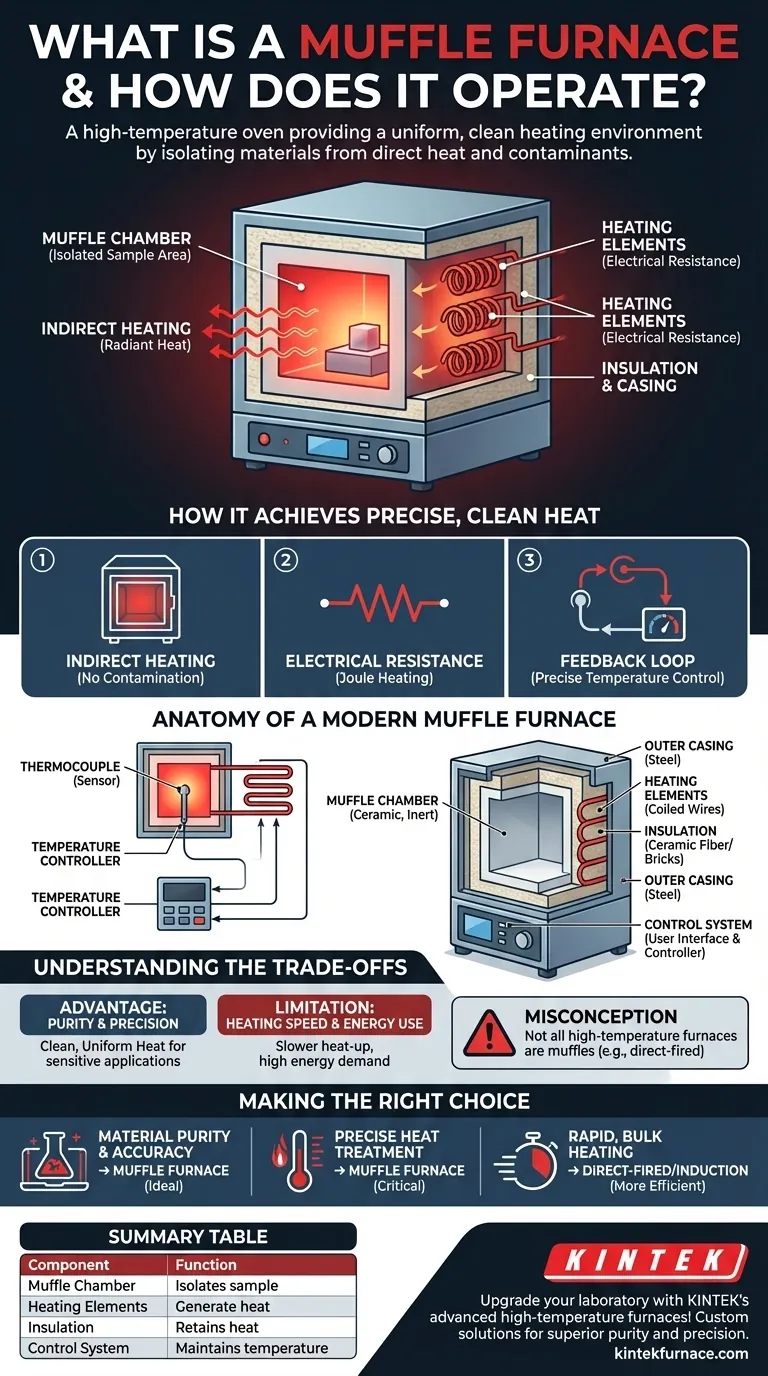
In essence, a muffle furnace is a high-temperature oven that isolates the material being heated from the direct heat source and any contaminants. Its primary function is to provide an extremely uniform, precisely controlled, and clean heating environment, which is critical for scientific and industrial processes where material purity is paramount.
The core principle differentiating a muffle furnace is indirect heating. By placing the sample in an isolated chamber (the "muffle") and heating it externally with electrical elements, it ensures the material is never exposed to combustion byproducts or the heating elements themselves.
