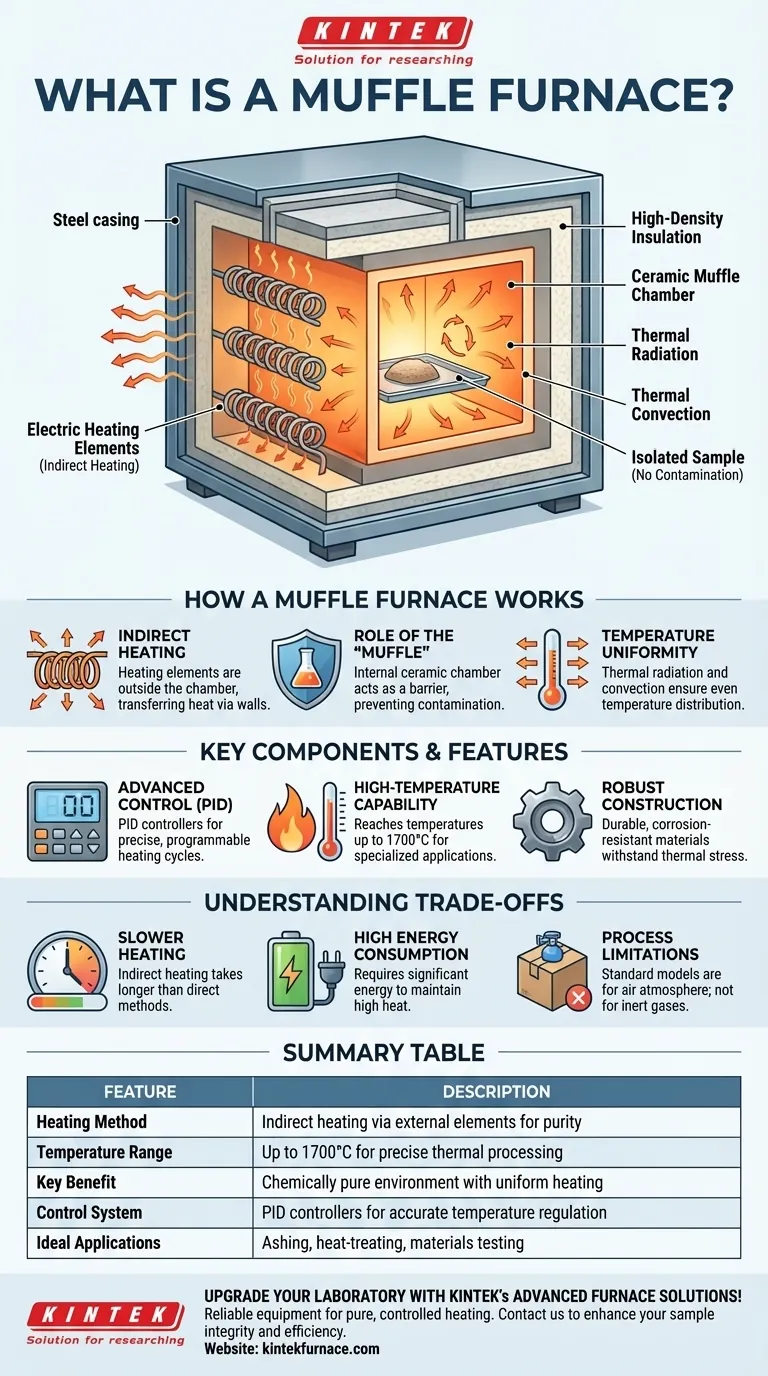
At its core, a muffle furnace is a high-temperature oven that heats materials inside an insulated chamber while completely isolating them from the heating elements and any external contaminants. This design ensures that processes like ashing, heat-treating, or materials testing are performed with exceptional temperature uniformity and without the risk of the sample reacting with fuel or combustion byproducts.
The critical function of a muffle furnace is not just to generate high heat, but to provide a chemically pure and precisely controlled thermal environment. This makes it an indispensable tool for scientific and industrial applications where sample integrity is the highest priority.
