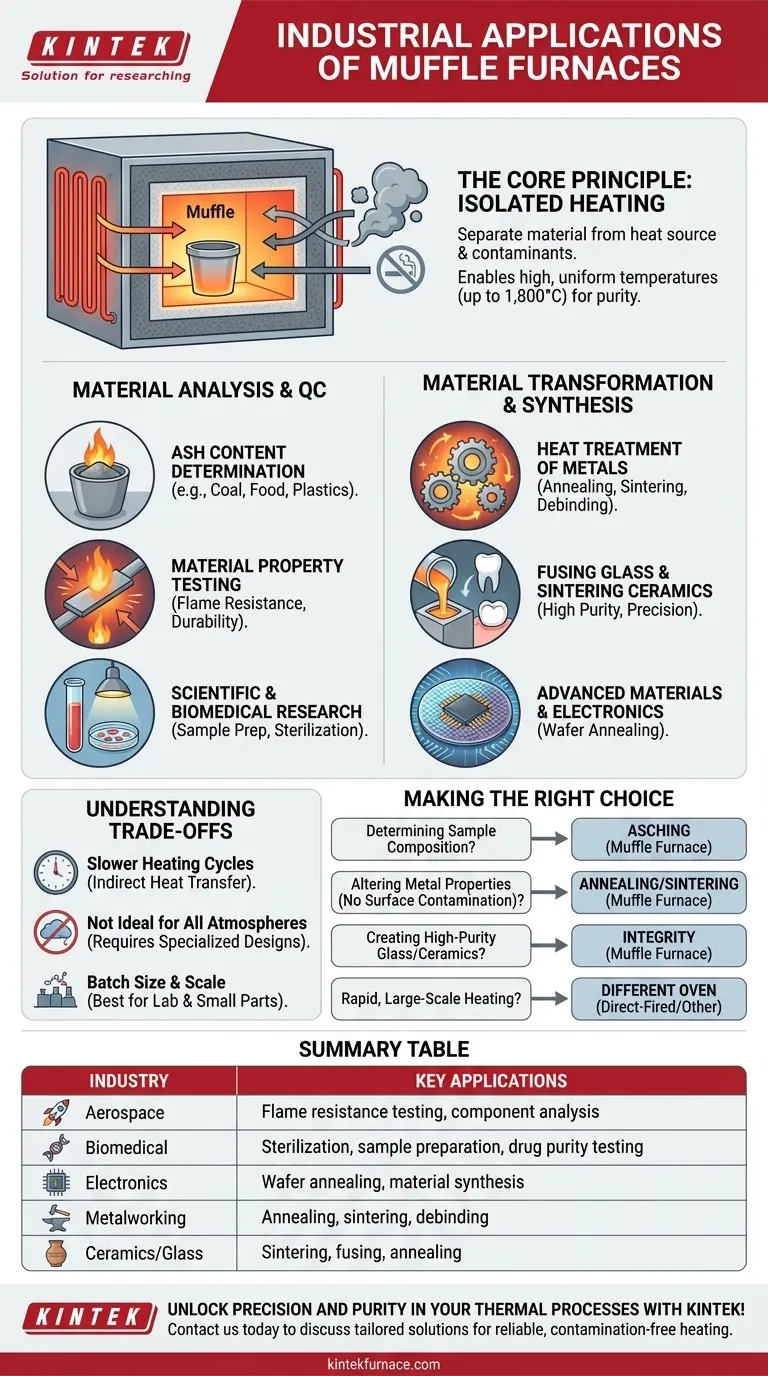
From aerospace components to pharmaceutical research, muffle furnaces are used across a vast range of industries for applications requiring high heat in a contamination-free environment. Their primary functions are material analysis (like determining ash content), material transformation (such as the heat treatment of metals), and synthesis (like fusing glass or sintering ceramics). Industries as diverse as metalworking, biomedical, textiles, and electronics rely on them for precise thermal processing.
A muffle furnace's core value lies in its design: it isolates the material being heated from the heat source and any fuel byproducts. This allows for extremely high, uniform temperatures without compromising the chemical purity or integrity of the sample, making it essential for both sensitive analysis and advanced manufacturing.

The Core Principle: Why a "Muffle"?
A muffle furnace is not defined by its heat source but by its internal structure. Understanding this design is key to understanding its applications.
Isolating the Material from Contaminants
The term "muffle" refers to the insulated inner chamber that separates the workpiece from the heating elements and the furnace's exterior.
In traditional fuel-fired furnaces, combustion byproducts like soot or gases can directly interact with and contaminate the material. A muffle furnace, particularly a modern electric one, completely avoids this.
The heating elements warm the muffle chamber, which then transfers heat to the sample via conduction, convection, and blackbody radiation, ensuring a clean process.
