At its core, a muffle furnace is a high-temperature oven that heats materials inside an insulated chamber, completely isolating them from the heating source and any contaminants. Its significance comes directly from this principle of isolation. By preventing contamination from fuel or combustion byproducts, it provides a chemically pure environment for precise material testing, analysis, and heat treatment.
A muffle furnace isn't just about achieving high temperatures; it's about achieving clean, controlled heat. Its primary value lies in creating a sterile thermal environment, ensuring that any changes to a material are a direct result of the heat itself, not from external chemical interference.
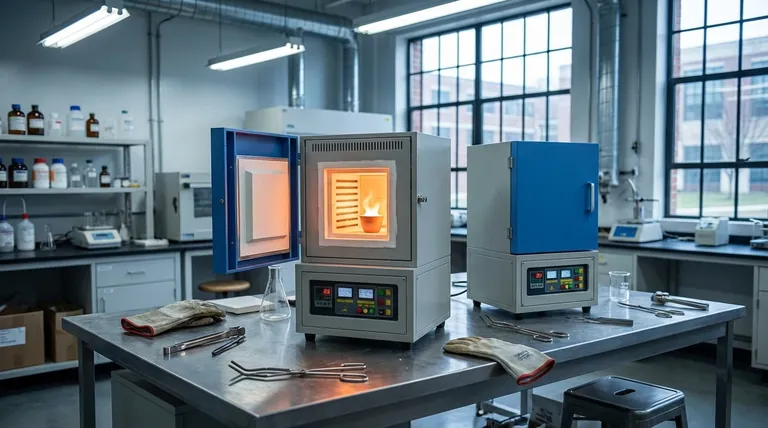

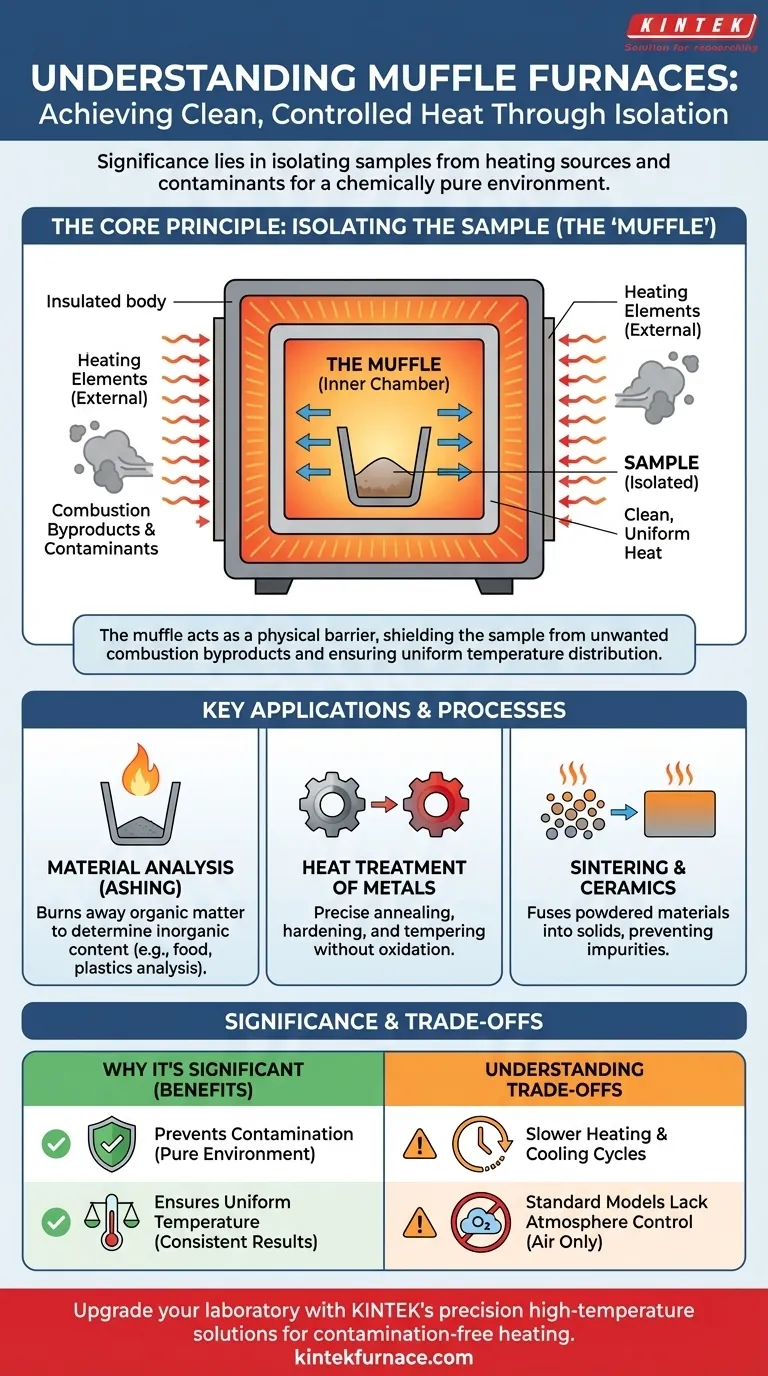
The Core Principle: Isolating the Sample
The defining feature of a muffle furnace is the "muffle" itself—an inner chamber that separates the material being processed from the actual heating elements and the external environment. This design is fundamental to its function and value.
