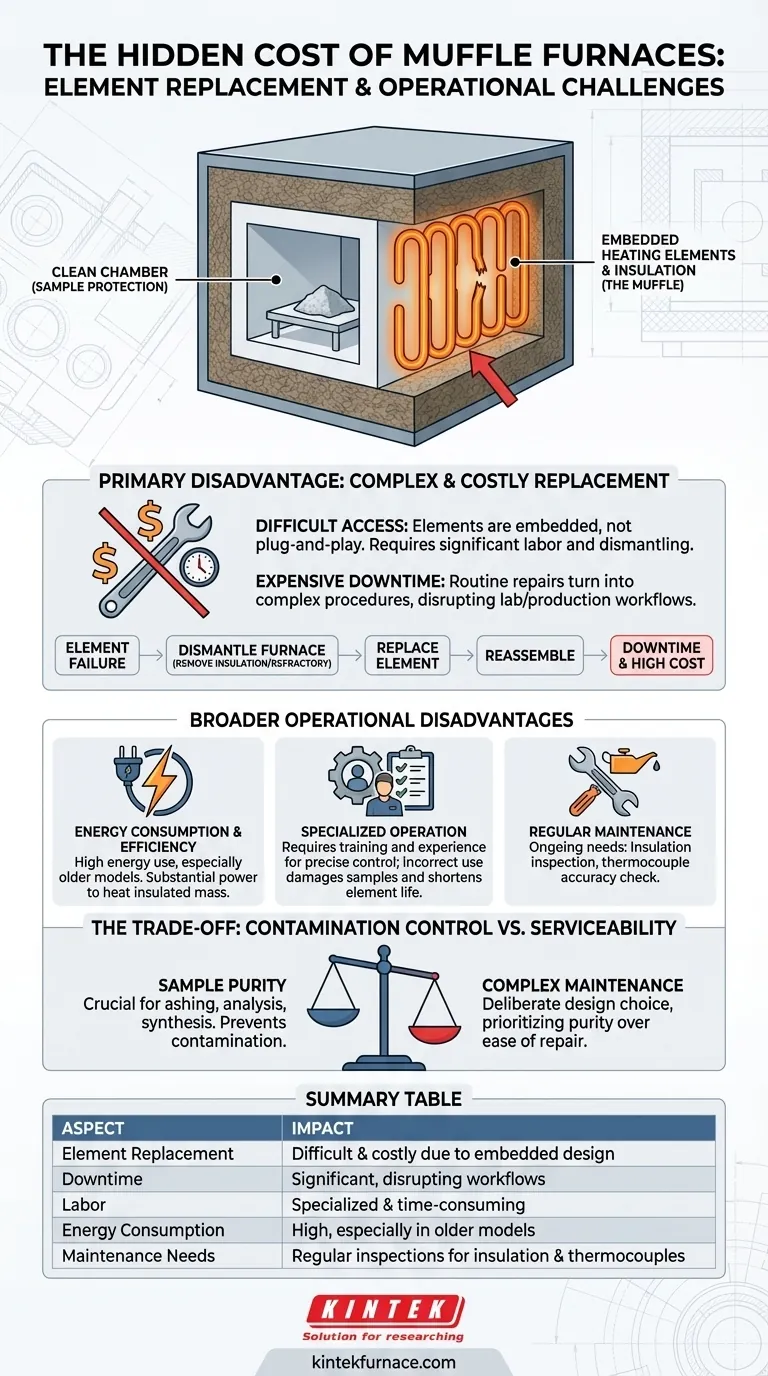
A primary disadvantage of muffle furnaces is the difficulty and cost associated with replacing the heating elements. Because the elements are embedded within the furnace's insulated refractory walls to protect the sample, accessing them for service requires significant labor and downtime, turning a routine repair into a complex and expensive procedure.
The core challenge of a muffle furnace lies in its design: the very feature that ensures a clean, contaminant-free heating environment—the "muffle" separating the sample from the heating elements—is also what makes servicing those elements inherently difficult and costly.

The Hidden Cost of Integrated Heating Elements
The defining characteristic of a muffle furnace is that the heating elements are not exposed to the heating chamber. While this provides superior temperature uniformity and prevents sample contamination, it creates a significant maintenance hurdle.
Why Replacement is Difficult
The heating elements are typically wound around or embedded directly into the ceramic or fiber insulation that forms the furnace chamber. This is not a simple "plug-and-play" component.
To replace a failed element, a technician must often dismantle a substantial portion of the furnace's core structure. This can involve carefully removing layers of insulation and refractory brick without causing damage.
The Impact on Cost and Downtime
This complexity directly translates into higher operational costs. The labor required for an element replacement is specialized and time-consuming, leading to expensive service bills.
Furthermore, the furnace will be out of commission for the duration of the repair. This unplanned downtime can disrupt critical lab or production workflows, adding an indirect cost that can exceed the repair itself.
Broader Operational Disadvantages
The challenge of element replacement is part of a larger set of operational considerations that potential users must weigh.
Energy Consumption and Efficiency
Muffle furnaces, particularly older or less advanced models, can have lower heating efficiency and consume a significant amount of energy. The insulated mass must be brought to temperature, which requires substantial power input, especially for high-temperature applications.
The Need for Specialized Operation
Properly operating a muffle furnace to achieve precise temperatures and ramp rates requires training and experience. Incorrect use can not only damage the samples but can also shorten the lifespan of the heating elements, leading to more frequent and costly replacements.
Regular Maintenance Requirements
Beyond element replacement, these furnaces require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance and longevity. This includes inspecting the insulation for cracks and ensuring thermocouple accuracy.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The disadvantages of a muffle furnace do not exist in a vacuum; they are the direct consequence of its primary advantage.
The Muffle's Purpose: Contamination Control
The entire reason for this design is to protect the material being heated. By isolating the chamber from the heating elements, the furnace prevents flakes from a degrading element from falling onto and contaminating the sample.
This is non-negotiable for applications like ashing, materials analysis, or specific chemical synthesis where sample purity is paramount.
Maintenance as a Design Consequence
Therefore, the difficult maintenance is not a design flaw but a deliberate trade-off. The furnace prioritizes a clean heating environment over ease of serviceability.
Understanding this balance is crucial when evaluating if a muffle furnace is the right tool for your specific process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing a furnace requires balancing your technical requirements with long-term operational realities.
- If your primary focus is minimizing maintenance and cost: Carefully investigate the element replacement procedure for any model you consider, or explore alternative furnace types where elements are more accessible.
- If your primary focus is absolute sample purity and process integrity: Accept that the complex maintenance of a muffle furnace is the necessary trade-off for its superior contamination control.
Ultimately, understanding this core trade-off between sample protection and serviceability is key to selecting the right furnace for your operational needs.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Impact |
|---|---|
| Element Replacement | Difficult and costly due to embedded design |
| Downtime | Significant, disrupting workflows |
| Labor | Specialized and time-consuming |
| Energy Consumption | High, especially in older models |
| Maintenance Needs | Regular inspections required for insulation and thermocouples |
Struggling with muffle furnace maintenance? KINTEK offers advanced high-temperature furnace solutions with deep customization to minimize downtime and costs. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is backed by exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing. Let us tailor a furnace to your unique needs—contact us today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production



















