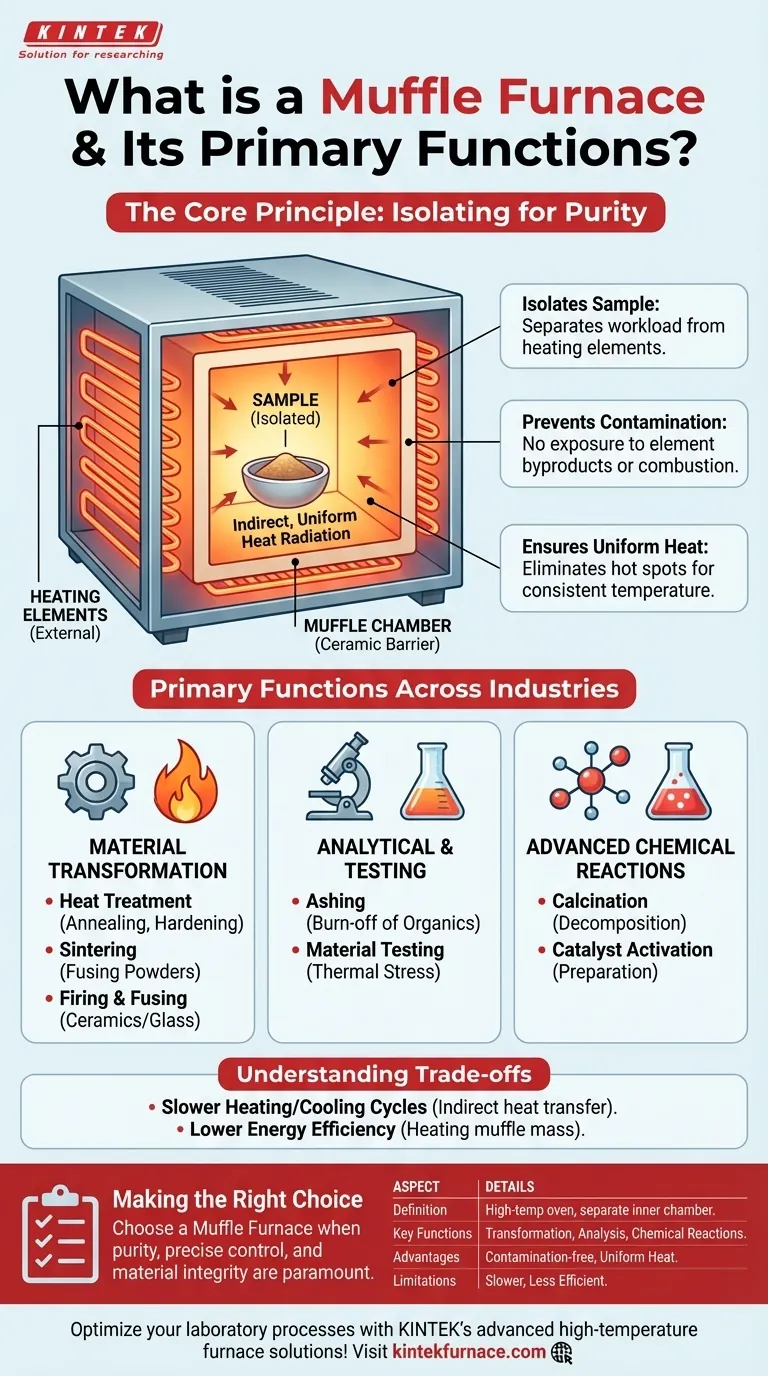
In essence, a muffle furnace is a high-temperature oven that provides an extremely pure, controlled heating environment. Its defining feature is a separate inner chamber—the "muffle"—that isolates the material being heated from direct contact with the heating elements and any potential contaminants from combustion. This design makes it indispensable for sensitive laboratory and industrial processes where material integrity is paramount.
The core value of a muffle furnace is not just its ability to generate high heat; it is its capacity to deliver heating without contamination. By shielding the sample within a closed chamber, it ensures that the process is defined purely by temperature, free from external impurities that could alter the outcome.
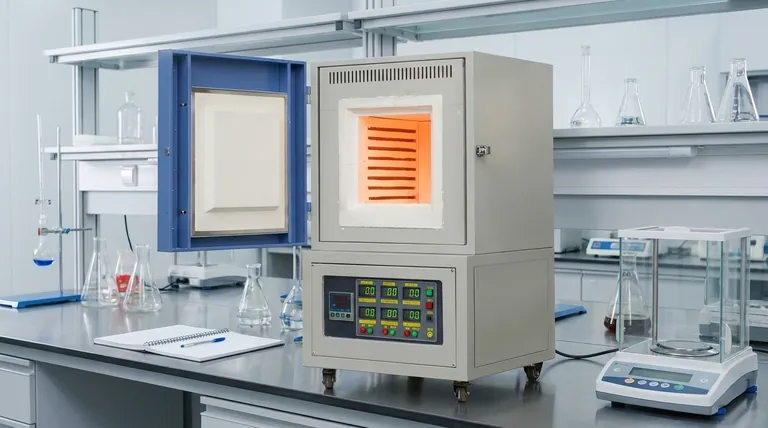

The Core Principle: Why a 'Muffle' Matters
The key to understanding a muffle furnace is understanding the function of the muffle itself. This isn't just a simple oven; it's a system designed for process purity.
