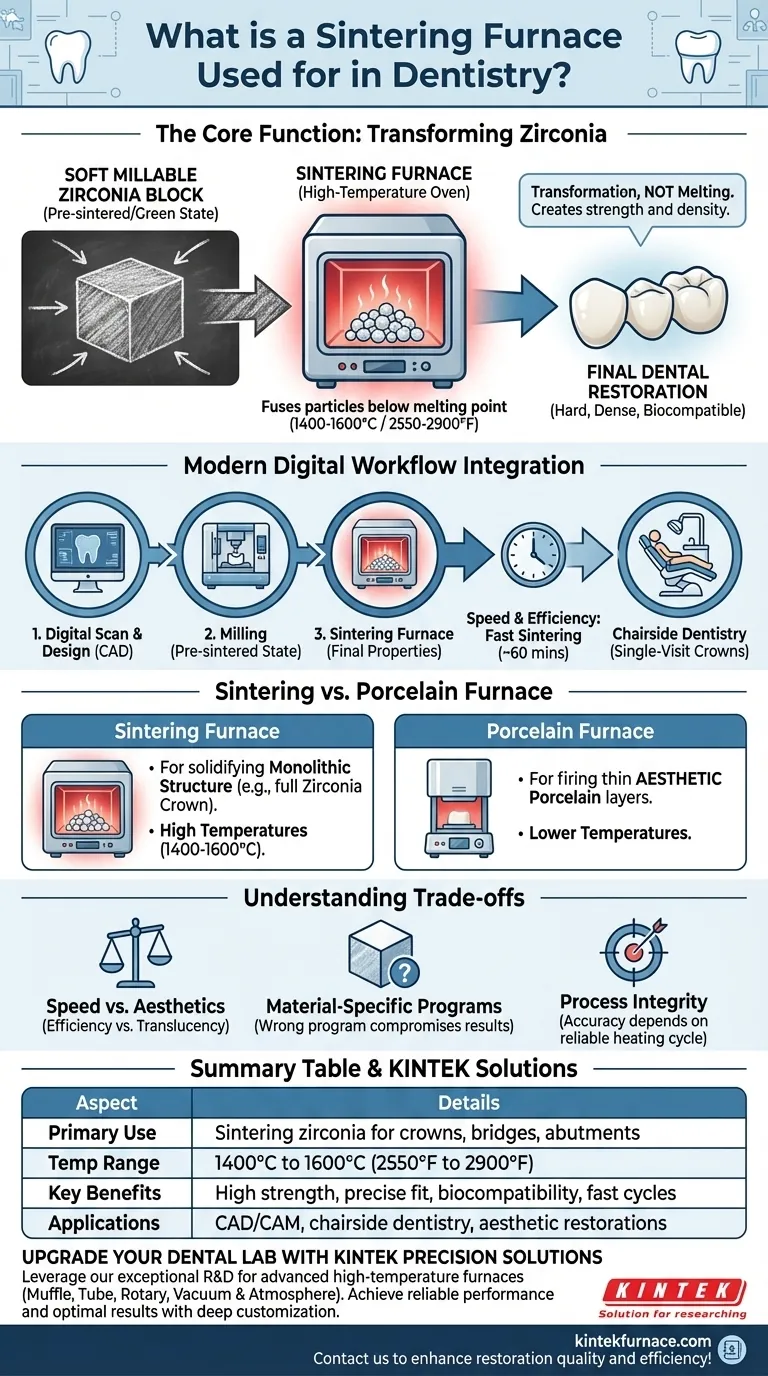
In dentistry, a sintering furnace is a specialized high-temperature oven used to transform soft, milled ceramic blocks into incredibly hard and dense final dental restorations. Its primary function is to process materials like zirconia, which is used to make crowns, bridges, and implant abutments. The furnace heats the material in a highly controlled manner, causing the ceramic particles to fuse together and solidify, giving the restoration its final strength and aesthetic properties.
The core purpose of a sintering furnace is not to melt material, but to transform it. It takes a pre-shaped but fragile ceramic part and, through precise heating, converts it into a final, biocompatible prosthetic with the necessary strength and density for clinical use in a patient's mouth.
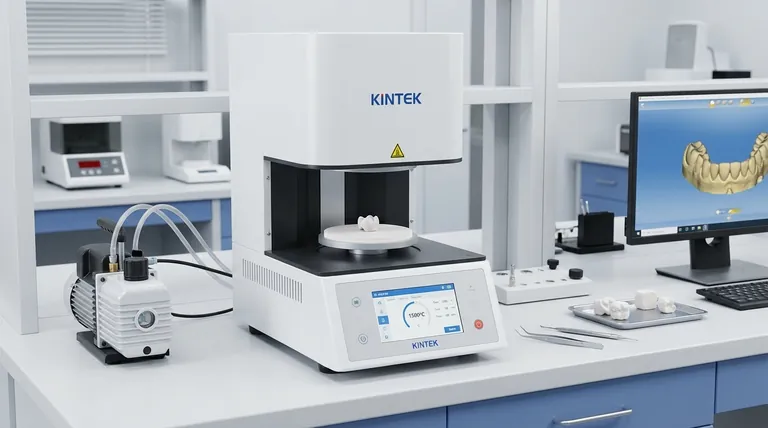

The Core Function: Transforming Zirconia
A sintering furnace is the critical link between a digitally designed restoration and a functional, final product. The process it performs is fundamental to the success of modern ceramic dentistry.
