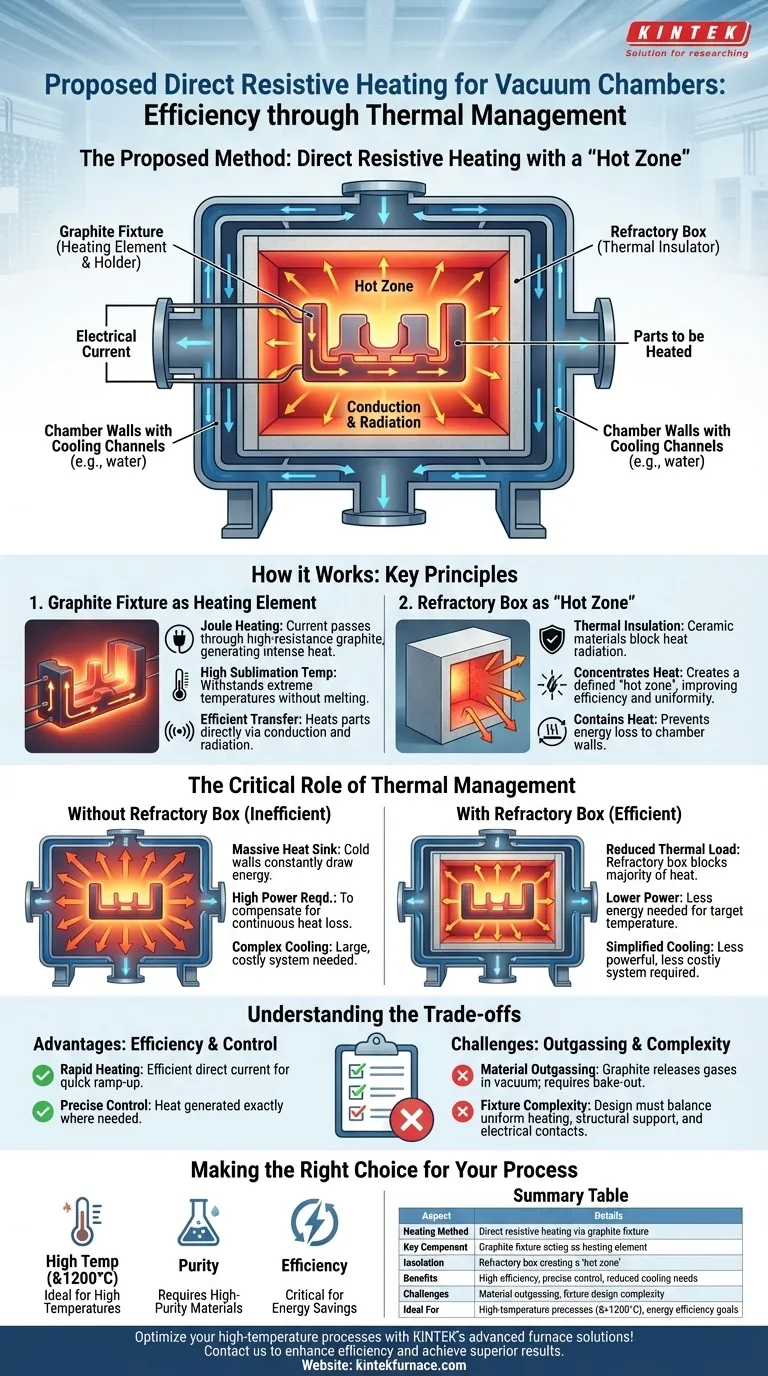
The proposed heating method for the vacuum chamber is a form of direct resistive heating. It works by passing a controlled electrical current through a specially designed graphite fixture, which heats the parts it is holding, while a refractory material box is used to contain the heat and protect the chamber.
This approach leverages the graphite fixture itself as the heating element, creating a highly efficient and localized "hot zone." The core challenge then becomes managing this intense heat to protect the surrounding vacuum chamber.

How This Heating System Works
This method combines two key principles: direct heating of the workpiece and thermal insulation to manage the resulting energy. It is a common and effective design for high-temperature vacuum furnaces.
