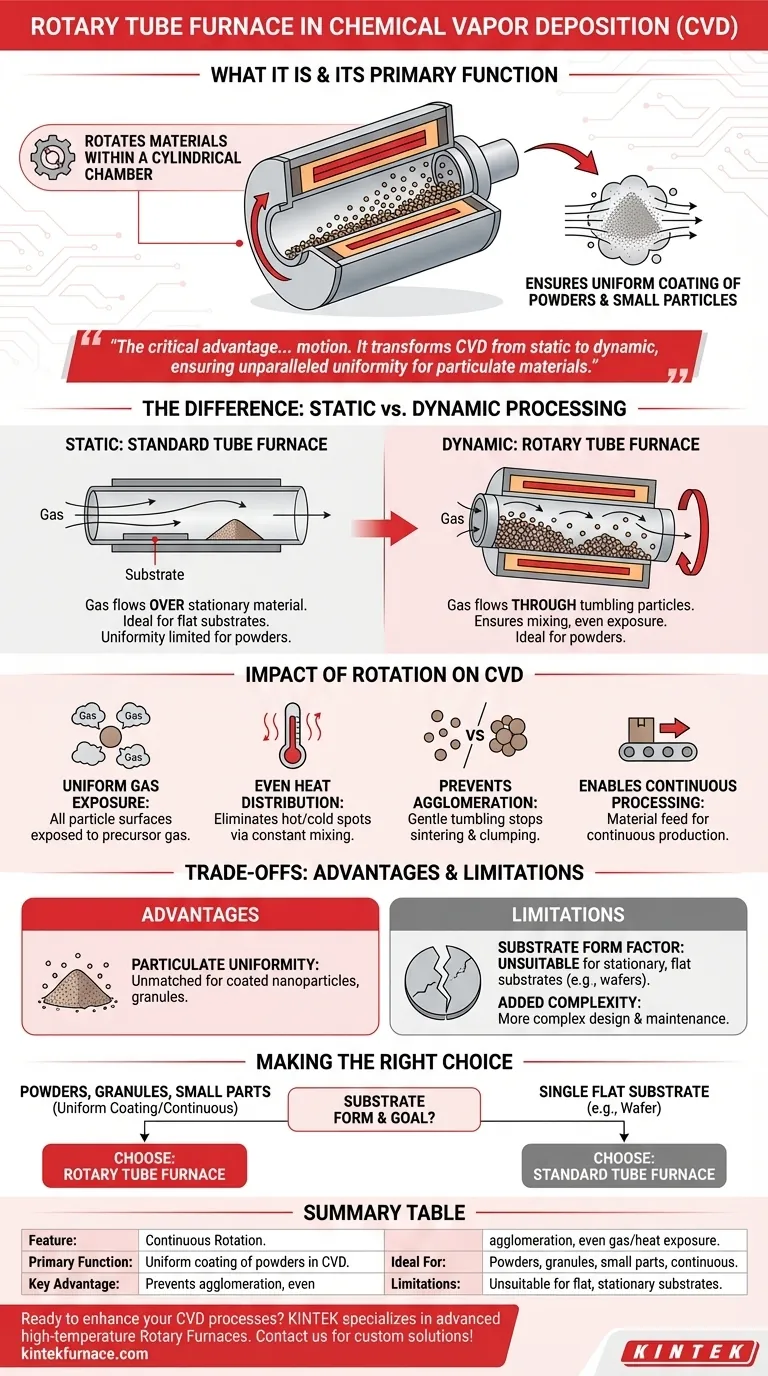
In essence, a rotary tube furnace is a specialized piece of laboratory equipment that heats materials within a rotating cylindrical chamber. Its primary function in Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is to ensure powders or small particles are coated uniformly by continuously tumbling the material, which guarantees every surface is evenly exposed to the reactive gases and high temperatures required for deposition.
The critical advantage of a rotary tube furnace is not just heat, but motion. By rotating the sample, it transforms the CVD process from a static, surface-level event into a dynamic, three-dimensional one, ensuring unparalleled uniformity for particulate materials.

