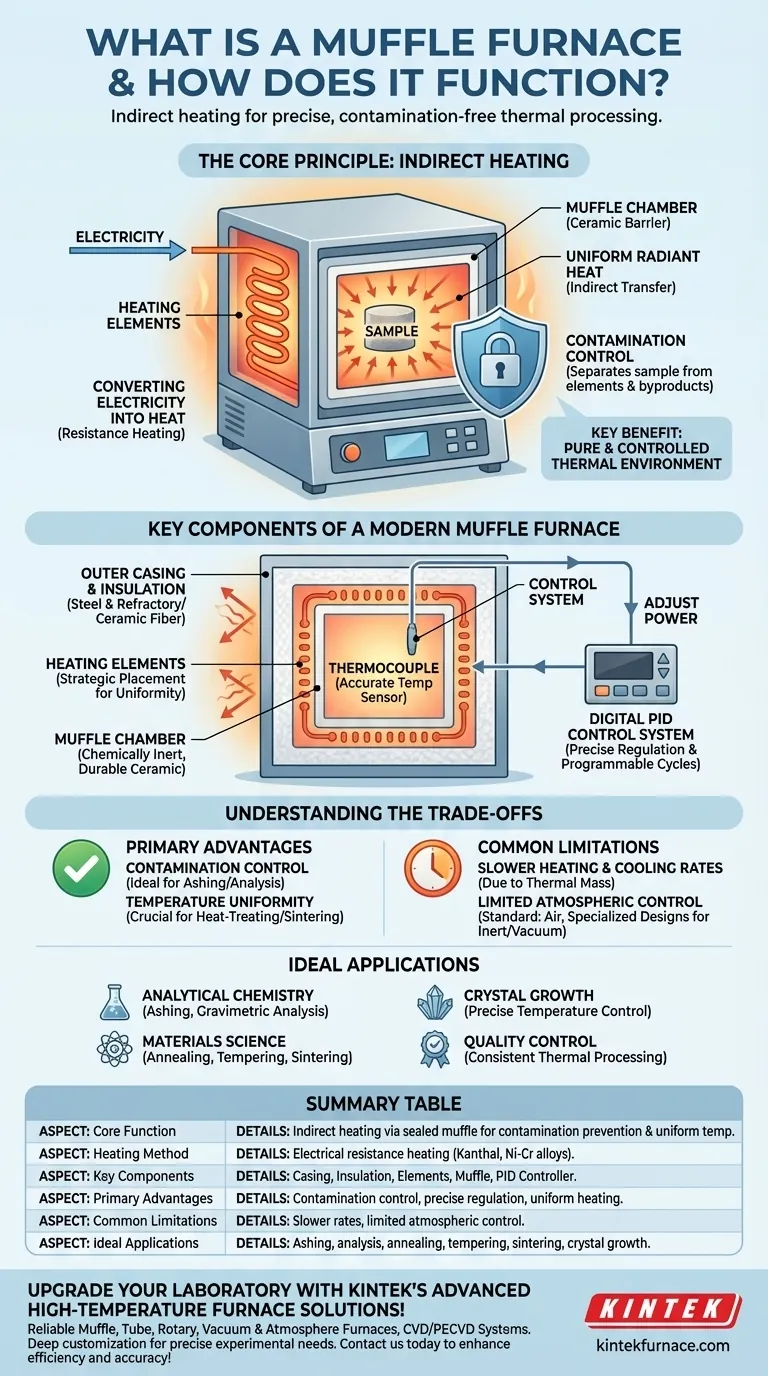
At its core, a muffle furnace is a high-temperature oven that heats materials within a specialized, isolated chamber. Its defining feature is the "muffle"—an enclosure that separates the sample from the heating elements and any potential contaminants like combustion byproducts. This design ensures a pure and precisely controlled thermal environment, which is critical for applications where sample integrity is paramount.
A muffle furnace operates on the principle of indirect heating. By placing the heat source outside the sample chamber, it guarantees that the material is heated uniformly without being contaminated by fuel byproducts or direct contact with the elements, making it essential for sensitive scientific and industrial processes.
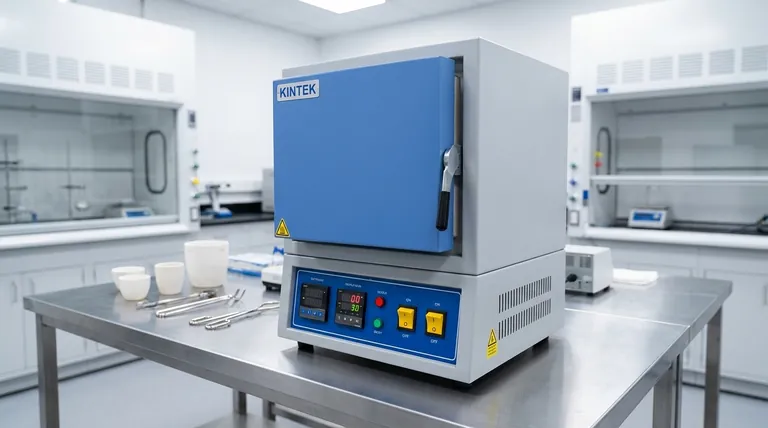

The Core Principle: How Indirect Heating Works
The function of a muffle furnace is defined by its ability to heat a sample cleanly and evenly. This is achieved through a multi-step process rooted in electrical resistance and thermal radiation.