The Graphite Fixture as a Heating Element
The system's heat source is the graphite fixture. Graphite is selected for its unique properties: it has high electrical resistance and an extremely high sublimation temperature, allowing it to get very hot without melting.
When a high electrical current is passed through it, the fixture's internal resistance causes it to heat up rapidly. This phenomenon is known as Joule heating.
Because the parts being processed are in direct contact with or in close proximity to this hot fixture, heat is transferred to them efficiently through conduction and radiation.
The Refractory Box as a "Hot Zone"
To prevent this intense heat from radiating throughout the entire vacuum chamber, a box is built around the fixture using refractory materials. These are ceramics designed to withstand extreme temperatures and act as excellent thermal insulators.
This box creates a defined "hot zone." Its purpose is twofold: it concentrates the thermal energy on the parts, improving heating efficiency and temperature uniformity, and it contains the heat, preventing it from reaching the chamber walls.
By insulating the hot zone, the overall power required to reach a target temperature is significantly reduced.
The Critical Role of Thermal Management
The primary benefit of this design is its impact on the rest of the vacuum system, specifically the chamber walls and cooling apparatus.
Insulating the Heat
Without the refractory box, the graphite element would radiate heat in all directions. The cold walls of the vacuum chamber would act as a massive heat sink, constantly drawing energy away from the process.
This would require a much larger power supply to compensate for the continuous heat loss, making the process highly inefficient.
Reducing Wall Cooling Requirements
The vacuum chamber walls must be kept cool to maintain their structural integrity and ensure the vacuum seals (like O-rings) do not fail. This is typically done by circulating a coolant, such as water, through channels in the chamber walls.
By using the refractory box to block the majority of the radiant heat, the thermal load on the chamber walls is dramatically reduced. This means a less powerful, less complex, and less costly cooling system is required to maintain safe operating temperatures.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While effective, this heating method presents specific design considerations and potential challenges that must be managed.
Advantage: Efficiency and Control
Passing current directly through the heating element is a very efficient way to generate heat. It allows for rapid temperature ramp-up and precise control, as the heat is generated exactly where it is needed.
Challenge: Material Outgassing
Graphite, especially certain grades, can release trapped gases (outgassing) when heated in a vacuum. This can contaminate the vacuum environment and interfere with sensitive processes.
Proper material selection and a pre-process "bake-out" cycle are often required to drive off these volatile compounds and ensure a clean operating environment.
Challenge: Fixture Complexity
Designing the graphite fixture is not trivial. It must be shaped to heat the parts uniformly, provide stable mechanical support at high temperatures, and handle the significant electrical current without failing. The electrical contact points are a critical design feature.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
The suitability of this method depends entirely on your specific process goals.
- If your primary focus is reaching very high temperatures (>1200°C): This resistive heating method is an excellent choice due to its efficiency and the high-temperature capabilities of graphite.
- If your primary focus is process purity and avoiding contamination: Pay close attention to selecting a high-purity, low-outgassing grade of graphite and refractory material.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency and operational cost: The use of a well-designed refractory hot zone is critical to minimizing power consumption and the load on your cooling systems.
Ultimately, this design represents an engineered solution that balances direct heating power with intelligent thermal management.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Heating Method | Direct resistive heating via graphite fixture |
| Key Component | Graphite fixture acting as heating element |
| Insulation | Refractory box creating a 'hot zone' |
| Benefits | High efficiency, precise control, reduced cooling needs |
| Challenges | Material outgassing, fixture design complexity |
| Ideal For | High-temperature processes (>1200°C), energy efficiency goals |
Optimize your high-temperature processes with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with reliable high-temperature furnace systems, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to enhance efficiency and achieve superior results in your applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the proper procedures for handling the furnace door and samples in a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Integrity & Safety
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in LP-DED? Optimize Alloy Integrity Today
- Why does heating steel rod bundles in a vacuum furnace eliminate heat transfer paths? Enhance Surface Integrity Today
- What are the functions of a high-vacuum furnace for CoReCr alloys? Achieve Microstructural Precision and Phase Stability
- How does a vacuum heat treatment furnace influence Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Optimize Ductility and Fatigue Resistance



