How Rotation Transforms the Deposition Process
A standard tube furnace is a powerful tool for thermal processing. However, its static nature presents limitations that a rotary furnace is specifically designed to overcome.
The Standard Tube Furnace: A Static Environment
A conventional tube furnace is a pipe-shaped chamber surrounded by heating elements. It excels at providing precise, uniform heat to a stationary sample within a controlled atmosphere.
This setup is ideal for processes like growing a thin film on a flat, stationary substrate, such as a silicon wafer.
Introducing Rotation: The Key Differentiator
A rotary tube furnace adds a crucial mechanical element: the entire tube chamber rotates during operation. This continuously tumbles the material inside, like a small, high-tech kiln.
This simple addition of motion fundamentally changes how the material interacts with its environment. Instead of gases flowing over a static pile of powder, the gases flow through a constantly moving and mixing bed of particles.
The Impact on Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
In CVD, precursor gases react at high temperatures to deposit a solid thin film onto a substrate. The rotation directly enhances this process in several key ways.
- Uniform Gas Exposure: Rotation ensures that all surfaces of every particle are repeatedly exposed to the fresh precursor gas, preventing the outer layers of a powder from shielding the inner layers.
- Even Heat Distribution: It eliminates hot or cold spots within the material batch by constantly mixing it, leading to more consistent chemical reactions.
- Prevents Agglomeration: For fine powders, the gentle tumbling action prevents particles from sintering or clumping together, which is a common problem in static high-temperature processes.
- Enables Continuous Processing: The design allows for material to be fed into one end of the tilted, rotating tube and exit the other, enabling a continuous production line rather than a one-at-a-time batch process.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a rotary furnace is a specialized tool. Its strengths for certain applications are its weaknesses for others.
Key Advantage: Particulate Uniformity
The primary benefit is achieving exceptionally uniform coatings or thermal treatments on powders, granules, and other small, loose materials. For synthesizing coated nanoparticles or functionalizing powders, its performance is unmatched by static systems.
Key Limitation: Substrate Form Factor
A rotary tube furnace is entirely unsuitable for applications requiring a stationary, flat substrate. You cannot use it to deposit a uniform film on a wafer, a glass slide, or any single large object, as the tumbling motion would be destructive and counterproductive.
Added Complexity
The mechanical rotation system, seals, and tilting mechanism add complexity to the furnace's design, operation, and maintenance compared to a simpler, static tube furnace.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct furnace depends entirely on the physical form of your substrate and your processing goals.
- If your primary focus is coating powders, granules, or small parts: A rotary tube furnace is the superior choice for achieving uniform deposition and preventing agglomeration.
- If your primary focus is depositing a film on a single, flat substrate (e.g., a wafer): A standard, static tube furnace is the correct and necessary tool.
- If your primary focus is creating a continuous production line for particulate material: A rotary furnace is specifically designed to enable this workflow, offering a major efficiency advantage over batch processing.
Ultimately, understanding the role of motion is key to choosing the right thermal processing tool for your specific material science objective.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Uniform coating of powders in CVD via continuous rotation |
| Key Advantage | Prevents agglomeration and ensures even exposure to gases and heat |
| Ideal For | Powders, granules, small parts, and continuous processing |
| Limitations | Unsuitable for flat, stationary substrates like wafers |
Ready to enhance your CVD processes with precise, uniform powder coatings? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Rotary Furnaces, designed for diverse laboratory needs. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our Rotary Tube Furnaces can optimize your material science applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
People Also Ask
- What types of materials are suitable for processing in rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Free-Flowing Powders and Granules
- What are the main structural components of a rotary furnace? Explore Key Parts for Efficient Material Processing
- How do rotary tube furnaces achieve precise temperature control? Master Uniform Heating for Dynamic Processes
- What materials can be used to make the rotating tube assembly of these furnaces? Choose the Best for Your High-Temp Needs
- What types of materials can be processed in a rotary tube furnace? Discover Ideal Materials for High-Temp Processing



















