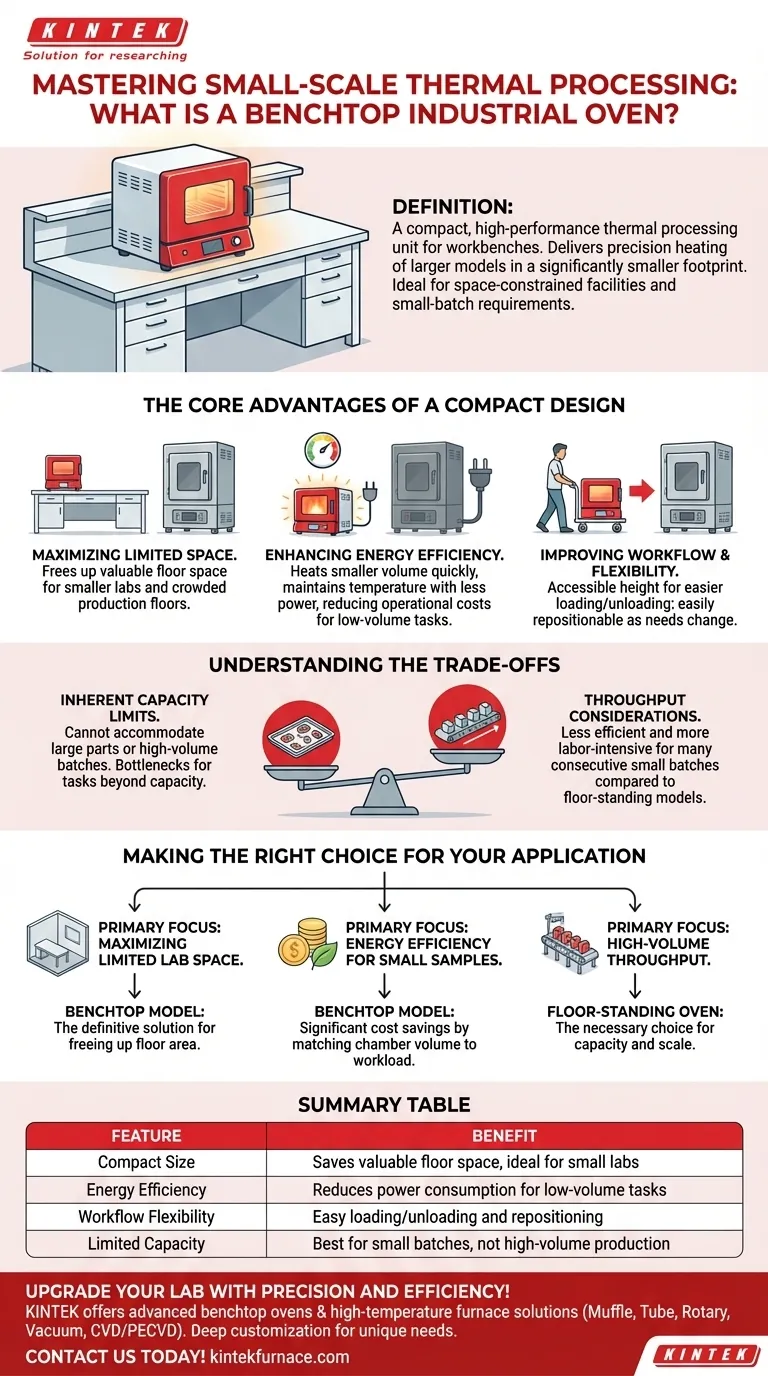
In industrial and laboratory settings, a benchtop oven is a compact, high-performance thermal processing unit designed to sit on a workbench. It delivers the same precision heating capabilities as larger, floor-standing models but in a significantly smaller footprint, making it a specialized tool for facilities with space constraints or small-batch requirements.
Choosing a benchtop industrial oven is not merely a matter of its size; it's a strategic decision to optimize workflow, energy consumption, and laboratory flexibility, especially when dealing with small-scale applications.

The Core Advantages of a Compact Design
The decision to use a benchtop oven is driven by a need for efficiency in a compact form. Its design directly addresses several key operational challenges found in modern labs and workshops.
Maximizing Limited Space
A benchtop oven's most obvious benefit is its small footprint. It is specifically engineered to fit on a standard workbench.
This frees up valuable floor space that would otherwise be occupied by a much larger, upright oven, a critical advantage for smaller labs or crowded production floors.
Enhancing Energy Efficiency
For processing a small number of samples, a benchtop oven is far more energy-efficient than its larger counterparts.
Heating a large, mostly empty chamber wastes a significant amount of energy. A compact oven heats its smaller volume quickly and maintains temperature with less power consumption, reducing operational costs for low-volume tasks.
Improving Workflow and Flexibility
The accessible height and size of a benchtop oven make loading and unloading samples easier and faster.
Furthermore, these units are often light enough to be repositioned within the lab as workflow needs change. This provides a level of layout flexibility that is impossible with heavy, floor-standing equipment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective for its intended purpose, the compact nature of a benchtop oven introduces important limitations that must be considered. Objectivity requires acknowledging what this tool is not designed for.
Inherent Capacity Limits
The primary trade-off is limited chamber volume. A benchtop oven cannot accommodate large parts or high-volume production batches.
Its purpose is for small components, sample testing, or low-quantity runs. Attempting to use it for tasks beyond its capacity will create bottlenecks in your process.
Throughput Considerations
If your batch volume fluctuates or is expected to grow, a benchtop oven may hinder throughput.
Running many consecutive small batches can be less efficient and more labor-intensive than processing a single, large batch in a floor-standing oven. It is a tool for specialization, not mass production.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right oven requires a clear understanding of your primary operational goal.
- If your primary focus is maximizing limited lab space: A benchtop model is the definitive solution, freeing up floor area for other critical equipment.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency for small samples: The benchtop oven provides significant cost savings by perfectly matching chamber volume to your workload.
- If your primary focus is high-volume throughput: A larger, floor-standing industrial oven is the necessary choice to handle the required capacity and scale.
Ultimately, the benchtop oven empowers you to achieve precise thermal processing without sacrificing space or efficiency for smaller-scale work.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Compact Size | Saves valuable floor space, ideal for small labs |
| Energy Efficiency | Reduces power consumption for low-volume tasks |
| Workflow Flexibility | Easy loading/unloading and repositioning |
| Limited Capacity | Best for small batches, not high-volume production |
Upgrade your lab with precision and efficiency! KINTEK offers advanced benchtop ovens and a full range of high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With our strong R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to find the perfect thermal processing solution for your laboratory!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Why is a precision furnace required after TiO2-alpha-Ga2O3 synthesis? Master Phase Transformation & Interface Bonding
- Why is dual heat treatment required for SnO2 nanoparticles? Optimize Oxidation for Superior Performance
- What is the function of a laboratory high-temperature furnace in eggshell powder pretreatment? Optimize AA6061 Composites
- What role does a high-temperature laboratory oven play in catalyst activation? Boost Surface Area and Performance
- How does a box-type high-temperature furnace contribute to 6Mo stainless steel? Optimize Solution Treatment Now



