Achieving High, Uniform Temperatures
Modern electric muffle furnaces can achieve precise and stable temperatures, often reaching up to 1,800°C (3,272°F).
This capability enables sophisticated metallurgical and ceramic processes that are impossible in standard ovens, providing a controlled environment for complex chemical and physical transformations.
Key Application #1: Material Analysis and Quality Control
One of the most common uses for a muffle furnace is to test what a material is made of. This is critical for quality control, research, and regulatory compliance.
Ash Content Determination
This is a fundamental analytical technique. A sample (like coal, food, plastic, or textiles) is heated to a high temperature to completely burn off all its organic components.
The inorganic, non-combustible residue that remains is called ash. Weighing this ash allows analysts to determine the composition and quality of the original material.
Material Property Testing
Industries use muffle furnaces to test how materials behave under extreme heat.
Examples include flame resistance testing for aerospace and automotive components, evaluating the durability of paints and coatings, and assessing the strength of plastics after thermal stress.
Scientific and Biomedical Research
In research labs, muffle furnaces are workhorses for sample preparation. This can involve removing organic matter to isolate specific compounds or preparing samples for further analysis.
In the biomedical and pharmaceutical fields, they are used for sterilizing instruments and testing the purity of drug components.
Key Application #2: Material Transformation and Synthesis
Beyond analysis, muffle furnaces are used to fundamentally change a material's physical properties or to create new materials altogether.
Heat Treatment of Metals
In metallurgy, heat treatment is used to alter a metal's strength, hardness, and ductility.
Common processes include annealing (softening metal to make it more workable), sintering (fusing powdered metal into a solid mass below its melting point), and debinding (removing binder material in metal injection molding).
Fusing Glass and Sintering Ceramics
The clean, high-heat environment is perfect for creating high-purity glass and advanced ceramics.
Applications range from crafting fine glassware and annealing it for strength to sintering dental ceramics for crowns and bridges, where both precision and biocompatibility are essential.
Advanced Materials and Electronics
In the semiconductor industry, muffle furnaces are used for processes like wafer annealing, which helps repair damage to the crystal lattice of silicon wafers during manufacturing.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly versatile, a muffle furnace is not always the right tool for every heating job. Its specific design creates certain limitations.
Slower Heating Cycles
Because heat is transferred indirectly to the sample through the muffle chamber, heating and cooling cycles can be slower compared to direct-fired furnaces where flames impinge directly on the material.
Not Ideal for All Atmospheres
A standard muffle furnace provides a clean, ambient air atmosphere. Creating a specific reactive, inert, or vacuum atmosphere requires more specialized and expensive furnace designs, such as a tube or vacuum furnace.
Batch Size and Scale
Muffle furnaces are ideal for laboratory-scale work, quality control batches, and the creation of smaller, high-value parts (like dental crowns). They are generally not used for massive industrial processes like melting tons of steel, where larger, direct-fired furnaces are more efficient.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct thermal processing equipment depends entirely on your need for purity, precision, and scale.
- If your primary focus is determining a sample's composition (ashing): A muffle furnace is the industry standard for its ability to cleanly and completely burn away organic matter.
- If your primary focus is altering a metal's properties without surface contamination: A muffle furnace provides the clean, high-heat environment essential for processes like annealing and sintering.
- If your primary focus is creating high-purity glass or ceramic parts: The furnace's isolation from fuel byproducts ensures the final product's chemical integrity and quality.
- If your primary focus is rapid, large-scale heating of non-sensitive materials: A direct-fired furnace or a different type of industrial oven may be a more cost-effective and faster choice.
Ultimately, choosing a muffle furnace is a decision to prioritize material purity and thermal precision above all else.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Key Applications |
|---|---|
| Aerospace | Flame resistance testing, component analysis |
| Biomedical | Sterilization, sample preparation, drug purity testing |
| Electronics | Wafer annealing, material synthesis |
| Metalworking | Annealing, sintering, debinding |
| Ceramics/Glass | Sintering, fusing, annealing |
| Textiles/Plastics | Ash content determination, thermal property testing |
Unlock precision and purity in your thermal processes with KINTEK! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capability to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you're in aerospace, biomedical, electronics, or other industries, KINTEK delivers reliable, contamination-free heating for material analysis, transformation, and synthesis. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can enhance your lab's efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a muffle furnace used to determine the ash content of biochar? Master Your Material Purity Analysis
- What is the primary role of a muffle furnace in the annealing process of AlCrTiVNbx alloys? Enhance Alloy Strength
- How does a stainless steel reactor function within a muffle furnace for PET to graphene? Master Carbon Synthesis
- What role does a muffle furnace play in analyzing the combustion residues? Optimize Your Composite Char Analysis
- Why are precision stirring and drying equipment necessary for photocatalytic materials? Master Microstructure Control



