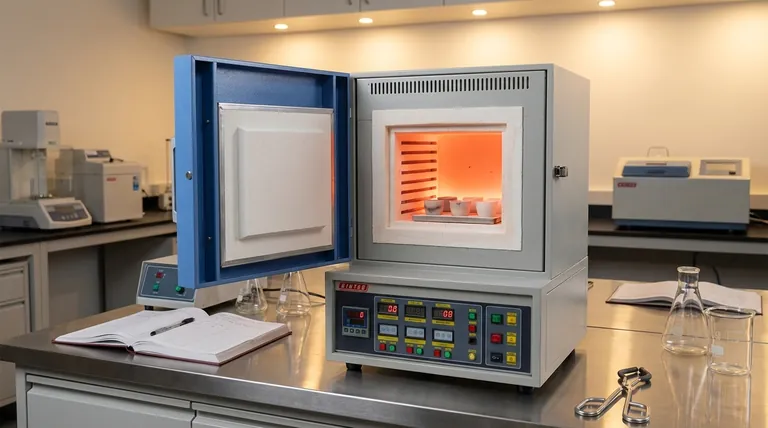

How a Muffle Furnace Achieves Precise, Clean Heat
A muffle furnace is not just about getting things hot; it's about achieving that heat with control and purity. This is accomplished through a combination of three key operational principles.
The Principle of Indirect Heating
The defining feature is the muffle chamber. This is a sealed, high-temperature box, typically made of ceramic, that contains the sample.
The heating elements are located outside this chamber. This physical separation is what prevents any contamination of the sample from fuel, combustion gases, or particles flaking off the heating elements.
The Role of Electrical Resistance
Modern muffle furnaces generate heat by passing a high electrical current through specialized heating elements.
These elements are made of a high-resistance material, such as Kanthal or nickel-chromium alloy. As electricity struggles to pass through this resistance, the electrical energy is converted directly into heat, following the principle of Joule heating.
This heat then radiates through the furnace walls and into the muffle chamber, warming the sample uniformly from all sides.
The Feedback Loop for Temperature Control
Achieving a specific temperature is useless without the ability to hold it there. This is managed by a closed-loop control system.
A sensor, called a thermocouple, is placed inside the chamber to constantly measure the actual temperature.
This temperature reading is sent to a digital temperature controller, which compares it to the desired setpoint. The controller then switches the power to the heating elements on or off to maintain the target temperature with remarkable precision.
Anatomy of a Modern Muffle Furnace
While designs vary, the core components that enable its function are consistent across nearly all laboratory and industrial models.
The Muffle Chamber
This is the furnace's workspace. It must withstand extreme thermal stress and be chemically inert to avoid reacting with the samples being processed.
Heating Elements
These are the engine of the furnace. They are typically coiled wires or rods embedded within the insulating walls surrounding the muffle chamber to maximize heat transfer.
Insulation and Casing
To reach and maintain temperatures that can exceed 1200°C (2192°F), a muffle furnace requires extensive insulation. Layers of refractory ceramic fiber and bricks prevent heat from escaping, ensuring energy efficiency and keeping the outer steel casing cool and safe to the touch.
The Control System
This is the furnace's brain. It consists of the user interface for setting temperature and time, the internal controller that executes the heating program, and the thermocouple that provides real-time feedback.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No technology is perfect for every application. Understanding the advantages and limitations of a muffle furnace is key to using it effectively.
Advantage: Purity and Precision
The absolute separation of the sample from the heat source is the muffle furnace's greatest strength. This makes it indispensable for applications like ashing food samples, heat-treating sensitive alloys, or growing crystals where any contamination would invalidate the results.
Limitation: Heating Speed and Energy Use
Because the heat must radiate through the chamber walls, a muffle furnace can take longer to reach its target temperature compared to a direct-fired furnace. Maintaining these high temperatures also requires a significant and continuous supply of electrical energy.
Misconception: Not All High-Temperature Furnaces Are Muffles
The term "furnace" is broad. Some industrial furnaces operate by burning fuel directly within the heating chamber. While effective for smelting or forging, these are not muffle furnaces, as the material is directly exposed to combustion gases and lacks the pristine environment a true muffle provides.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct heating equipment depends entirely on your process requirements.
- If your primary focus is material purity and analytical accuracy: A muffle furnace is the ideal choice due to its clean, indirect heating environment.
- If your primary focus is precise heat treatment of sensitive components: The uniform heating and tight temperature control of a muffle furnace are critical for achieving desired material properties.
- If your primary focus is rapid, bulk heating where contamination is not a concern: A direct-fired or induction furnace may be a more time and energy-efficient solution.
Ultimately, a muffle furnace is the definitive tool for any high-temperature process that demands control and absolute cleanliness.
Summary Table:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Muffle Chamber | Isolates sample from heat source for purity |
| Heating Elements | Generate heat via electrical resistance |
| Insulation | Retains heat and ensures energy efficiency |
| Control System | Maintains precise temperature with feedback |
Upgrade your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnaces! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capability ensures solutions tailored to your unique experimental needs for superior purity and precision. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can enhance your processes and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production



















