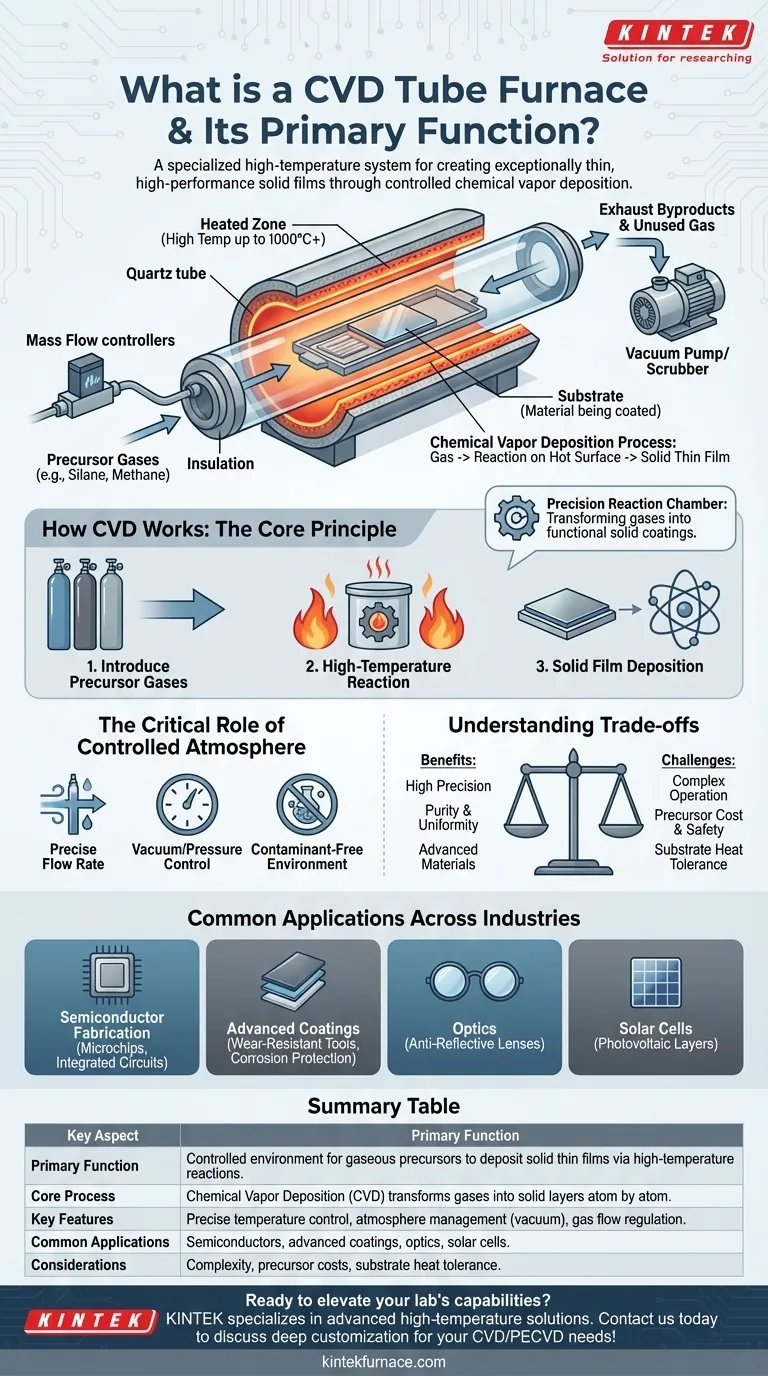
At its core, a CVD tube furnace is a specialized high-temperature system designed to create exceptionally thin, high-performance solid films on the surface of a material. Its primary function is to provide a highly controlled environment where gaseous chemical compounds, known as precursors, react and deposit a solid layer onto a heated object, or substrate, placed inside it.
A CVD furnace is not merely an oven; it is a precision reaction chamber. Its purpose is to transform carefully selected gases into a solid, functional coating on a substrate's surface through a controlled chemical process.

How the CVD Process Works
To understand the furnace, you must first understand the process it enables: Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). This is a method for building materials one layer of atoms at a time.
The Core Principle: From Gas to Solid
The fundamental idea is to introduce one or more volatile precursor gases into the furnace chamber. These gases contain the atoms you want to deposit.
