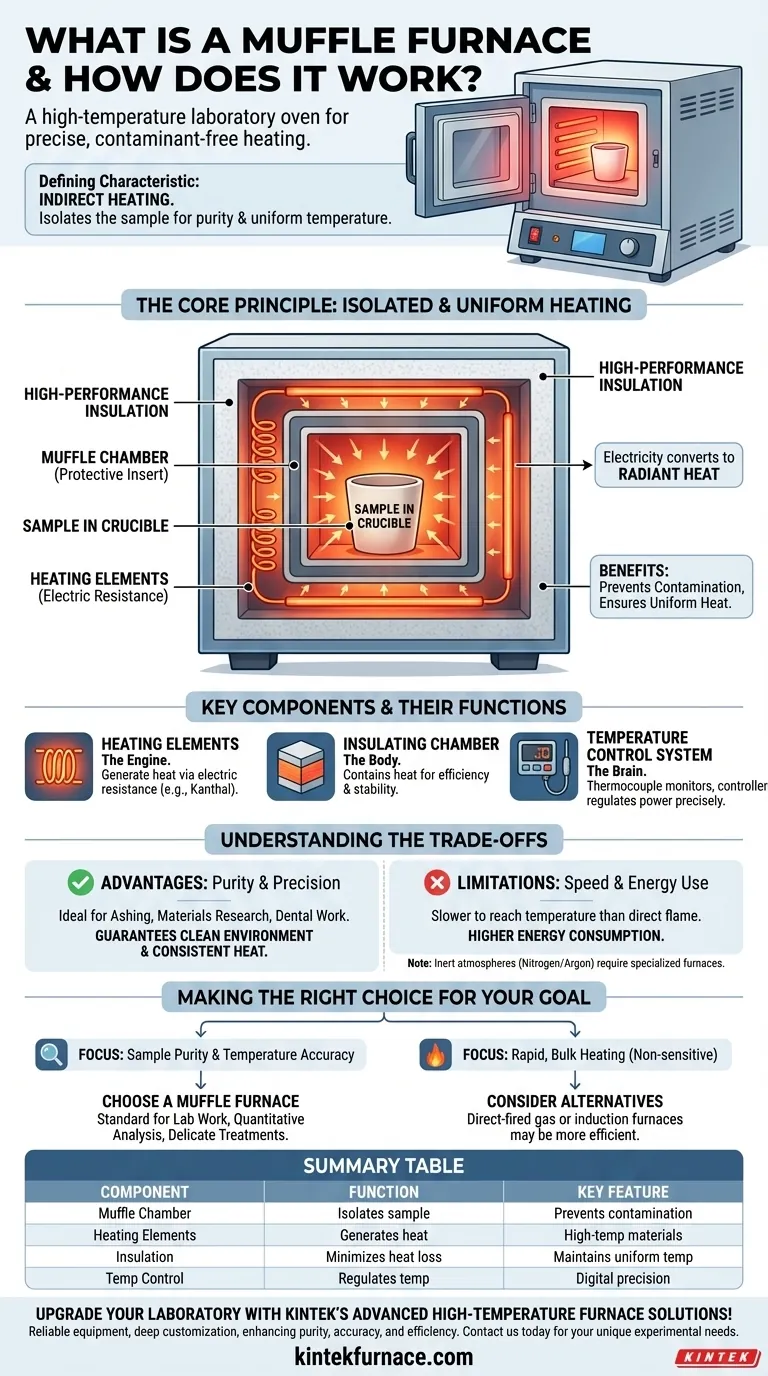
In essence, a muffle furnace is a high-temperature laboratory oven that heats materials within a self-contained chamber. It works by using electric resistance heating elements to heat the air inside an insulated box. Crucially, the material being heated is placed inside a protective insert or "muffle," which isolates it from direct contact with the heating elements, ensuring uniform heat and preventing contamination.
The defining characteristic of a muffle furnace is not just its ability to reach high temperatures, but its use of indirect heating. This design principle isolates the sample, guaranteeing a clean, controlled environment free from the byproducts of combustion or direct element contact, which is critical for precise scientific and industrial processes.