Isolating the Sample
The "muffle" is an inner chamber, typically made of a high-temperature refractory ceramic. It acts as a complete barrier, separating the workload from the heat source.
Heating elements are positioned on the outside of this muffle chamber. They heat the muffle, which in turn radiates heat evenly into the interior, warming the sample through indirect radiation and convection.
Preventing Contamination
In many heating processes, direct exposure to heating elements or fuel combustion can introduce impurities. For example, particles from degrading electric elements or byproducts from gas flames can settle on or react with the sample.
A muffle furnace completely eliminates this risk. The sample is only exposed to the atmosphere sealed within the chamber, which can be ambient air or a specific controlled gas.
Ensuring Uniform Heat
By heating the entire muffle chamber, the furnace creates a highly uniform temperature zone inside. This indirect heating method prevents "hot spots" that can occur from direct exposure to heating elements, ensuring the entire sample is processed at the same temperature.
Primary Functions Across Industries
The unique capabilities of a muffle furnace make it essential for a wide range of applications where precision and purity are non-negotiable. Its functions can be grouped into a few key categories.
Material Transformation and Synthesis
This is a primary use case, involving changing a material's physical properties or structure.
- Heat Treatment: Annealing, hardening, or stress-relieving metals to achieve specific mechanical properties. Purity is critical to prevent surface oxidation or embrittlement.
- Sintering: Fusing powdered materials (like ceramics or metals) into a solid mass using heat below the melting point.
- Firing and Fusing: Processing ceramics and fusing glass, where a clean finish and predictable chemical outcome are essential.
Analytical and Testing Processes
Muffle furnaces are a cornerstone of quality control and materials analysis laboratories.
- Ashing: This is one of the most common functions. A sample (like coal, polymers, or food) is heated to high temperatures to burn off all organic matter, leaving only the non-combustible ash. The isolated environment ensures that the final weight is accurate and uncontaminated.
- Material Testing: Determining how a material behaves under extreme thermal stress in a controlled environment.
Advanced Chemical Reactions
Chemists and material scientists rely on muffle furnaces for creating specific reaction conditions.
- Calcination: Decomposing a substance or driving off volatile components with heat.
- Catalyst Activation: Preparing chemical catalysts by heating them to a specific temperature in a controlled atmosphere.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the design of a muffle furnace presents certain operational considerations. Understanding these is key to knowing when it's the right tool.
Slower Heating Rates
Because the heat is transferred indirectly—from the elements to the muffle and then to the sample—heating and cooling cycles are typically slower than in a direct-fired furnace or oven.
Energy Efficiency
This two-step heating process can be less energy-efficient than direct heating methods. Some energy is lost in heating the mass of the muffle itself. However, modern furnaces mitigate this with advanced insulation.
Process Suitability
A muffle furnace is overkill for simple drying or warming applications where contamination is not a concern. For those tasks, a standard laboratory oven is a more practical and economical choice.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a furnace comes down to the requirements of your specific process. The need for purity is the deciding factor.
- If your primary focus is material analysis or ashing: A muffle furnace is the industry-standard tool required to achieve accurate and repeatable results.
- If your primary focus is heat-treating metals or firing ceramics: A muffle furnace is ideal when material purity, surface finish, and precise atmospheric control are critical to the final product's properties.
- If your primary focus is simply high-temperature heating without strict purity needs: A simpler, direct-heat laboratory oven or industrial furnace may be a more cost-effective and faster solution.
Ultimately, choosing a muffle furnace is a decision to prioritize process integrity and the chemical purity of your material above all else.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | High-temperature oven with a separate inner chamber (muffle) for pure, controlled heating. |
| Key Functions | Material transformation (e.g., annealing, sintering), analytical processes (e.g., ashing), and chemical reactions (e.g., calcination). |
| Industries | Laboratories, materials science, metallurgy, ceramics, and quality control. |
| Advantages | Contamination-free heating, uniform temperature distribution, precise control. |
| Limitations | Slower heating rates, lower energy efficiency compared to direct-heat methods. |
Optimize your laboratory processes with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with reliable equipment like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, enhancing efficiency and accuracy. Ready to elevate your research? Contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a muffle furnace contribute to kaolin-modified biochar? Optimize Pyrolysis & Mineral Integration
- How does a stainless steel reactor function within a muffle furnace for PET to graphene? Master Carbon Synthesis
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the conversion of S-1@TiO2? Achieve Precision Calcination of Nanospheres
- What role does a muffle furnace play in analyzing the combustion residues? Optimize Your Composite Char Analysis
- What is the primary role of a muffle furnace in the annealing process of AlCrTiVNbx alloys? Enhance Alloy Strength



