What is Sintering?
Sintering is a thermal process that uses high heat to fuse particles together into a solid, dense mass. Critically, the material reaches a temperature just below its melting point.
This process causes the restoration to shrink and densify significantly, which is what gives it its immense strength.
The Role of High-Strength Ceramics
The most common material used in these furnaces is zirconia. Dental labs and chairside milling units shape zirconia in a soft, "pre-sintered" or "green" state.
This chalk-like consistency makes it easy to mill precisely. However, in this state, it is far too weak for clinical use. The sintering process is what makes it one of the strongest materials in dentistry.
The Sintering Cycle
A sintering furnace executes a precise heating program, raising the temperature to between 1,400°C and 1,600°C (2,550°F to 2,900°F).
This cycle is carefully controlled, with specific ramp rates (how fast the temperature rises) and hold times. This precision ensures the zirconia achieves optimal density and strength without warping or cracking.
How Sintering Fits into the Modern Digital Workflow
The sintering furnace is a key component in the CAD/CAM (Computer-Aided Design/Computer-Aided Manufacturing) workflow that defines modern dentistry.
From Digital Scan to Final Crown
The typical process involves scanning a patient's mouth, designing the restoration on a computer, and then milling it from a zirconia block.
The final, essential step is placing this milled restoration into the sintering furnace to give it its final properties. The design software automatically accounts for the predictable shrinkage that will occur during this stage.
The Drive for Speed and Efficiency
Modern furnaces now offer "fast sintering" cycles, which can reduce the process from many hours to around 60 minutes.
This advancement is crucial for chairside dentistry, enabling a dentist to scan, design, mill, and deliver a permanent zirconia crown in a single patient visit.
Sintering Furnace vs. Porcelain Furnace
It's important to distinguish between these two pieces of equipment.
A sintering furnace is for solidifying a monolithic structure, like a full zirconia crown. A porcelain furnace operates at lower temperatures and is used to fire thin layers of aesthetic porcelain onto a substructure (which could be metal or already-sintered zirconia).
Understanding the Trade-offs
While essential, the sintering process involves considerations that impact the final outcome. Understanding these trade-offs is key to achieving consistent, high-quality results.
Speed vs. Aesthetics
Fast sintering cycles are incredibly efficient but may result in slightly lower translucency for certain zirconia materials compared to traditional, slower cycles. Technicians often choose a cycle based on the balance between speed and the desired aesthetic outcome.
Material-Specific Programs
Not all zirconia is the same. Different brands and types (e.g., high-strength vs. high-translucency) require specific sintering programs recommended by the manufacturer. Using the wrong program can compromise the restoration's strength, fit, or color.
Process Integrity
The accuracy of the final restoration depends on the entire digital workflow. The furnace must perform its heating cycle reliably and accurately to ensure the shrinkage is exactly as predicted by the design software. Any deviation can lead to a poor fit.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The application of a sintering furnace depends entirely on the clinical or laboratory objective.
- If your primary focus is same-day chairside crowns: A furnace with a validated, rapid sintering cycle is non-negotiable for achieving single-visit efficiency.
- If your primary focus is fabricating multi-unit bridges: A standard, slower sintering cycle is often preferred to ensure maximum strength and minimize any risk of warpage across a longer span.
- If your primary focus is creating highly aesthetic layered restorations: You will need a sintering furnace for the zirconia core and a separate porcelain furnace for applying the aesthetic ceramic layers.
Ultimately, the sintering furnace is the enabling technology that unlocks the full potential of modern dental ceramics.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Primary Use | Sintering zirconia for crowns, bridges, and implant abutments |
| Temperature Range | 1,400°C to 1,600°C (2,550°F to 2,900°F) |
| Key Benefits | High strength, precise fit, biocompatibility, and support for fast cycles |
| Common Applications | CAD/CAM workflows, chairside dentistry, and aesthetic restorations |
Upgrade Your Dental Lab with Precision Sintering Solutions from KINTEK
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides dental laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental and production needs. Whether you're focused on fast chairside cycles or complex multi-unit bridges, our furnaces ensure reliable performance and optimal results.
Contact us today to discuss how our sintering furnaces can enhance your dental restoration quality and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Vacuum Press Furnace
- Chairside Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Furnace with Transformer for Ceramic Restorations
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Why is proper ventilation important in dental sintering furnaces? Ensure Quality and Safety in Your Lab
- What factors determine the quality of sintered zirconia restorations? Master Material, Equipment, and Technique
- What are some common mistakes when operating dental sintering furnaces? Avoid Costly Errors for Perfect Zirconia Restorations
- What factors should be considered when choosing a dental sintering furnace? Ensure Quality and Efficiency for Your Lab
- Why is precise temperature control important in dental sintering furnaces? Ensure Strong, Aesthetic Dental Restorations



