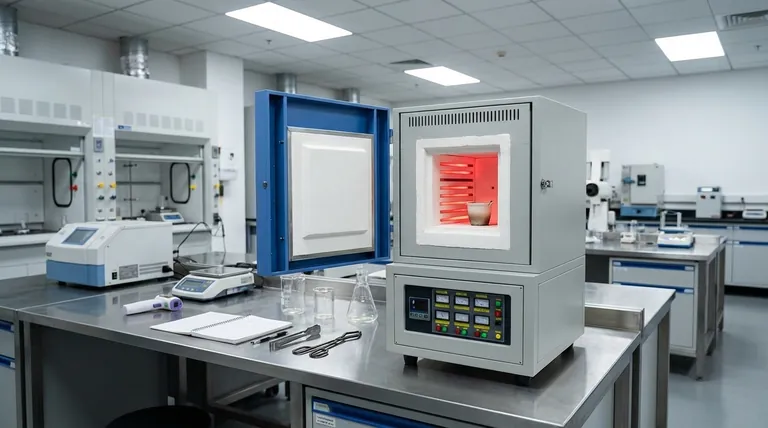

The Core Principle: Isolated and Uniform Heating
A muffle furnace's design is entirely centered on creating a pure and stable thermal environment. Unlike a simple oven or a direct-fired forge, its primary value comes from separating the heat source from the workload.
What is the "Muffle"?
The term "muffle" refers to the enclosed inner chamber, typically made of high-temperature ceramic or metallic alloys. This chamber acts as a crucial barrier.
It physically shields the sample from the raw heating elements. This prevents any particles from the elements from flaking off and contaminating the sample.
How Electric Resistance Creates Heat
Modern muffle furnaces almost exclusively use electricity. High-resistance wires or rods, often made of materials like Kanthal or nickel-chromium, are routed around the outside of the muffle chamber.
When a high electric current is passed through these elements, their resistance causes them to glow red-hot, converting electrical energy into radiant heat. This is the same principle used in a common toaster, but engineered for much higher temperatures.
Achieving a Uniform Thermal Environment
The heat generated by the elements radiates inward, heating the muffle chamber and the air inside it.
The entire assembly is encased in a thick layer of high-performance insulation, such as refractory bricks or ceramic fiber. This insulation minimizes heat loss and helps the internal temperature stabilize, ensuring the sample is heated evenly from all sides.
Key Components of a Modern Furnace
Understanding the main parts of a muffle furnace clarifies how it achieves its precision. Each component serves a distinct and vital function.
The Heating Elements
These are the engine of the furnace. Their composition determines the furnace's maximum temperature and lifespan. They are designed to withstand thousands of hours of extreme thermal cycling.
The Insulating Chamber
This is the main body of the furnace. Its purpose is to contain the heat, ensuring energy efficiency and temperature stability. The quality of the insulation dictates how quickly the furnace heats up and how much power it consumes to maintain temperature.
The Temperature Control System
This is the brain of the furnace. A thermocouple probe inside the chamber constantly measures the temperature and sends this data to a digital controller.
The controller then precisely modulates the power sent to the heating elements to maintain the set temperature with incredible accuracy, often within a few degrees Celsius.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While muffle furnaces are indispensable for many applications, their design comes with inherent advantages and limitations.
The Advantage: Purity and Precision
The single greatest benefit is the prevention of contamination. For applications like ashing (burning off organic material to measure inorganic content), materials research, or dental lab work, any foreign material can invalidate the results. The isolated design guarantees a pure process.
Furthermore, the controlled, static environment provides exceptionally uniform heating, which is critical for consistent heat treatment and material testing.
The Limitation: Heating Speed and Energy Use
Indirect heating is inherently less efficient at transferring energy than direct flame impingement. A muffle furnace can take a significant amount of time to reach its target temperature.
These furnaces also consume a substantial amount of electricity to generate and maintain high temperatures, making them more costly to operate than some fuel-fired alternatives.
A Note on Atmospheres
While the muffle isolates the sample, the default atmosphere inside is simply air. For processes that require an inert atmosphere (like nitrogen or argon) to prevent oxidation, specialized muffle furnaces with gas-tight seals and inlet ports are necessary.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right heating equipment depends entirely on the requirements of your process. The muffle furnace excels in scenarios where control and cleanliness are paramount.
- If your primary focus is sample purity and temperature accuracy: A muffle furnace is the standard for lab work, quantitative analysis, materials testing, and delicate heat treatments.
- If your primary focus is rapid, bulk heating of non-sensitive materials: A direct-fired gas furnace or an induction furnace may be a more time and cost-effective solution.
Ultimately, understanding the core principle of isolated heating empowers you to select the precise tool for your thermal processing needs.
Summary Table:
| Component | Function | Key Feature |
|---|---|---|
| Muffle Chamber | Isolates sample from heating elements | Prevents contamination, ensures purity |
| Heating Elements | Generates heat via electric resistance | High-temperature materials like Kanthal |
| Insulation | Minimizes heat loss | Maintains uniform temperature |
| Temperature Control | Regulates and monitors temperature | Digital precision within a few degrees Celsius |
Upgrade your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with reliable equipment like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs, enhancing purity, accuracy, and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your thermal processing goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency



