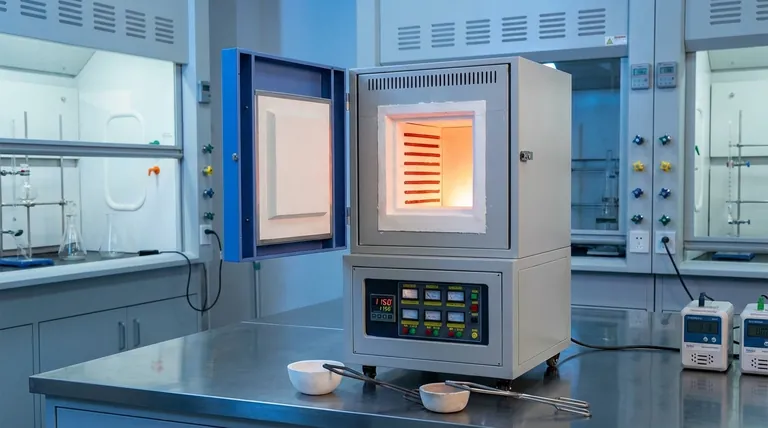

How a Muffle Furnace Achieves Clean, Precise Heat
The name "muffle" refers to the furnace's core principle: to muffle, or separate, the sample from the direct source of heat. This is achieved through a specific design that prioritizes purity and stability.
The Principle of Indirect Heating
A muffle furnace operates via indirect heating. Electric heating elements, typically made of materials like nichrome or silicon carbide, are wrapped around the outside of the central chamber.
When electricity passes through these elements, they get extremely hot. This heat is then transferred through the chamber walls to the interior space, heating the sample without any direct contact.
The Role of the "Muffle"
The "muffle" itself is the internal chamber, which is typically made of a high-temperature ceramic material. This chamber acts as a physical barrier, preventing any gases, flames, or particles from the heating source from contaminating the sample inside.
Ensuring Temperature Uniformity
Uniform heating is achieved through two primary mechanisms working together:
- Thermal Radiation: The hot inner walls of the muffle radiate heat evenly toward the sample from all directions.
- Thermal Convection: Air trapped inside the sealed chamber circulates, distributing heat and eliminating hot or cold spots.
This dual-action approach ensures that the entire sample experiences the same temperature, which is critical for achieving accurate and repeatable results.
The Importance of Insulation
To reach and maintain temperatures that can exceed 1700°C (3092°F), muffle furnaces are built with multiple layers of high-density insulation, such as imported glass wool blankets.
This heavy insulation minimizes heat loss, which not only improves thermal efficiency but also helps maintain a highly stable internal temperature.
Key Components and Features
Modern muffle furnaces are sophisticated instruments designed for precision and reliability. Several key features enable their performance.
Advanced Temperature Control
The brain of the furnace is its controller. Most units use a PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) controller, which constantly monitors the chamber temperature via a sensor and makes tiny, rapid adjustments to the power sent to the heating elements.
This allows for programmable heating cycles, where a user can define specific ramp rates, hold times, and cooling profiles with high accuracy.
High-Temperature Capability
Muffle furnaces are defined by their ability to operate at very high temperatures. Standard laboratory models often range from 800°C to 1200°C, while specialized industrial models can reach 1700°C or even higher.
Robust Construction
Given the extreme thermal stress, these furnaces are built with durable, corrosion-resistant materials. The outer casing is typically steel, while the internal components are designed to withstand constant expansion and contraction without degrading.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While invaluable, the muffle furnace design comes with inherent trade-offs that are important to understand.
Slower Heating Cycles
Because the heat must transfer indirectly through the muffle chamber walls, heating a sample can be slower compared to methods like a direct-fired kiln or an open flame.
Energy Consumption
Maintaining extremely high temperatures, even in a well-insulated box, requires a significant and continuous supply of electrical energy. This makes them more power-intensive than lower-temperature ovens.
Process Limitations
A standard muffle furnace is designed for heating in an air atmosphere. If a process requires an inert or reactive gas environment (like nitrogen or argon), a more specialized tube furnace or vacuum furnace is necessary.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct heating instrument depends entirely on the requirements of your application.
- If your primary focus is sample purity and precise temperature control: The muffle furnace is the ideal choice for applications like ashing, material analysis, or annealing metals.
- If your primary focus is rapid, bulk heating where contamination is not a concern: A direct-fired furnace or kiln may be a more time- and energy-efficient solution.
- If your primary focus is low-temperature drying or baking (under 500°C): A standard laboratory or convection oven is often more suitable and cost-effective.
Ultimately, choosing a muffle furnace is a decision to prioritize control and purity over raw speed.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Heating Method | Indirect heating via external elements for purity |
| Temperature Range | Up to 1700°C for precise thermal processing |
| Key Benefit | Chemically pure environment with uniform heating |
| Control System | PID controllers for accurate temperature regulation |
| Ideal Applications | Ashing, heat-treating, materials testing |
Upgrade your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with reliable equipment like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can precisely meet your unique experimental needs for pure, controlled heating. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can enhance your sample integrity and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating



















