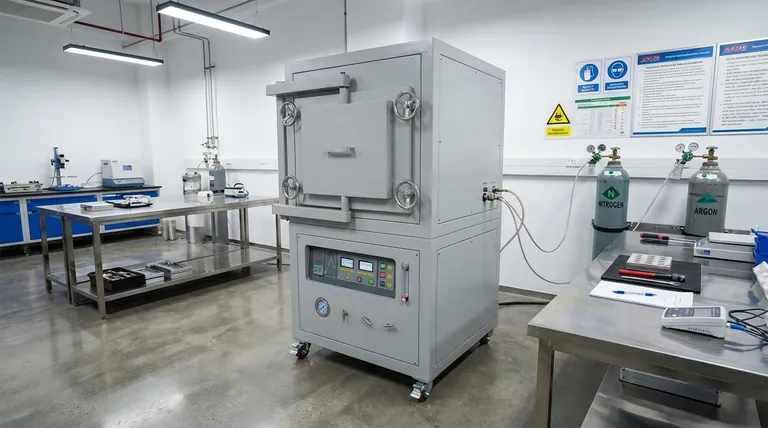

The Fundamental Purpose: Controlling Chemistry at High Temperatures
Nearly all advanced material processing involves heat. However, heating a material in normal air introduces oxygen, nitrogen, and moisture, which can cause detrimental chemical reactions. The atmosphere furnace is designed specifically to prevent this.
Why Ambient Air Is a Problem
At high temperatures, oxygen is highly reactive. It can cause oxidation on the surface of metals, forming a layer of scale that can ruin the component's dimensions and finish. This uncontrolled environment can also introduce contaminants, altering the material's fundamental chemical composition and performance.
How a Controlled Atmosphere Solves This
An atmosphere furnace purges the ambient air from its chamber and replaces it with a specific, pure gas or gas mixture. This atmosphere can be one of two types.
- Protective (Inert) Atmospheres: Gases like nitrogen and argon are used to create an inert environment. They do not react with the material being heated, effectively shielding it from oxidation and contamination.
- Reactive Atmospheres: Gases like hydrogen, oxygen, or carbon-based gases are sometimes introduced intentionally. This is done to cause a specific, desirable chemical reaction, such as reducing surface oxides or carburizing steel to harden it.
Key Applications Across Industries
By precisely managing the thermal and chemical environment, atmosphere furnaces enable a wide range of critical industrial and research processes.
Heat Treatment of Metals
This is one of the most common uses. Processes like annealing (softening), hardening, and tempering are performed in a controlled atmosphere to achieve the desired mechanical properties without forming destructive oxide layers.
Sintering of Powders
Sintering is the process of heating compacted powders (metal or ceramic) to fuse them into a solid, dense object without melting them. A controlled atmosphere is essential to prevent oxidation of the fine particles and ensure strong bonding between them.
Advanced Material Synthesis and Coating
Processes like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) use the furnace's atmosphere as a key ingredient. Precursor gases are introduced into the hot chamber, where they react and deposit a thin, solid film onto a substrate. This is fundamental to manufacturing semiconductors and durable coatings.
Research and Development
In laboratories, atmosphere furnaces are indispensable. They allow researchers to test how materials behave under specific temperature and atmospheric conditions, accelerating the development of new alloys, composites, and ceramics.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, an atmosphere furnace is not the only solution for controlled heating. The primary alternative is a vacuum furnace.
When to Choose an Atmosphere Furnace
An atmosphere furnace is often the more cost-effective choice when absolute purity is not the primary concern. It is also the necessary choice when a reactive gas is required as part of the process, which is impossible in a vacuum.
When a Vacuum Furnace Is Superior
A vacuum furnace provides the highest level of purity by removing virtually all gases from the chamber. It is the preferred tool for processing highly reactive metals like titanium or for applications in aerospace and medical implants where even trace contamination is unacceptable.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right thermal process depends entirely on the material and the desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is improving metal properties: You will use an atmosphere furnace for heat treatments like annealing to prevent oxidation and achieve precise hardness.
- If your primary focus is creating dense ceramic or metal parts: You will use it for sintering to bond powders in an inert gas, ensuring part strength and integrity.
- If your primary focus is depositing a functional coating: You will use a process like CVD where the reactive atmosphere itself builds the new material layer.
Ultimately, an atmosphere furnace gives you precise control over material chemistry, transforming a simple heating process into a predictable and repeatable manufacturing tool.
Summary Table:
| Application | Purpose | Common Atmospheres |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Treatment | Improve metal properties (e.g., annealing, hardening) | Nitrogen, Argon |
| Sintering | Fuse powders into solid parts without melting | Inert gases (e.g., Nitrogen) |
| Material Synthesis | Deposit coatings via processes like CVD | Reactive gases (e.g., Hydrogen) |
| R&D | Test material behavior under specific conditions | Custom gas mixtures |
Unlock the full potential of your material processes with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with reliable atmosphere furnaces, tube furnaces, and CVD/PECVD systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs, from heat treatment to advanced coatings. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is nitrogen used for in a furnace? Prevent Oxidation and Control Heat Treatment Quality
- What is the use of nitrogen in furnace? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Heat Treatment
- How does a chemically inert atmosphere function in a furnace? Prevent Oxidation and Ensure Material Purity
- What does inert mean in furnace atmospheres? Protect materials from oxidation with inert gases.
- How does the inert atmosphere heat treating process work? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Material Quality



















