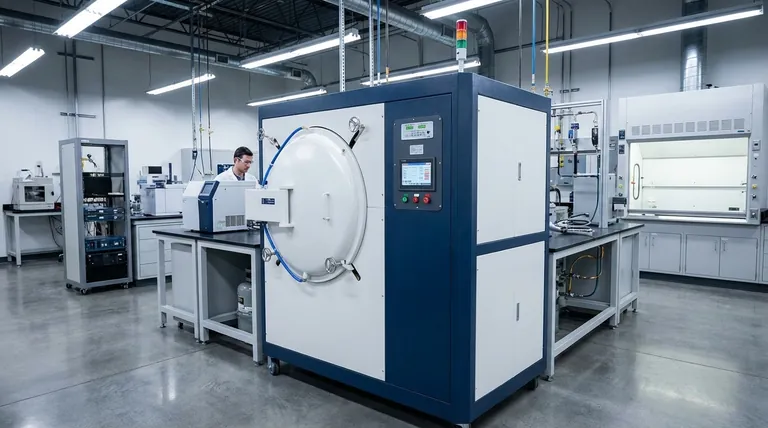
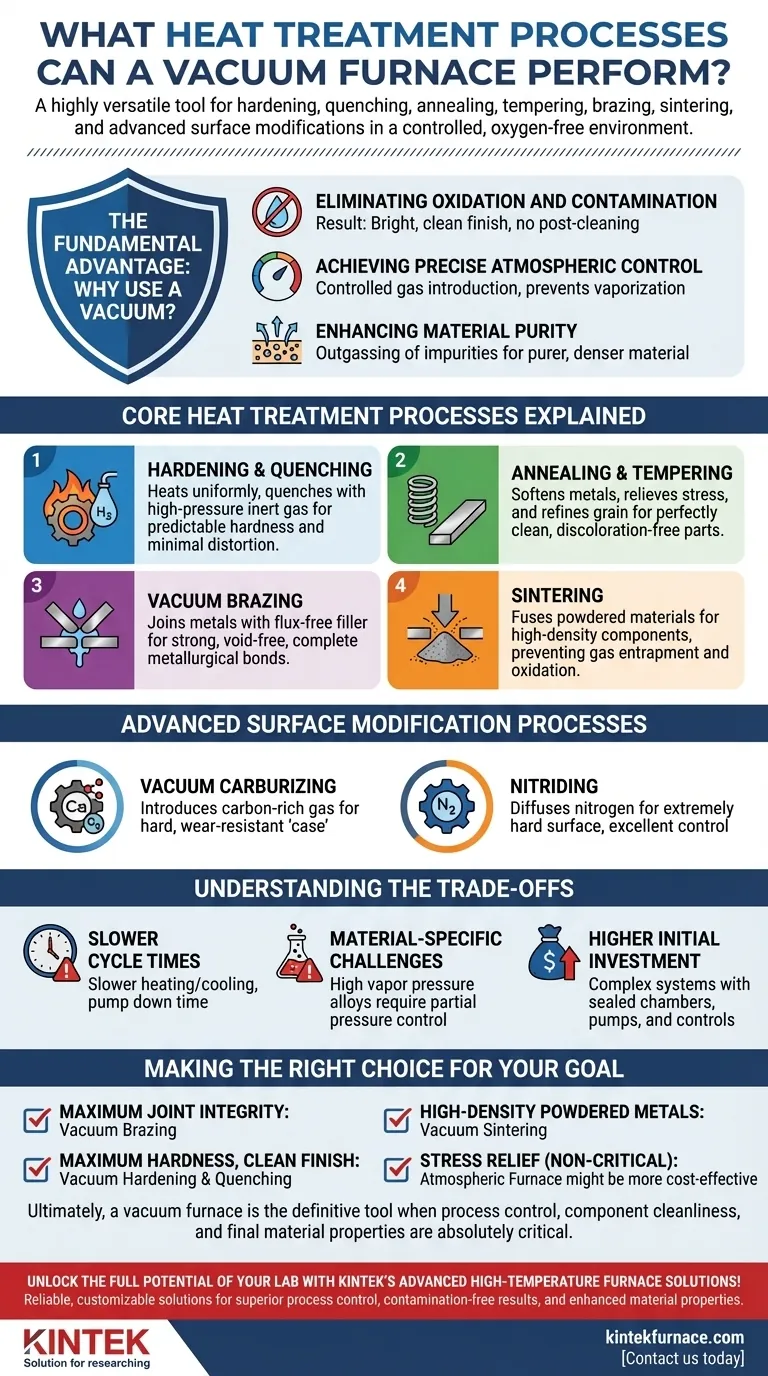
At its core, a vacuum furnace is a highly versatile tool capable of performing a wide range of heat treatment and material processing operations. These include hardening and quenching, annealing, tempering, brazing, sintering, and advanced surface modification processes like carburizing and nitriding, all conducted within a controlled, oxygen-free environment.
The defining advantage of a vacuum furnace is not just the processes it can perform, but the unparalleled level of control it provides. By eliminating atmospheric gases, it prevents oxidation and contamination, resulting in cleaner parts, superior material properties, and process repeatability that is often impossible to achieve in traditional furnaces.

The Fundamental Advantage: Why Use a Vacuum?
The decision to use a vacuum furnace stems from the need for absolute control over the material's environment during heating and cooling. This control delivers several key benefits.