What is the "Muffle"?
The muffle is a box-like enclosure, typically made from high-temperature ceramics or metallic alloys. It sits inside the furnace's main insulated body.
Heating elements wrap around the outside of the muffle, heating it through radiation and convection. The sample is then placed inside the muffle, ensuring it never comes into direct contact with the heating source.
Preventing Contamination
In many high-temperature processes, the byproducts of combustion—such as soot, carbon, or various gases—can react with the sample. This contamination can alter the material's chemical composition or physical properties, rendering test results inaccurate.
The muffle acts as a physical barrier, shielding the sample from these unwanted contaminants. This guarantees that the process, whether it's for analysis or treatment, occurs in a pure environment.
Ensuring Uniform Temperature
The insulated muffle chamber retains and distributes heat evenly. This temperature uniformity is critical for obtaining consistent, repeatable results.
Whether you are heat-treating a metal part or ashing a food sample, ensuring the entire sample experiences the same temperature is essential for accurate outcomes.
Key Applications and Processes
The ability to provide clean, uniform heat makes the muffle furnace indispensable across scientific and industrial fields for a range of thermal processes.
Material Analysis (Ashing)
Ashing is a process used to determine the inorganic, non-combustible content of a sample by burning away all organic matter. It is a common procedure in food science, environmental testing, and plastics analysis.
A muffle furnace is the ideal tool for ashing because it ensures a complete and clean burn-off without introducing contaminants that could be mistaken for part of the sample's ash residue.
Heat Treatment of Metals
Processes like annealing, hardening, and tempering are used to change the physical properties of metals, such as their hardness or ductility.
These processes require precise heating and cooling cycles. Using a muffle furnace prevents unwanted reactions like oxidation on the metal's surface, which could compromise its integrity.
Sintering and Ceramics Manufacturing
Sintering is the process of fusing powdered materials into a solid mass using heat, without melting them. This is fundamental to creating ceramics, certain metal components, and other advanced materials.
The clean, high-temperature environment of a muffle furnace is perfect for sintering, as it prevents impurities from being baked into the final product.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly useful, a muffle furnace is a specialized tool with specific characteristics that are not suitable for every application.
Atmosphere Control Requires Specialization
A standard muffle furnace heats a sample in the air present within the chamber. It isolates the sample from combustion byproducts, but not necessarily from oxygen.
Creating a specific, controlled atmosphere—such as an inert gas environment (using argon or nitrogen) or a vacuum—requires a more advanced and specialized type of furnace.
Slower Heating and Cooling Cycles
The heavy insulation required to reach very high temperatures and maintain uniformity means muffle furnaces typically heat up and cool down slowly.
For applications requiring rapid thermal cycling, other types of ovens or furnaces might be more appropriate.
Energy Consumption and Cost
Reaching and maintaining temperatures that can exceed 1000°C (1832°F) requires significant energy. These are robust, heavy-duty instruments, and their cost reflects their specialized construction and capabilities.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the core function of a muffle furnace helps clarify when it is the right tool for the job.
- If your primary focus is determining the inorganic content of a sample (ashing): A muffle furnace is the industry standard, providing a clean burn that guarantees accurate results.
- If your primary focus is altering the properties of metals or ceramics: A muffle furnace delivers the controlled, uniform, and non-contaminating heat necessary for reliable heat treatment and sintering.
- If your primary focus is simply removing moisture at low temperatures: A standard laboratory drying oven is a more efficient and cost-effective choice.
Ultimately, a muffle furnace is the definitive tool when the chemical purity of your high-temperature process is non-negotiable.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Core Principle | Isolates samples in a chamber from heating elements to prevent contamination and ensure pure thermal environment. |
| Key Applications | Ashing for material analysis, heat treatment of metals (e.g., annealing), sintering for ceramics and advanced materials. |
| Temperature Uniformity | Provides even heat distribution for consistent, repeatable results in high-temperature processes. |
| Contamination Prevention | Shields samples from combustion byproducts, ensuring accurate chemical and physical property changes. |
| Limitations | Standard models lack atmosphere control; slower heating/cooling cycles; higher energy consumption and cost. |
Upgrade your laboratory with precision high-temperature solutions from KINTEK! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide advanced furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we meet your unique experimental needs for contamination-free heating and reliable results. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored furnace solutions can enhance your material testing and processing efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production



















