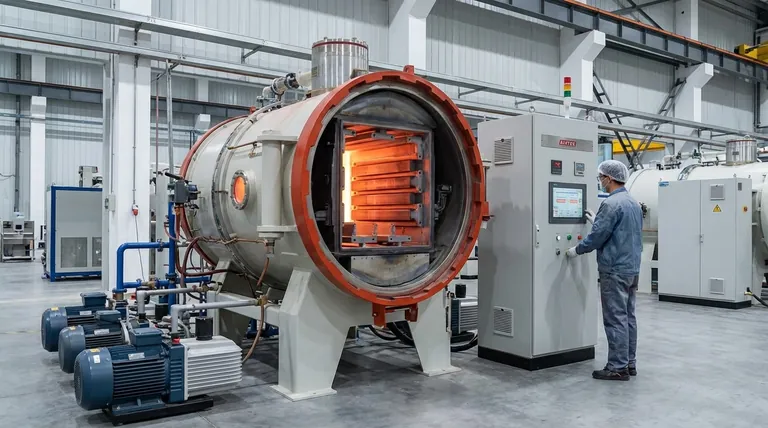
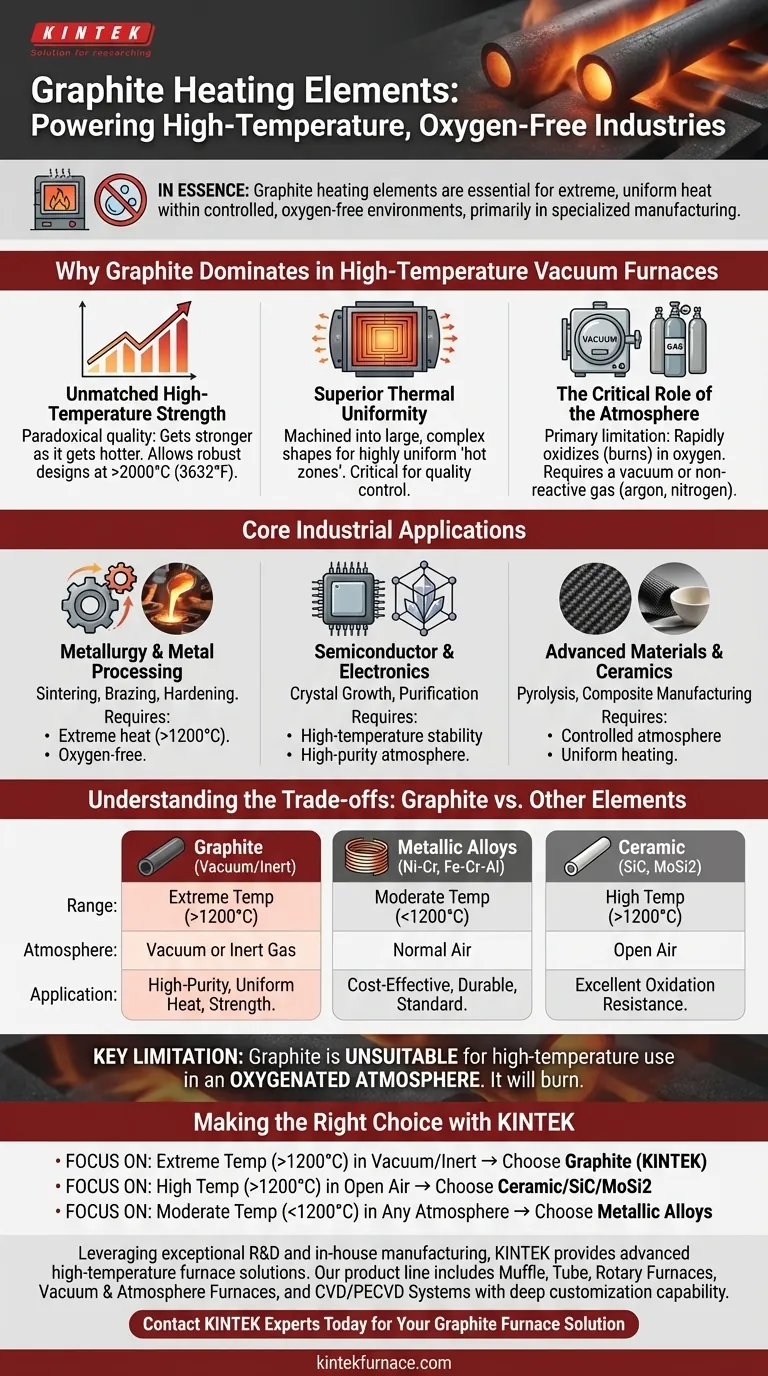
In essence, industries that require extreme, uniform heat within a controlled, oxygen-free environment rely on graphite heating elements. This is most common in specialized manufacturing processes like metal sintering, hardening, and brazing, which all take place inside high-temperature vacuum or inert-gas furnaces.