Eliminating Oxidation and Contamination
By removing reactive gases like oxygen, a vacuum furnace prevents the formation of oxides (scale) on the metal's surface. This results in a bright, clean finish that requires little to no post-process cleaning, preserving precise dimensions and surface integrity.
Achieving Precise Atmospheric Control
A vacuum environment can be precisely altered. Once a vacuum is established, specific gases like nitrogen or argon can be introduced at controlled partial pressures. This allows for processes like nitriding or prevents issues such as the vaporization of alloying elements like chromium from the surface of steel.
Enhancing Material Purity
Heating a material in a vacuum can pull trapped gases and volatile impurities out of the metal itself, a process known as outgassing. This leads to a purer, denser final material with improved mechanical and physical properties.
Core Heat Treatment Processes Explained
While many of these processes can be done in atmospheric furnaces, performing them in a vacuum unlocks a higher level of quality and performance.
Hardening and Quenching
Hardening involves heating a metal to a critical temperature and then cooling it rapidly (quenching) to lock in a hard, strong metallurgical structure. In a vacuum, the part is heated uniformly without surface degradation, and quenching can be precisely controlled using high-pressure inert gas, leading to predictable hardness and minimal distortion.
Annealing and Tempering
Annealing softens metals, relieves internal stresses, and refines the grain structure. Tempering is a lower-temperature process used after hardening to reduce brittleness and increase toughness. Performing these in a vacuum ensures the resulting part is perfectly clean and free from the surface discoloration that occurs in air.
Vacuum Brazing
Brazing joins two or more metal items by melting a filler metal into the joint. Vacuum brazing is superior because it produces exceptionally strong, clean, and void-free joints without the need for corrosive flux. The vacuum pulls the filler metal into even the tightest capillaries, creating a complete metallurgical bond.
Sintering
Sintering is the process of fusing powdered materials (often powdered metals) into a solid, high-density component by applying heat below the material's melting point. Vacuum sintering is critical for reactive materials and produces parts with higher density and strength by preventing gas entrapment and oxidation between particles.
Advanced Surface Modification Processes
Vacuum furnaces also excel at case hardening, where the chemical composition of the component's surface is altered to make it harder and more wear-resistant.
Vacuum Carburizing
Also known as low-pressure carburizing, this process introduces a carbon-rich gas into the furnace at a high temperature. The carbon diffuses into the surface of the steel, creating a hard, wear-resistant "case" over a tougher core. The vacuum ensures excellent carbon transfer and uniformity.
Nitriding
Similar to carburizing, nitriding involves diffusing nitrogen into the surface of a steel part to create an extremely hard case. Plasma-activated or gas nitriding can be performed with exceptional control in a vacuum environment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum furnaces are not the solution for every heat treatment need. Understanding their limitations is key to making an informed decision.
Slower Cycle Times
Heating and cooling in a vacuum rely primarily on radiation and controlled gas convection, which can be slower than the high-convection rates in some atmospheric furnaces. The time required to pump down the chamber also adds to the total cycle time.
Material-Specific Challenges
Certain alloying elements, like chromium, zinc, and manganese, have high vapor pressures and can "boil off" the material's surface under a deep vacuum at high temperatures. This is managed by using a controlled partial pressure of an inert gas, but it requires precise process knowledge.
Higher Initial Investment
Vacuum furnaces are complex systems involving a sealed chamber, robust pumping systems, and sophisticated controls. This makes their initial purchase price and maintenance costs significantly higher than most standard atmospheric furnaces.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right process depends entirely on the desired outcome for your component.
- If your primary focus is joining complex assemblies with maximum joint integrity: Vacuum brazing is the ideal choice, as it eliminates flux and creates clean, strong, and complete bonds.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum hardness and a bright, clean finish on tool steels: Vacuum hardening and quenching provide superior control and prevent surface decarburization.
- If your primary focus is producing high-density parts from powdered metals: Vacuum sintering minimizes porosity and prevents gas entrapment for superior mechanical properties.
- If your primary focus is simply relieving stress in a non-critical component: While vacuum annealing works perfectly, a less complex atmospheric furnace may be more cost-effective if a bright finish is not required.
Ultimately, a vacuum furnace is the definitive tool when process control, component cleanliness, and final material properties are absolutely critical.
Summary Table:
| Process | Key Benefits |
|---|---|
| Hardening & Quenching | Uniform heating, minimal distortion, precise gas quenching |
| Annealing & Tempering | Clean finish, stress relief, no surface discoloration |
| Vacuum Brazing | Strong, flux-free joints, complete metallurgical bond |
| Sintering | High-density parts, prevents gas entrapment and oxidation |
| Carburizing & Nitriding | Hard, wear-resistant surface, excellent control and uniformity |
Unlock the full potential of your lab with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with reliable vacuum furnaces, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, delivering superior process control, contamination-free results, and enhanced material properties. Ready to elevate your heat treatment processes? Contact us today for a tailored solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- What are the general operational features of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Material Purity & Precision
- What is the vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Surface Quality and Material Performance
- How does a vacuum heat treatment furnace influence Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Optimize Ductility and Fatigue Resistance
- Why does heating steel rod bundles in a vacuum furnace eliminate heat transfer paths? Enhance Surface Integrity Today



