When these gases reach the hot surface of the substrate (the material being coated), they undergo a chemical reaction or decomposition.
The result of this reaction is the formation of a solid thin film on the substrate's surface, while other gaseous byproducts are exhausted from the system.
The Critical Role of High Temperature
Heat is the catalyst. The furnace's heating elements create a high-temperature zone (often hundreds or even thousands of degrees Celsius).
This thermal energy is what drives the chemical reactions, giving the precursor molecules the energy needed to break their bonds and re-form as a solid on the substrate.
The Need for a Controlled Atmosphere
A CVD system is more than just a hot tube; it's a sealed environment. The process requires precise control over the atmosphere inside the furnace.
This includes managing the flow rate of precursor gases, maintaining a specific pressure (often a vacuum), and ensuring no contaminants like oxygen or water vapor disrupt the reaction. This control is what guarantees the film's purity and uniformity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the CVD process and the furnaces that enable it involve important considerations and limitations.
Precision vs. Complexity
The high degree of control that makes CVD so valuable also makes the equipment complex. Operating a CVD furnace requires significant expertise to manage gas flows, temperature profiles, and vacuum systems.
Precursor Handling and Cost
The chemical precursors used can be expensive, toxic, corrosive, or flammable. Handling and storing these materials safely adds a layer of operational cost and requires strict safety protocols.
Uniformity and Substrate Limitations
Achieving a perfectly uniform coating across a large or complexly shaped substrate is a major engineering challenge. Furthermore, the high process temperatures mean the substrate material itself must be able to withstand the heat without deforming or degrading.
Common Applications Across Industries
The ability to create high-purity, high-performance thin films makes CVD furnaces essential in many advanced technology sectors.
Semiconductor Fabrication
CVD is fundamental to manufacturing microchips. It's used to deposit the insulating, conducting, and semiconducting layers that form the intricate circuits on silicon wafers.
Advanced Coatings
The process is used to apply extremely hard, wear-resistant coatings (like titanium nitride) onto cutting tools, extending their lifespan dramatically. It's also used for corrosion-resistant layers in aerospace and chemical processing.
Optics and Solar Cells
In optics, CVD is used to create anti-reflective coatings on lenses. In the solar industry, it's used to deposit the silicon layers that are critical for converting sunlight into electricity.
Applying This to Your Project
Your choice of a CVD system or process depends entirely on your end goal.
- If your primary focus is fundamental research: You require a versatile, lab-scale furnace with maximum control over temperature, pressure, and gas mixing to explore new materials and processes.
- If your primary focus is industrial production: You need a larger, often automated system optimized for high throughput, repeatability, and uniform coating over many parts at once.
- If your primary focus is coating a specific part: You must first verify that your substrate material can tolerate the required temperatures and that the CVD process can achieve a conformal coating on its geometry.
Ultimately, mastering the CVD furnace is about mastering the controlled transformation of matter at the atomic level.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Provides a controlled environment for gaseous precursors to deposit solid thin films on substrates via high-temperature reactions. |
| Core Process | Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) transforms gases into solid layers atom by atom. |
| Key Features | Precise temperature control, atmosphere management (e.g., vacuum), and gas flow regulation. |
| Common Applications | Semiconductor fabrication, advanced coatings (e.g., wear-resistant), optics (e.g., anti-reflective), and solar cells. |
| Considerations | Complexity in operation, high precursor costs, and substrate heat tolerance requirements. |
Ready to elevate your lab's capabilities with a customized CVD tube furnace? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With our strong R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs—whether for research, production, or specific coatings. Contact us today to discuss how we can help you achieve precise, high-performance thin-film deposition!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station CVD Machine
People Also Ask
- Where is a CVD Tube Furnace commonly used? Essential for High-Tech Materials and Electronics
- What types of atmosphere control does a CVD Tube Furnace support? Master Vacuum and Gas Control for Precision
- Which industries and research fields benefit from CVD tube furnace sintering systems for 2D materials? Unlock Next-Gen Tech Innovations
- Why are advanced materials and composites important? Unlock Next-Gen Performance in Aerospace, Auto, and More
- What role do CVD tube furnace sintering systems play in 2D material synthesis? Enabling High-Quality Atomic Layer Growth



















