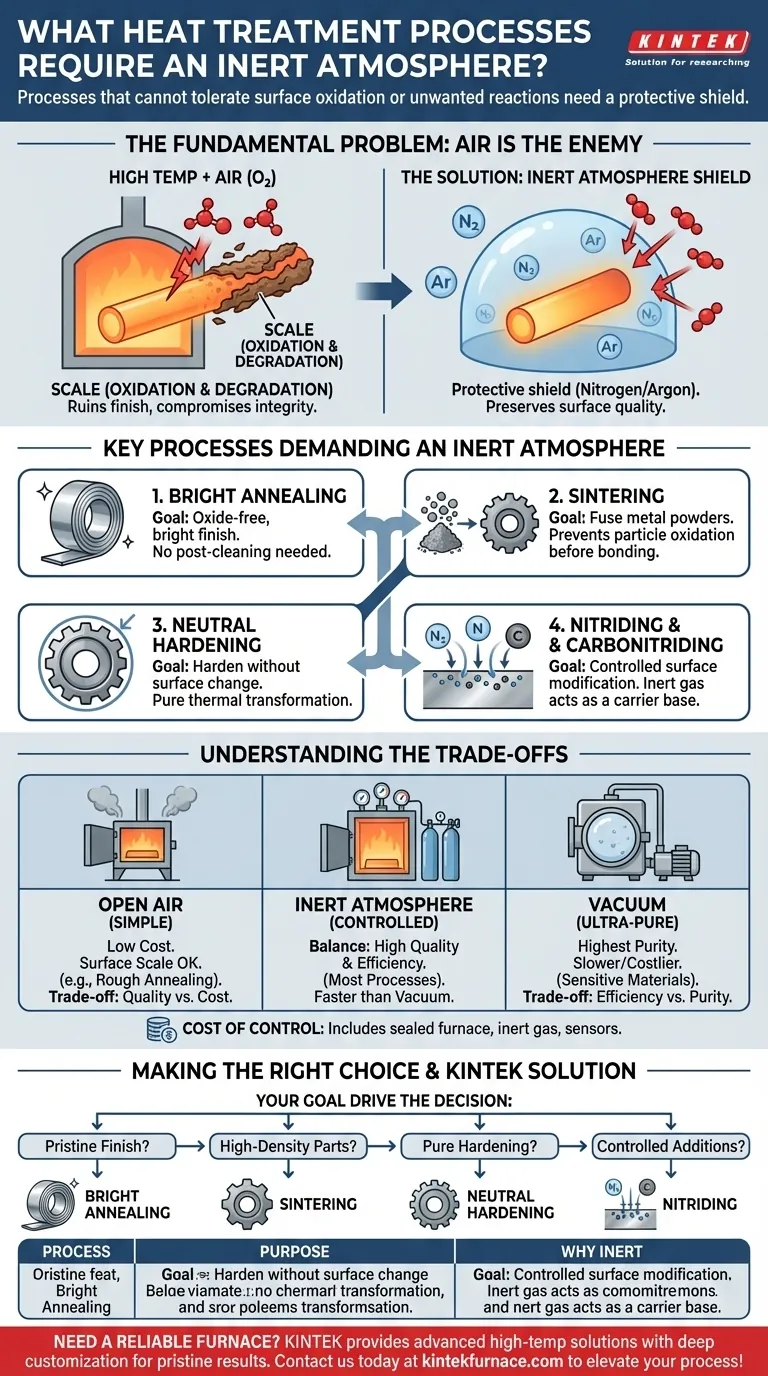
In short, heat treatment processes that cannot tolerate any surface oxidation or unwanted chemical reactions require an inert atmosphere. Key examples include bright annealing, sintering, neutral hardening, and specific gas-based surface treatments like nitriding and carbonitriding, where the goal is to achieve a pristine finish and precise control over the material's final properties.
The core purpose of an inert atmosphere is not about the heat itself, but about creating a protective shield. At high temperatures, oxygen becomes highly reactive, causing scaling and degradation. An inert atmosphere replaces the reactive air with a non-reactive gas, preserving the material's integrity and surface quality.

The Fundamental Problem: Why Air is the Enemy
During heat treatment, high temperatures act as a catalyst for chemical reactions. The normal air around us, composed of roughly 21% oxygen and other trace gases, becomes aggressive and damaging to the metal workpiece.
The Challenge of Oxidation
Oxidation is the primary reaction that must be prevented. When hot metal is exposed to oxygen, it forms a layer of metallic oxide on the surface, commonly known as scale.