Converting Electricity into Heat
Modern muffle furnaces almost exclusively use electrical resistance heating. An electric current is passed through specialized heating elements made of high-resistance materials, such as Kanthal (an iron-chromium-aluminum alloy) or nickel-chromium.
As the current encounters resistance, electrical energy is converted directly into heat. This is the same principle that makes an electric stovetop or a toaster work.
The Role of the "Muffle"
The heating elements are positioned around the outside of a separate, sealed chamber—the muffle. This chamber, typically made of a high-temperature ceramic, is the heart of the furnace.
The muffle's sole purpose is to act as a barrier. It shields the sample inside from direct contact with the intensely hot heating elements and protects the elements from any fumes or off-gassing that the sample might produce.
Ensuring Uniform Temperature
The heat generated by the elements radiates inward, heating the exterior of the muffle chamber. The chamber's material absorbs this energy and then radiates it uniformly throughout its interior.
This indirect heat transfer ensures that the sample is heated evenly from all sides, eliminating hot spots that could occur with direct heating. The heavy insulation surrounding the entire assembly minimizes heat loss and further contributes to thermal stability.
Precise Temperature Regulation
A sensor, typically a thermocouple, is placed inside or near the heating chamber to measure the temperature accurately. This sensor feeds real-time data to a digital control system.
The controller compares the actual temperature to the desired setpoint and precisely adjusts the power supplied to the heating elements, maintaining the target temperature with remarkable accuracy.
Key Components of a Modern Muffle Furnace
While designs vary, nearly all electric muffle furnaces share a common set of components that work in unison.
The Outer Casing and Insulation
The exterior body is typically made of steel. Inside this casing are layers of high-performance insulation, such as refractory bricks or ceramic fiber, designed to withstand extreme temperatures and prevent heat from escaping.
The Heating Elements
These are the workhorses of the furnace. They are strategically placed around the muffle to provide the most uniform heat coverage possible. Their material composition is chosen for longevity and stability at very high temperatures.
The Muffle Chamber
As previously described, this is the isolated ceramic box where the sample is placed. It is designed to be chemically inert and durable enough to handle rapid temperature changes.
The Control System
This is the brain of the furnace. Modern controllers are typically digital PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) units that allow users to program complex heating cycles, including ramp rates and dwell times, for highly repeatable results.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single piece of equipment is perfect for every task. Choosing a muffle furnace involves recognizing its distinct advantages and limitations.
Primary Advantage: Contamination Control
The separation between the heat source and the sample is the single most important benefit. This makes muffle furnaces indispensable for processes like ashing materials for chemical analysis, where even trace contamination would invalidate the results.
Advantage: Temperature Uniformity
The indirect heating method produces an exceptionally stable and uniform thermal environment. This is crucial for heat-treating metals, sintering ceramics, or growing crystals, where precise temperature control dictates the final material properties.
Limitation: Heating and Cooling Rates
The thermal mass of the ceramic muffle and the heavy insulation means these furnaces generally heat up and cool down more slowly than direct-heating alternatives like induction furnaces. For applications requiring rapid thermal cycling, this can be a drawback.
Limitation: Atmospheric Control
A standard muffle furnace operates in an air atmosphere. While some models can be modified for use with inert gases, creating a true vacuum or a highly controlled reactive atmosphere often requires more specialized and expensive furnace designs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To determine if a muffle furnace is the correct tool, consider your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is analytical chemistry (e.g., ashing or gravimetric analysis): A muffle furnace is essential to prevent sample contamination and ensure accurate, repeatable results.
- If your primary focus is materials science (e.g., annealing, tempering, or sintering): Its uniform and precisely controlled heating environment is ideal for achieving specific material properties consistently.
- If your primary focus is extremely rapid heating or high-volume industrial production: You may need to evaluate alternatives like induction or direct-fired furnaces that prioritize speed over absolute purity.
Ultimately, understanding the principle of indirect heating is the key to leveraging a muffle furnace for precise, clean, and reliable thermal processing.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Core Function | Indirect heating via a sealed muffle chamber to prevent contamination and ensure uniform temperature. |
| Heating Method | Electrical resistance heating using elements like Kanthal or nickel-chromium alloys. |
| Key Components | Outer casing, insulation, heating elements, muffle chamber, and digital PID control system. |
| Primary Advantages | Contamination control, precise temperature regulation, and uniform heating for sensitive processes. |
| Common Limitations | Slower heating/cooling rates and limited atmospheric control compared to direct-heating alternatives. |
| Ideal Applications | Ashing, gravimetric analysis, annealing, tempering, sintering, and crystal growth in labs and materials science. |
Upgrade your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with reliable equipment like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, delivering contamination-free, uniform heating for superior results. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can enhance your thermal processing efficiency and accuracy!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating



