The choice to use a graphite heating element is fundamentally a decision about the furnace atmosphere. While other materials can operate in the open air, graphite's unique ability to grow stronger at extreme temperatures makes it the definitive choice for high-heat applications where oxygen can be eliminated.

Why Graphite Dominates in High-Temperature Vacuum Furnaces
Graphite is not a general-purpose heating element. It is a specialized tool used when metallic or ceramic elements reach their operational limits. Its adoption is driven by a unique set of physical properties that align perfectly with the demands of vacuum furnace applications.
Unmatched High-Temperature Strength
Unlike metals, which soften and lose structural integrity as they approach their melting point, graphite exhibits a paradoxical quality: it gets stronger as it gets hotter. This allows for the design of robust, self-supporting heating elements that can operate reliably at temperatures exceeding 2000°C (3632°F).
Superior Thermal Uniformity
Graphite elements can be machined into large, complex shapes, such as cylinders or flat panels. This allows them to radiate heat evenly over a large surface area, creating a highly uniform "hot zone" inside the furnace. This uniformity is critical for processes where precise temperature control determines the quality of the final product.
The Critical Role of the Atmosphere
Graphite’s primary limitation defines its use case. At high temperatures, graphite will rapidly oxidize (burn) in the presence of oxygen. Therefore, it can only be used in a vacuum or in a furnace filled with a non-reactive (inert) gas, such as argon or nitrogen.
Core Industrial Applications
The need for high heat in a controlled atmosphere concentrates graphite's use in several key, high-value manufacturing sectors.
Metallurgy and Metal Processing
This is the primary domain for graphite heaters. Processes like sintering (fusing powdered metal together), brazing (joining metals like copper or nickel with a filler material), and hardening all require precise, high temperatures in an oxygen-free environment to prevent material degradation.
Semiconductor and Electronics Manufacturing
The production of semiconductors and advanced electronics often involves crystal growth and other purification processes. These require extremely high and stable temperatures in a high-purity, non-reactive environment to avoid contamination, making graphite an ideal choice.
Advanced Materials and Ceramics
Manufacturing certain types of industrial ceramics, carbon fibers, and other composite materials requires a high-temperature firing process called pyrolysis. Graphite furnaces provide the necessary heat and controlled atmosphere to transform raw materials without unwanted chemical reactions.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Graphite vs. Other Elements
Choosing a heating element involves balancing temperature requirements, atmospheric conditions, and cost. Graphite is powerful but not always the right tool for the job.
When to Use Metallic Elements (Ni-Cr, Fe-Cr-Al)
For most industrial heating applications below 1200°C (2192°F) that operate in normal air, metallic alloys are the standard. They are cost-effective, durable, and do not require a specialized vacuum or inert gas furnace.
When to Use Ceramic, SiC, or MoSi2 Elements
For high-temperature applications that must occur in an air atmosphere, Silicon Carbide (SiC) and Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) are superior choices. They offer excellent resistance to oxidation at high temperatures and are common in glass manufacturing, ceramic firing, and laboratory settings.
The Key Limitation of Graphite
It cannot be overstated: graphite is unsuitable for high-temperature use in an oxygenated atmosphere. Attempting to use a graphite element in an air furnace will result in its rapid destruction. The entire system—the furnace, the controls, and the process—must be designed around this fundamental requirement.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct heating technology comes down to your specific operational parameters.
- If your primary focus is extreme temperature (>1200°C) in a vacuum or inert atmosphere: Graphite is the superior choice for its structural strength, thermal uniformity, and high-purity heating.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature heating (>1200°C) in an open-air environment: You must consider specialized elements like Silicon Carbide (SiC) or Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2).
- If your primary focus is moderate-temperature heating (<1200°C) in any atmosphere: Standard metallic alloy elements are almost always the most practical and cost-effective solution.
Understanding the fundamental trade-off between the furnace atmosphere and your temperature target is the key to selecting the correct heating element technology for your goal.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Key Applications | Primary Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| Metallurgy & Metal Processing | Sintering, Brazing, Hardening | Extreme heat (>1200°C), Oxygen-free environment |
| Semiconductor & Electronics | Crystal Growth, Purification | High-temperature stability, High-purity atmosphere |
| Advanced Materials & Ceramics | Pyrolysis, Composite Manufacturing | Controlled atmosphere, Uniform heating |
Need a high-temperature furnace solution tailored to your unique process?
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our graphite heating element furnaces can enhance your metallurgy, semiconductor, or advanced materials production.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the significance of vacuum in relation to graphite components in furnaces? Prevent Oxidation for Extreme Temperatures
- Why is graphite a preferred material for heating elements in high-temperature vacuum furnaces?
- How does graphite contribute to energy efficiency in vacuum furnaces? Achieve Faster, More Uniform Heating
- Why are vacuum furnaces used for the re-quenching of samples after a boriding treatment? Master Core Toughness
- How does vacuum heat treatment reduce workpiece deformation? Achieve Superior Dimensional Stability



