This scale is detrimental. It causes discoloration, ruins the surface finish, and can interfere with subsequent manufacturing steps like plating or painting.
Compromising Material Integrity
Beyond surface appearance, unwanted reactions can alter the chemical composition of the material's surface layer.
This can lead to a loss of specific properties, such as hardness or fatigue resistance, compromising the performance and reliability of the final component.
Key Processes Demanding an Inert Atmosphere
Certain processes are defined by their need for a controlled environment. The inert gas—typically nitrogen, argon, or a blend—ensures the heat treatment achieves its intended goal without side effects.
Bright Annealing
The very name "bright annealing" implies the desired outcome: a clean, bright, mirror-like surface finish. This process softens metal without creating any surface oxide, making it ready for use with no need for post-treatment cleaning or pickling.
Sintering
Sintering is the process of fusing powdered materials (often metals) into a solid mass using heat. An inert atmosphere is critical to prevent the fine metal particles from oxidizing before they can bond, ensuring a strong, dense final part.
Neutral Hardening
In neutral hardening, the goal is to increase the hardness of a steel component without changing its surface chemistry. An inert atmosphere is "neutral," meaning it doesn't add or subtract elements like carbon, allowing for pure hardening through thermal transformation alone.
Controlled Surface Modification (Nitriding & Carbonitriding)
While seemingly counterintuitive, processes designed to add specific elements to a surface also require a controlled atmosphere. In nitriding or carbonitriding, a precise amount of nitrogen or carbon-carrying gas is introduced.
An inert gas is used as the base or carrier gas, preventing oxygen from interfering while allowing the intended elements to diffuse into the surface in a highly controlled manner.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing to use an inert atmosphere furnace involves balancing quality requirements against operational complexity and cost. It is not the default choice for all heat treatment.
Inert Atmosphere vs. Open Air
The simplest furnaces operate in open air. This is acceptable for processes like rough annealing or stress relieving where surface finish is not a primary concern and a layer of scale can be tolerated or removed later. The trade-off is quality vs. cost.
Inert Atmosphere vs. Vacuum Furnaces
A vacuum furnace achieves a similar goal by removing nearly all atmospheric gases rather than replacing them. Vacuum is often superior for extremely sensitive materials (like titanium or refractory metals) and provides the absolute highest level of purity.
However, inert atmosphere furnaces can often reach temperature faster and can be more cost-effective for processes that do not require a hard vacuum, offering a balance of high quality and process efficiency.
The Cost of Control
Implementing an inert atmosphere adds expense. This includes the higher initial cost of a sealed furnace, the ongoing cost of purchasing inert gas, and the need for sophisticated sensors and control systems to monitor and maintain the atmosphere's purity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your decision should be driven by the non-negotiable requirements of your final product.
- If your primary focus is a pristine, oxide-free surface finish: Bright annealing in an inert atmosphere is essential to avoid costly and damaging post-processing steps.
- If your primary focus is creating high-density parts from metal powders: Sintering in an inert environment is necessary to ensure proper bonding and material integrity.
- If your primary focus is hardening a part without altering its surface carbon content: Neutral hardening in a controlled atmosphere is the only way to achieve this.
- If your primary focus is precisely controlling the addition of elements to the surface: Processes like nitriding depend on an inert carrier gas to prevent unwanted side reactions.
Ultimately, specifying an inert atmosphere is a decision to invest in control to guarantee the final quality and performance of the component.
Summary Table:
| Process | Key Purpose | Why Inert Atmosphere is Needed |
|---|---|---|
| Bright Annealing | Achieve oxide-free, mirror-like surface finish | Prevents oxidation for no post-cleaning |
| Sintering | Fuse metal powders into dense solid parts | Avoids particle oxidation before bonding |
| Neutral Hardening | Harden steel without surface chemistry changes | Maintains neutrality for pure hardening |
| Nitriding/Carbonitriding | Add nitrogen/carbon to surface in controlled way | Uses inert gas as base to prevent interference |
Need a reliable inert atmosphere furnace for your lab? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With strong deep customization capabilities, we precisely meet your unique experimental needs—ensuring pristine finishes, precise control, and enhanced efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can elevate your heat treatment processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the use of nitrogen in furnace? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Heat Treatment
- What is the main purpose of heat treatment? Transform Metal Properties for Superior Performance
- What are the benefits of inert atmosphere heat treating? Prevent Oxidation and Preserve Material Integrity
- What are the environmental benefits of using inert gases in furnaces? Reduce Waste and Emissions for a Greener Process
- How does the inert atmosphere heat treating process work? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Material Quality



















